В данной статье будут рассмотрены основы командной строки Windows, а именно:
- Понятие командной строки;
- Справочник по командам командной оболочки;
- Последовательность событий при выполнение команды;
- Создание сценариев командной строки;
- Управление отображением текста и команд;
- Команды для изучение системной информации;
- Команды для использования реестра;
- Управление системными службами;
- Перезагрузка и выключение систем из командной строки;
- Управление приложениями и процессами из командной строки.
Содержание
- Понятие командной строки
- Краткий справочник по командам командной оболочки (Cmd.exe)
- Последовательность событий при выполнение команды
- Создание сценариев командной строки
- Управление отображением текста и команд
- Изучение системной информации
- Команды для использования реестра
- Управление системными службами
- Перезагрузка и выключение систем из командной строки
- Управление приложениями, процессами и производительностью
Понятие командной строки
Поддержка командной строки встроена в операционную систему Microsoft Windows и доступна через окно командной оболочки. Командная строка поддерживается во всех версиях Windows и служит для запуска встроенных команд, утилит и сценариев. Несмотря на мощь и гибкость командной строки, некоторые администраторы Windows никогда ее не используют. Если вам хватает графических средств администрирования, можно применять только их, щелкая мышью элементы пользовательского интерфейса.
Однако опытные администраторы Windows, квалифицированные специалисты по технической поддержке и «продвинутые» пользователи не могут обойтись без командной строки. Зная, как правильно применять командную строку, в частности, какие средства командной строки выбрать, как и когда их использовать, чтобы они работали эффективно, можно избежать многочисленных проблем и добиться четкого выполнения операций. Если вы занимаетесь поддержкой нескольких доменов или сетей, то для автоматизации ежедневных операций не только важно, но и необходимо иметь представление об экономящих время способах работы с командной строкой.
С каждой новой версией Windows командная строка совершенствовалась, а ее возможности расширялись. Командная строка претерпела значительные изменения, связанные не только с повышением производительности, но и с увеличением гибкости. Теперь с помощью командной строки Windows можно решать задачи, которые нельзя было решить в предыдущих версиях Windows.
Среду командной оболочки Windows запускают разными способами, в частности указывая параметры при запуске Cmd.exe или используя собственный стартовый файл, хранящийся в каталоге %SystemRoot%System32.
Кроме того, командная строка может работать в пакетном режиме для выполнения набора команд. В пакетном режиме командная строка считывает и выполняет команды одну за другой.
Работая с командной строкой Windows, Вы должны понимать, откуда берутся используемые Вами команды. «Родные» команды (встроенные в операционную систему) бывают двух видов:
- Внутренние – существуют внутри командной оболочки, у них нет отдельных исполняемых файлов;
- Внешние — реализованы в отдельных исполняемых файлах, которые обычно хранятся в каталоге %SystemRoot% System32.
Краткий справочник по командам командной оболочки (Cmd.exe)
- assoc — выводит или изменяет сопоставления (associations) типов файлов;
- break — задает точки останова при отладке
- call — вызывает из сценария процедуру или другой сценарий;
- cd (chdir) — показывает имя текущего каталога или выполняет смену текущего каталога;
- cls — очищает окно командной строки и буфер экрана;
- color — задает цвета текста и фона окна командной оболочки;
- сору — копирует файлы или выполняет конкатенацию файлов;
- date — показывает или устанавливает текущую дату;
- del (erase) — удаляет заданный файл, группу файлов или каталог;
- dir — показывает список подкаталогов и файлов в текущем или заданном каталоге;
- echo — выводит текст в окно командной строки или задает, надо ли отображать команды на экране (on|off);
- endlocal — отмечает конец локализации (локальной области видимости) переменных;
- exit — выход из оболочки командной строки;
- for — выполняет заданную команду для каждого файла в наборе;
- ftype выводит или изменяет текущие типы файлов в сопоставлениях расширений файлов с программами;
- goto — указывает, что интерпретатор команд должен перейти на строку с заданной меткой в пакетном сценарии;
- if — выполняет команды по условию;
- md (mkdir) — создает подкаталог в текущем или заданном каталоге;
- move — перемещает файл или группу файлов из текущего или заданного исходного каталога в указанный каталог. Также может переименовывать каталог;
- path — показывает или задает путь к командам, используемый операционной системой при поиске исполняемых файлов и сценариев;
- pause — останавливает выполнение пакетного файла и ожидает ввода с клавиатуры;
- popd — делает текущим каталог, имя которого было сохранено командой PUSHD;
- prompt — указывает, какой текст должен показываться в строке приглашения;
- pushd — сохраняет имя текущего каталога и при необходимости делает текущим заданный каталог;
- rd (rmdir) — удаляет каталог или каталог вместе с его подкаталогами;
- rem — помечает комментарии в пакетном сценарии или Config.nt;
- ren (rename) — Переименовывает файл или группу файлов;
- set — показывает текущие переменные окружения или задает временные переменные для текущей командной оболочки;
- setlocal — отмечает начало локализации (локальной области видимости) переменных в пакетных сценариях;
- shift — сдвигает позицию замещаемых параметров в пакетных сценариях;
- start — запускает заданную программу или команду в отдельном окне;
- time — показывает или устанавливает системное время;
- title — задает заголовок окна командной оболочки;
- type — показывает содержимое текстового файла;
- verify — включает режим проверки файлов после записи на диск;
- vol — показывает метку и серийный номер дискового тома.
Синтаксис любой внутренней команды (и большинства внешних) можно получить, введя в командной строке имя команды и /?, например:
copy /?
Командная оболочка — весьма мощная среда работы с командами и сценариями. В командной строке можно запускать команды разных типов: встроенные команды, утилиты Windows и версии приложений, рассчитанные на командную строку. Независимо от типа каждая команда, которую вы будете использовать, должна соответствовать одним и тем же синтаксическим правилам. Согласно этим правилам, за именем команды идут обязательные или необязательные аргументы. Кроме того, аргументы могут использовать перенаправление ввода, вывода или стандартных ошибок.
Последовательность событий при выполнение команды
- Командная оболочка заменяет любые переменные, введенные в тексте команд, их текущими — значениями;
- Если введена группа или цепочка из нескольких команд, строка разбивается на отдельные команды, которые в свою очередь разбиваются на имя и аргументы команды. Далее команды обрабатываются по отдельности;
- Если в имени команды указан путь, командная оболочка ищет команду по этому пути. Если в указанном каталоге такой команды нет, командная оболочка возвращает ошибку;
- Если в имени команды не задан путь, командная оболочка сначала пытается разрешить имя команды на внутреннем уровне. Если найдена внутренняя команда с таким именем, значит, вызвана внутренняя команда, которую сразу же можно выполнить. Если внутренней команды с таким именем нет, командная оболочка сначала ищет исполняемый файл команды в текущем каталоге, а затем в каталогах, перечне в переменной окружения PATH. Если файла команды нет ни в одном из этих каталогов, командная оболочка возвращает ошибку;
- Если команда найдена, она выполняется с заданными аргументами и при необходимости ввод считывается из источника, указанного в этих аргументах. Вывод и ошибки команд показываются в окне командной строки или направляются заданному приемнику вывода и ошибок.
- Как видите, на выполнение команд влияют многие факторы, в том числе пути к командам, перенаправление ввода-вывода, группирование или создание цепочек команд.
При работе с командной оболочкой Вы, вероятно, запускали ее, открывая меню Start (Пуск) и выбирая Programs (Программы) или All Programs (Все программы), затем Accessories (Стандартные) и Command Prompt (Командная строка). Другие способы запуска командной строки — диалоговое окно Run (Запуск программы) или ввод cmd в другом, уже открытом окне командной оболочки. Эти способы позволяют при запуске командной строки указывать аргументы: ключи, управляющие работой командной строки, и параметры, инициирующие выполнение дополнительных команд. Например, можно запустить командную оболочку в «молчаливом» режиме (т. е. отключить эхо-вывод) командой cmd /q или сделать так, чтобы командная оболочка выполнила заданную команду и завершила свою работу, — для этого нужно ввести cmd /с, а затем текст команды в кавычках.
В следующем примере командная оболочка запускается, выполняет команду ipconfig с выводом результатов в файл и завершается:
cmd /c "ipconfig > c:ipconfig.txt"
Создание сценариев командной строки
Сценарии командной строки — текстовые файлы с командами, которые вы хотите выполнить. Это те же команды, которые обычно вводятся в командной оболочке Windows. Однако вместо того чтобы вводить команды каждый раз, когда они понадобятся, можно создать соответствующий сценарий и упростить себе жизнь.
Поскольку сценарии состоят из стандартных текстовых символов, их можно создавать и редактировать в любом стандартном текстовом редакторе, скажем, в Notepad (блокнот). Вводя команды, убедитесь, что каждая команда или группа команд, которые должны выполняться совместно, разметаются с новой строки. Это обеспечит их корректное выполнение. Закончив создание сценария командной строки, сохраните файл сценария с расширением .bat или .cmd. Оба расширения работают одинаково. Например, если вам надо создать сценарий для вывода имени системы, версии Windows и конфигурации IP, включите в файл SysInfo.bat или SysInfo.cmd следующие три команды:
hostname ver ipconfig -all
Управление отображением текста и команд
Команда ECHO служит двум целям: для записи текста в вывод (например, в окно командной оболочки или текстовый файл) и для включения/выключения эхо-отображения команд. Обычно при выполнении команд сценария сами команды и вывод этих команд отображаются в консольном окне. Это называется эхо-отображением команд (comand echoing).
Чтобы использовать команду ECHO для отображения текста, введите echo и текст, который надо вывести:
echo The system host name Is: hostname
Чтобы с помощью ECHO управлять эхо-отображением команд, введите echo off или echo on, например:
echo off echo The system host name is: hostname
Чтобы направить вывод в файл, а не в окно командной оболочки, используйте перенаправление вывода, например:

echo off echo The system host name is: > current.txt hostname » current.txt
Теперь посмотрим, как подавляется эхо-отображение команд. Запустите командную оболочку, введите echo off, затем другие команды. Вы увидите, что приглашение командной строки больше не выводится. Вместо него появляется только то, что набирается в консольном окне, и вывод выполненных команд. В сценариях команда ECHO OFF отключает эхо-отображение команд и приглашение командной строки. Добавляя в свои сценарии команду ECHO OFF, вы предотвращаете загромождение окна командной оболочки или файла текстом команд, если Вас интересует лишь вывод от этих команд.
Изучение системной информации
Часто при работе с компьютером пользователя или удаленным сервером возникает необходимость в получении базовой информации о системе вроде имени зарегистрированного в ней пользователя, текущего системного времени или местоположения определенного файла. Команды, которые позволяют собрать основную информацию о системе, включают:
- NOW — отображает текущую системную дату и время в 24-часовом формате, например Sal May 9 12:30:45 2003. Доступна только в Windows Server 2003 Resource Kit;
- WHOAMI — сообщает имя пользователя, зарегистрированного в системе на данный момент, например adatumadmi-nistrator;
- WHERE — выполняет поиск файлов по шаблону поиска (search pattern) и возвращает список совпавших результатов.
Чтобы использовать NOW или WHOAMI, просто введите команду в окне командной оболочки и нажмите Enter. Наиболее распространенный синтаксис для WHERE выглядит так:
where /r базовый_каталог_имя_файла
Здесь параметр /r указан для рекурсивного поиска, начиная от указанного каталога (базовый_каталог) и включая все его подкаталоги, а имя_файла — полное или частичное имя искомого файла, которое может включать символы подстановки (wildcards): знак ? заменяет один символ, а знак * — группу символов, например data???.txt или data*.*. В следующем примере в каталоге С: и всех его подкаталогах выполняется поиск всех текстовых файлов, имена которых начинаются с data.
where /r C: data*.txt
Также можно найти файлы всех типов, имена которых начинаются с data:
where /r C: data*.*
Иногда нужно получить информацию о конфигурации системы или о системном окружении. В критически важных системах эту информацию можно сохранить или распечатать для справки. Ниже перечислены команды, позволяющие собирать информацию о системе.
- DRIVERQUERY — выводит список всех установленных драйверов устройств и их свойства, в том числе имя модуля (module name), отображаемое имя (display name), тип драйвера и дату сборки (driver link date). В режиме отображения всей информации (/V) сообщается статус (status) и состояние (state) драйвера, режим запуска, сведения об использовании памяти и путь в файловой системе. Параметр /V также включает вывод детальной информации обо всех неподписанных драйверах.
- SYSTEMINFO — выдает подробную информацию о конфигурации системы, в том числе сведения о версии, типе и изготовителе операционной системы, процессоре, версии BIOS, объеме памяти, региональных стандартах, часовом поясе и конфигурации сетевого адаптера.
- NLSINFO — отображает подробную информацию о региональных стандартах, включая язык по умолчанию (default language), кодовую страницу Windows, форматы отображения времени и чисел, часовой пояс и установленные кодовые страницы. Эта команда доступна лишь в Windows Server 2003 Resource Kit.
Чтобы использовать эти команды на локальном компьютере, просто введите имя нужной команды в окне командной оболочки и нажмите Enter.
Команды для использования реестра
Реестр Windows хранит конфигурационную информацию операционной системы, приложений, пользователей и оборудования. Эти данные содержатся в разделах (keys) и параметрах (values) реестра, которые размещаются в определенном корневом разделе (root key), который контролирует, как и когда используются разделы и параметры.
Если Вы знаете пути к разделам и понимаете допустимые типы данных в разделах, то можете использовать команду REG для просмотра разделов и параметров и манипуляций над ними самыми разнообразными способами. REG поддерживает несколько подкоманд:
- REG add — добавляет в реестр новый подраздел или элемент;
- REG delete — удаляет из реестра подраздел или элемент;
- REG query — выводит список элементов раздела и имена подразделов (если они есть);
- REG compare — сравнивает подразделы или элементы реестра;
- REG сору — копирует элемент реестра по указанному пути раздела на локальной или удаленной системе;
- REG restore — записывает в реестр ранее сохраненные подразделы, элементы и параметры;
- REG save — сохраняет копию указанных подразделов, элементов и параметров реестра в файл.
Управление системными службами
Службы обеспечивают ключевые функции рабочих станций и серверов. Для управления системными службами на локальных и удаленных системах используется команда контроллера служб (service controller command) SC, имеющая набор подкоманд, ниже описывается лишь их часть:
- SC config — настройка учетных записей регистрации и запуска служб;
- SC query — вывод списка всех служб, настроенных на компьютере;
- SC qc — отображение конфигурации определенной службы;
- SC start — запуск служб;
- SC stop — остановка служб;
- SC pause — приостановка работы служб;
- SC continue — возобновление работы служб;
- SC failure — задание действий, выполняемых при сбое службы;
- SC qfailure — просмотр действий, выполняемых при сбое службы.
Во всех командах можно указывать имя удаленного компьютера, со службами которого Вы хотите работать. Для этого вставьте UNC-имя или IP-адрес компьютера перед используемой подкомандой. Вот синтаксис:
sc ИмяСервера Подкоманда
Перезагрузка и выключение систем из командной строки
Системы нередко приходится перезагружать или выключать. Один из способов — использовать для этого утилиту Shutdown, которая позволяет работать с локальной и удаленными системами. Другой способ управлять выключением или перезагрузкой системы — назначить задание для выключения. Здесь можно использовать Schtasks, чтобы указать время выключения, или создать сценарий со списком команд выключения для индивидуальных систем.
Управлять перезагрузкой и выключением локальной системы позволяют следующие команды.
Выключение локальной системы:
shutdown /s /t ЗадержкаВыключения /1 /f
Перезагрузка локальной системы:
shutdown /r /t ЗадержкаВыключения /1 /f
Управление приложениями, процессами и производительностью
Всякий раз, когда операционная система или пользователь запускает службу, приложение или команду, Microsoft Windows запускает один или более процессов для управления соответствующей программой. Несколько утилит командной строки упростят вам мониторинг программ и управление ими. К этим утилитам относятся:
- Pmon (Process Resource Manager) — показывает статистические данные по производительности, включая использование памяти и процессора, а также список всех процессов, выполняемых в локальной системе. Позволяет получать детальные «снимки» задействованных ресурсов и выполняемых процессов. Pmon поставляется с Windows Resource Kit;
- Tasklist (Task List) — перечисляет все выполняемые процессы по имени и идентификатору процесса, сообщает информацию о сеансе пользователя и занимаемой памяти;
- Taskkill (Task Kill) — останавливает выполнение процесса, заданного по имени или идентификатору. С помощью фильтров можно останавливать процессы в зависимости от их состояния, номера сеанса, процессорного времени, занимаемой памяти, имени пользователя и других параметров.
Вот в принципе все, что я хотел рассказать об основах командной строки Windows.
В статье пойдет речь об инструменте командной строки в Windows, основных принципах работы с ней и наиболее полезных командах, которые способны существенно облегчить работу с операционной системой.
Оглавление
- Командная строка в Windows: CMD и PowerShell
- Как открыть командную строку
- Как вводить cmd команды
- Как вывести результат команды из CMD в текстовый файл
- Как применить команду сразу к нескольким файлам
- Как вызвать подсказку
- Команды cmd с файлами
- Стандартные действия с файлами – создание, удаление, копирование и пр.
- Сравнить два файла – FC и COMP
- Найти слово в файле – FIND
- Создать файл определенного размера – FSUTIL FILE CREATENEW
- Удалить отметку последнего открытия файла – FSUTIL BEHAVIOR SET DISABLELASTACCESS 1
- Посмотреть информацию о компьютере, ОС и т. п.
- Проверить свободное место на диске – FSUTIL VOLUME DISKFREE C:
- Установленные драйверы – DRIVERQUERY
- Все сведения об операционной системе – SYSTEMINFO
- Выполнить диагностику Windows
- Проверить диск на ошибки – CHKDSK
- Проверка системных файлов – SFC
- Поменять настройки Windows
- Включить или отключить гибернацию – POWERCFG /H <ON|OFF>
- Настройки конфигурации системы – MSCONFIG
- Редактировать реестр – REGEDIT и REG
- Сетевые команды CMD
- Настройка протокола IP – IPCONFIG
- Узнать имя компьютера – HOSTNAME
- Диагностика сети: пинг и трассировка – PING, TRACERT, PATHPING
Командная строка в Windows: CMD и PowerShell
Командная строка (она же консоль или интерпретатор команд) – это программа для управления операционной системой посредством ввода специальных текстовых команд. В Windows 10 есть два инструмента командной строки: cmd.exe и PowerShell. И если cmd была еще в самых древних версиях системы, то PowerShell появилась в Windows уже после 2005 года. Она выполняла те же функции, что и cmd, выглядела почти так же, но имела более широкие возможности. У PowerShell свой, отличный от cmd.exe язык, и она рассчитана в основном на работу с так называемыми командлетами, у которых немного другой синтаксис, и почти для каждой команды cmd есть свой аналогичный командлет у PowerShell. Однако все команды cmd можно использовать в их первоначальном виде в PowerShell.
Как открыть командную строку
Есть куча способов вызвать командную строку. Рассмотрим несколько из них. Обратите внимание, что для использования некоторых команд требуется запустить командную строку с правами Администратора, поэтому сразу наматывайте на ус, как это делается.
Вызываем CMD в Widows 10
- Меню «Пуск» > Из списка программ выбираем «Служебные» > Жмем правой кнопкой мыши по пункту «Командная строка» > Выбираем пункт «Дополнительно», а в нем «Запуск от имени Администратора».
- Нажмите комбинацию клавиш «Win + R» > в появившемся окне «Выполнить» вбиваем «cmd» и жмем Enter, а если хотим запустить программу с правами Админа, то жмем «Ctrl + Shift + Enter».
- В Поиске (рядом с меню «Пуск») набираем «Командная строка» или «cmd», и в результатах выбираем вариант запуска программы от Администратора.
Вызываем PowerShell в Widows 10
- С помощью двух предыдущих способов можно также вызвать и PowerShell, если вписать его название вместо cmd.
- Правый клик по меню «Пуск» > в выпавшем меню выбираем запуск Windows PowerShell от Администратора.
Как вводить cmd команды
Общий порядок ввода команды в строку следующий:
- Сначала вводим основную команду;
- Если у нее есть дополнительные параметры, вводим их через пробел и знак слэш — /
- Далее, если требуется, прописываем путь к нужному файлу, начиная с корневой директории. Если в названиях промежуточных папок этого пути встречаются пробелы, то весь путь заключаем в кавычки. Например: «C:UsersUSERNAMEDesktopСписок команд cmd.txt»
- После того, как мы написали команду со всеми доп. параметрами, нажимаем Enter, чтобы начать ее выполнение.
Не имеет значения, в каком регистре писать команды, но почему-то сложился обычай писать их в верхнем.
Например, чтобы посмотреть список установленных на компьютере драйверов устройств необходимо выполнить команду DRIVERQUERY. Но если вы еще хотите увидеть в этом списке подробную информацию об их состоянии, введите через пробел после команды дополнительный параметр /V. А чтобы эти данные выводились в формате таблицы, пропишите в команде еще один параметр /FO TABLE. Итоговая запись будет выглядеть так: DRIVERQUERY /V /FO TABLE
Как вывести результат команды из CMD в текстовый файл
«>» – Вывод данных результата выполнения команды в отдельный файл.
«>>» – Записать данные результата выполнения команды в конец существующего файла.
Если хотите вывести данные о драйверах не на экран консоли, а в текстовый файл, то после команды со всеми доп. параметрами пропишите знак «>» и далее пропишите путь к файлу.
Пример: DRIVERQUERY /V /FO TABLE > C:UsersLohmachDesktopДрайверы.txt
Если файла не существует, то он будет создан, если такой файл уже есть, то данные в нем перезапишутся.
Для того, чтобы файл не перезаписывался, а дополнялся новыми данными в конце, пропишите знак «>>» перед указанием пути к файлу. Например, выведем в конце нашего файла «Драйверы.txt» список только подписанных драйверов. Прописываем команду: DRIVERQUERY /SI >> C:UsersLohmachDesktopДрайверы.txt
Как применить команду сразу к нескольким файлам
*.* – обращение ко всем файлам каталога
*.txt – обращение ко всем файлам только формата txt
Указав знак * вместо имени конкретного файла, вы сможете одной командой сразу «убить всех зайцев». Например, чтобы переместить все файлы из папки «Работа» на диске C в папку «Все рабочие файлы» на диске D с помощью команды MOVE, сделайте запись в командной строке такого типа: move «C:UsersUSERNAMEДокументыРабота*.*» «D:Все рабочие файлы»
Как вызвать подсказку
Для работы с CMD совсем необязательно знать список всех команд и их свойств. Если ввести в консоли HELP – отобразится полный список cmd команд c их кратким описанием. А чтобы получить подсказку по конкретной команде, введите через пробел после нее /?, и на экран выведется ее описание и варианты дополнительных параметров с примерами.
В PowerShell вызвать список поддерживаемых cmd команд с помощью HELP уже не получится.
Итак, посмотрим, что полезного можно сделать с командной строкой.
Команды cmd с файлами
У консоли полно команд для удаления, перемещения, копирования, открытия, создания файлов и папок. Но вряд ли они будут вам полезны, если только не накрылась ваша операционка, и с помощью обычных графических средств работать с файлами невозможно. На этот случай приведу вам списочек таких команд. Для большинства из них требуется указать пути к файлам. Рекомендую сверяться с инструкцией как вводить команды.
- MOVE – перемещает файл из одного места в другое.
- COPY – копирует файлы/папки в указанное место.
- DEL или ERASE – удаляет файлы.
- RD или RMDIR – удаляет папки.
- DIR – показывает список файлов в заданном каталоге. Выведите подсказку /?, чтобы посмотреть все варианты сортировки файлов.
- MD или MKDIR – создает новую папку. Если в указанном пути к папке будут отсутствовать промежуточные каталоги, то система их создаст автоматически.
- PRINT – выведет указанный файл на печать.
- TYPE – выведет содержимое текстового файла на экран консоли.
- REN или RENAME – переименует файл или каталог. Команду следует прописать в таком формате: REN «путь к файлу/папке, которую следует переименовать» «новое имя указанного файла/папки».
- REPLACE – выполняет замену файлов в каталоге. Полезно для синхронизации данных на дисках. Дополнительный параметр /U заменяет в указанном каталоге исходные файлы на новые, если время последнего изменения этих файлов будет различно. Параметр /A добавит в указанный каталог только те файлы, которых нет в другом.
Вышеперечисленные действия, безусловно, удобнее выполнять с помощью файлового проводника Windows, а теперь посмотрим на команды, которым нет аналога в графическом интерфейсе.
FC и COMP – команды сравнивают два файла или группы файлов и выводят на экран результат этого сравнения с кратким сообщением о найденных (или нет) различиях.
FIND – ищет слова/строки в указанном файле (или сразу в нескольких) и выдает строки, в которых они содержатся.
FSUTIL FILE CREATENEW «тут путь файла» [тут размер файла в байтах] – создаст новый файл строго указанного размера. Может пригодиться в разных целях: для теста скорости передачи данных, или чтобы зарезервировать место на диске, забив его файлом нужного размера.
FSUTIL BEHAVIOR SET DISABLE LASTACCESS 1 – отключает формирование отметки о времени последнего использования файла. Полезно, если вы решили увеличить быстродействие своего компьютера: файлы и папки будут открываться быстрее. Но будьте осторожны: перестанут правильно работать программы для резервного копирования файлов, использующих такие отметки. Снова включить обновление отметок последнего доступа к файлу можно той же командой, изменив 1 на 0.
Посмотреть информацию о компьютере, ОС и т.п.
FSUTIL VOLUME DISKFREE C: – запрос свободного пространства на диске C (можно указать любой другой). Более подробную информацию о распределении пространства на указанном диске вы можете получить по команде fsutil volume allocationreport C:
DRIVERQUERY – выводит на экран список всех драйверов устройств. Наиболее интересные параметры команды:
- /V – показать подробную информацию о состоянии драйверов.
- /SI – покажет список только драйверов, имеющих цифровую подпись.
SYSTEMINFO – показывает всю информацию о компьютере: версию ОС, код продукта, инфу о процессоре, объем физической и виртуальной памяти, IP-адрес и прочее.
Выполнить диагностику Windows
CHKDSK (запуск от имени Администратора) – проверяет диск на ошибки. При использовании параметра /f – также исправляет их, а если еще в дополнение к нему указать параметр /r, то система найдет поврежденные сектора на диске и попытается восстановить уцелевшие данные с них. После команды через пробел укажите имя диска, а после него – дополнительные параметры. Учтите, что для проверки диска C потребуется перезагрузка системы. После введения команды CHKDSK C: /f консоль предложит вам выполнить ее.
SFC – Команда используется только в сочетании с дополнительными параметрами:
- SFC/verifyonly – сканирует систему на предмет поврежденных системных файлов.
- SFC/scannow – производит восстановление обнаруженных повреждений.
Запускать команду необходимо от имени Администратора, а после сканирования перезагрузить систему. Те файлы, которые системе не удалось восстановить, можете поискать в интернете или скопировать из аналогичной ОС той же версии.
Поменять настройки Windows
POWERCFG /H ON – включить режим гибернации.
POWERCFG /H OFF – отключить режим гибернации.
Для использования команды нужны права Администратора. В режиме гибернации компьютер перед отключением системы записывает все данные из оперативной памяти на жесткий диск и при следующем включении компьютера снова загружает их в оперативную память, так что вы можете начать работу с того же места, где ее закончили. Полезно для владельцев ноутбуков, чтобы не потерять несохраненные данные из-за неожиданной разрядки устройства. Если острой необходимости в гибернации на своем компьютере вы не испытываете, то её лучше отключить, т.к. гибернация изнашивает жесткий диск и резервирует на нем значительное пространство, что замедляет работу компьютера. По умолчанию гибернация отключена.
Примечание: если после применения команды, вы не обнаружили пункта «Гибернация» в меню завершения работы компьютера, попробуйте проделать следующий финт ушами (работает в Windows 10):
Клик правой кнопкой мыши по иконке меню «Пуск» > Управление электропитанием > Питание и спящий режим > Дополнительные параметры питания > Действие кнопок питания > Изменения параметров, которые сейчас недоступны > Поставьте галочку в окошке «Режим гибернации» > Сохраните изменения и наслаждайтесь результатом.
После этих манипуляций кнопка «Гибернация» должна появиться в меню «Пуск» наряду с пунктами «спящий режим», «перезагрузка» и «завершение работы».
MSCONFIG – команда открывает окно с настройками конфигурации системы, в котором вы можете выбрать варианты запуска ОС (и определить, какую именно ОС вы хотите загружать по умолчанию, если у вас их установлено несколько), параметры загрузки (например, загрузку в безопасном режиме), управлять работой вспомогательных служб системы (возможно, отключить что-то лишнее), а через раздел «Сервис» вызвать информацию о системе, запустить устранение неполадок Windows, посмотреть и настроить параметры сети, зайти в редактор реестра, восстановить систему из точки восстановления и прочее.
REGEDIT – команда вызывает стандартный редактор реестра Windows regedit.exe. С помощью дополнительного параметра /E удобно делать бэкап всего реестра в отдельный файл. Для этого пропишите в строке regedit /E и путь для файла. Например: regedit /e D:backup.reg
REG – позволяет редактировать реестр прямо в командной строке. Используется только в сочетании с дополнительными ключами, которые пишутся после основной через пробел без слэша. Например, можно сделать бэкап раздела реестра, прописав в консоли REG SAVE или REG EXPORT, далее через пробел путь нужного раздела реестра и через пробел путь к будущему файлу. А с подкомандами RESTORE и IMPORT можно загрузить в реестр данные из файла резервной копии.
Сетевые команды CMD
IPCONFIG – вызывает на экран информацию о вашем сетевом подключении (Ipconfig /all покажет детальные сведения): ваш IP-адрес, маску подсети, основной шлюз, список сетевых адаптеров – все, что требуется для настройки роутера. А в сочетании с доп.параметрами командой можно поменять сетевые настройки и исправить некоторые проблемы подключения.
HOSTNAME – выводит имя компа.
PING – позволяет проверить доступность узла в сети. Отправляет пакет данных к IP-адресу узла и получает от него в ответ пакет тех же данных. Если пакет от узла вернулся с потерями – это может указывать на проблему соединения. Обычно команду используют при проблемах подключения к Интернету. Тогда выполняют пингование какого-нибудь популярного сайта, например Яндекс или Google, для теста качества Интернет-соединения или пингуют IP роутера, чтобы проверить, нет ли проблем в локальной сети. Для начала диагностики, вводим в строку команду, затем IP-адрес узла или имя домена (консоль распознает IP автоматически), нажать Enter, и на экран выведется результат проведенной проверки соединения.
TRACERT – команда выполняет трассировку маршрута данных (так называемых пакетов) до конечного сервера, выводит на экран IP-адреса промежуточных узлов (т.е. всех маршрутизаторов встречающихся на его пути) и время прохождения этого сигнала между ними. Трассировка проводится для диагностики неполадок в сети, т.к. помогает определить, на каком узле прерывается цепь передачи данных.
PATHPING – сочетает в себе функционал двух предыдущих команд Tracert и Ping, одновременно выполняя трассировку маршрута до конечного IP-узла с отправкой пакетов данных к каждому из промежуточных. Так вы можете увидеть на каком из них происходит больше всего потерь данных.
Три последние команды незаменимы при обнаружении проблем с интернетом. Часто техподдержка провайдера просит предоставить им результат проверок, выполняемых этими командами, особенно PATHPING.
Упражнение 1.
А напоследок давайте потренируемся вводить команды в консоль.
Запустите программу cmd.exe от имени Администратора и введите команду: «SHUTDOWN /s /f /t 30» Нажмите клавишу Enter.
Поздравляю! Вы успешно выполнили упражнение и в полной мере усвоили материал. Больше учиться вам нечему. На этом и закончим наш вводный курс.
© Валентин Юльевич Арьков, 2021
ISBN 978-5-0055-4126-0
Создано в интеллектуальной издательской системе Ridero
Введение
В качестве введения мы обсудим так называемый «Дисклеймер» – Disclaimer – Отказ от претензий. Это модное нынче название для предупреждения читателя о последствиях чтения книги или просмотра фильма. Иногда помогает защититься от судебных претензий, особенно если у читателя напрочь отсутствует чувство юмора.
Данное произведение предназначено исключительно для изучения операционной системы. Текст составлен на основе многолетнего опыта автора по работе в самых разных вычислительных средах, начиная с больших машин серии ЕС ЭВМ и малых вычислительных машин серии СМ, далее через мини-ЭВМ и микро-ЭВМ – вплоть до наших дней с разнообразными настольными, мобильными, персональными и супер-компьютерами.
Любые совпадения с реальными людьми, корпорациями или событиями являются случайными и непреднамеренными. Все персонажи являются вымышленными. Все факты предлагается проверить читателю и убедиться в том, что переводы иностранных слов соответствуют словарным определениям, а описанные приёмы работы применимы на практике.
Любые высказывания по поводу истории разработки программного обеспечения, качества программных продуктов или уровня перевода являются оценочными суждениями автора и не призывают к каким-либо действиям, кроме как к углублённому изучению материала и большему пониманию смысла происходящего в мире информационных технологий.
Задание. Найдите в своих «интернетах» происхождение фразы «Не стреляйте в пианиста…» Выясните, как звучит эта фраза полностью и насколько она применима к компьютерному миру.
Задания
Для освоения материала студенту предстоит изучить небольшой раздел текста и рисунки. Именно изучить, а не прочитать, и не просмотреть, и не говорить: «Это я и так знаю, а это мне точно не пригодится». Узнать что-то новое. Достичь нового понимания. Увидеть, как всё в жизни связано.
Затем нужно выполнить задание. Можно выполнить его несколько раз. Можно слегка изменить действия, поработать с разными настройками, «поиграться» с командами. Научиться вызывать очередную команду. Это для тех, кто хочет просто «сдать лабы».
Задание. Выясните, что такое «знания» и «умения», что у них общего и в чём разница между «знать» и «уметь».
Кроме обычных заданий, в тексте есть творческие задания. Это задания повышенной сложности. Это для тех, кто хочет учиться. Простые задания – это как «колбаса для населения». Просто и доступно. Сложные задания заставляют человека подумать, разобраться, поэкспериментировать. Это ещё один шаг к тому, чтобы стать специалистом своего дела.
Творческое задание. Выясните, что означает выражение «колбаса для населения».
Знакомство с интерфейсом
Самый первый вид интерфейса пользователя, с которым мы познакомимся, – это командная строка – Command prompt. Здесь работа идёт в текстовом режиме.
Вот некоторые другие названия для «текстового» интерфейса:
– Command Window – командное окно
– Command Shell – командная оболочка
– Command Interpreter —интерпретатор команд
– Command Processor – командный процессор или обработчик команд
– CLI – Command Line Interface – Интерфейс командной строки
– Console – Консоль
В развитие идеи командной оболочки ОС была разработана оболочка для сисадмина – PowerShell.
Большинство перечисленных названий говорят о том, что данный интерфейс имеет отношение к вводу КОМАНД. Здесь пользователь вводит команды с клавиатуры.
Первоначально в качестве интерфейса пользователя использовалась электрическая печатная машинка с длинным рулоном бумаги. Рулон можно прокрутить вперёд и назад, чтобы просмотреть историю работы.
Затем была реализация командной строки на экране компьютера в текстовой режиме. И это действительно была СТРОКА. Это был текст – и никакого графического интерфейса.
Современная программная реализация командной строки в виде окна (в графическом режиме) тоже имеет возможность прокрутки результатов вверх и вниз – как на рулоне бумаги.
Мы будем знакомиться с интерпретатором командной строки (командным окном) на примере популярной ОС Microsoft Windows, сокращённо MS Windows, или просто Windows. Здесь мы встретим самые общие принципы и подходы, которые можно найти и в любой другой операционной системе.
Название компании, а точнее, корпорации, состоит из двух частей. Слово micro означает «маленькая». А вот что именно у них маленькое, доверяем узнать читателю самостоятельно.
Задание. Просмотрите в Википедии статью Microsoft. Выясните, сколько человек было в этой компании первоначально и что означает название этой корпорации.
Вторая часть названия имеет отношение к программному обеспечению – software. Буквально слово soft означает «мягкий», но у него есть и другие значения.
Одно из объяснений звучит так. Первые компьютеры 1940-х годов были очень большими и содержали много тяжёлых металлических деталей. За это компьютерное оборудование прозвали «железом». По-английски hardware, то есть «металлические изделия, изделия из металла». Здесь слово hard означает «металлический», хотя для нас более знакомо буквальное значение «твёрдый». Так что программы – тоже в шутку – назвали software в противоположность оборудованию hardware, обыгрывая буквальное значение этих слов. Получается, что «софт» – это «нечто, сделанное НЕ из металла».
Вокруг этих названий можно придумать много шуток, например название Microsoft Mouse можно буквально перевести как «маленькая мягкая мышка».
Для нас эта история – просто пример того, как появляются компьютерные термины и названия корпораций. Знание истории, происхождения слов помогает лучше понять значение слов и названий – и более грамотно ими пользоваться.
Запуск командного окна через [Win + R]
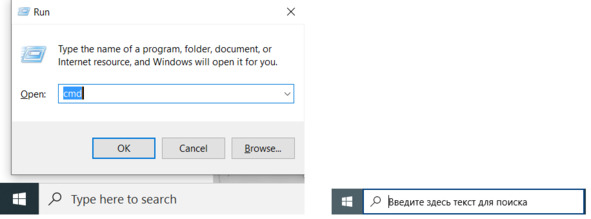
Командное окно можно запустить несколькими способами.
Нажимаем комбинацию клавиш [Windows + R].
Буква R – это начало слова Run – «Запуск программы на выполнение».
Клавиша Windows (или сокращённо Win) обычно расположена в левом нижнем ряду клавиатуры, см. рис. Она используется для вызова часто используемых функций ОС. Клавиша может отсутствовать на некоторых компьютерах.
Рис. Клавиша Windows
В диалоговом окне вводим название команды cmd и нажимаем клавишу Enter на клавиатуре или кнопку ОК на экране, см рис.
Рис. Запуск командной строки
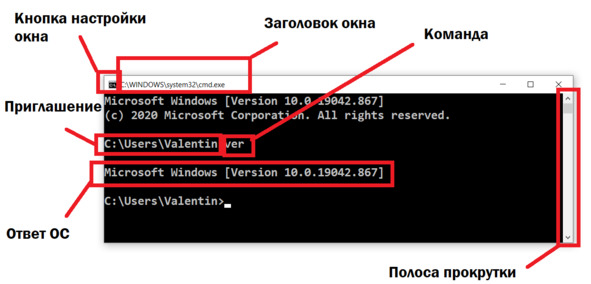
Запускается командное окно. В правой части окна видна полоса прокрутки. На рисунке показаны основные элементы интерфейса.
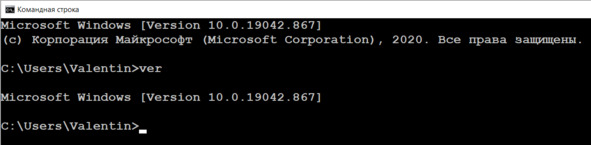
Рис. Интерфейс CMD
VER – Версия ОС
Команды можно вызывать по-разному. В простейшем случае достаточно ввести имя (название) команды и нажать Enter.
Задание. Введите команду ver и определите версию ОС.
Как видим на рис. выше, кроме номера версии, здесь можно узнать номер сборки (Build Number). Это может говорить о том, необходимо ли вам установить обновление для работы с какой-нибудь капризной программой.
Задание. Просмотрите в Википедии статью Сборка (программирование) и выясните, что означает слово build в программировании.
Кроме версии и номера сборки, возможности ОС определяются её редакцией (Edition).
Задание. Просмотрите в Википедии статью List of Microsoft Windows versions и выясните, какая редакция ОС установлена на вашем компьютере.
Команды ОС – это сокращение английских слов. В данном случае ver – это сокращение слова version – «версия».
Творческое задание. Выясните, что такое Wndows NT и как это название связано с современной версией Windows.
Творческое задание. Выясните, что такое Windows Server и есть ли в нём командная строка.
История ввода команд
Командное окно запоминает, какие команды вводил пользователь.
Чтобы просмотреть историю команд, нажимаем на клавиатуре стрелки «вверх» и «вниз». Это помогает быстро повторить длинную команду. Когда предыдущая команда появилась в командной строке, её можно отредактировать – исправить ошибку или изменить. Совсем не обязательно вводить одну и ту же команду много раз вручную. Можно просто вызвать её из истории.
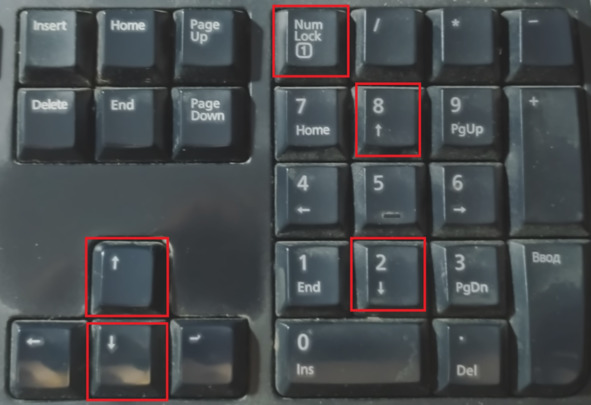
На полноценной клавиатуре можно обнаружить два набора стрелок – как отдельные клавиши и как клавиши цифрового блока. Чтобы использовать стрелки на числовом блоке клавиатуры, нужно нажать клавишу NumLock. Обычно на клавиатуре имеется индикатор нажатия этой клавиши.
Рис. Два вида стрелок
Задание. Просмотрите в Википедии статью NumLock и выясните, как расшифровывается это название.
Задание. Найдите клавишу NumLock и ознакомьтесь с её работой. Обратите внимание на индикатор NumLock.
Задание. Верните предыдущую команду и нажмите Enter. Повторите несколько раз.
Полоса прокрутки
В правой части командного окна имеется полоса прокрутки.
Этот инструмент позволяет прокрутить окно на несколько экранов назад и ознакомиться с историей работы пользователя.
Если закрыть командное окно, история ввода команд будет потеряна.
Задание. Прокрутите командное окно вверх и вниз.
Задание. Введите команду exit и нажмите Enter.
Запуск командного окна через поиск
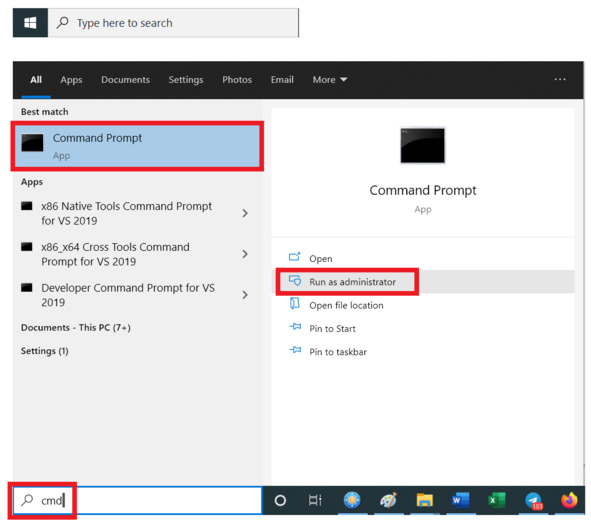
Второй способ запустить командное окно – воспользоваться поиском. В левом нижнем углу экрана находим окно поиска [Type here to search] и вводим название команды cmd, см. рис.
Рис. Запуск через поиск (EN)
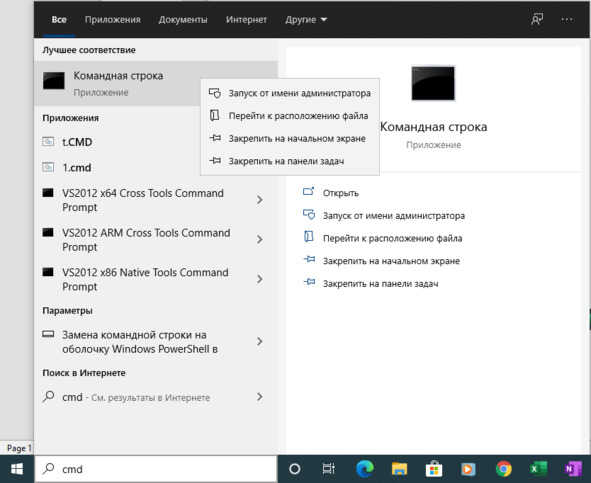
Указав на нужное приложение и нажав правую кнопку мыши, получаем контекстное меню. Как видим, оно дублирует варианты действий, предложенные в правой части окна с результатами поиска, см. рис.
Рис. Контекстное меню (RU)
Нам сразу предлагают запустить Command Prompt. Буквально это выражение означает «Приглашение к вводу команд». Здесь оно означает «Командная строка» или «Командное окно». Слово App – это сокращение от слова Application (Software) – «Прикладная программа».
В русскоязычном варианте ОС видим название Командная строка.
Задание. Просмотрите в Википедии статью Application software. Переключитесь на русскоязычную версию статьи. Обратите внимание на термины, которыми называют программы.
В данном варианте запуска у нас появляются дополнительные возможности. Можно запустить командное окно с правами системного администратора:
Запуск от имени администратора
Run as administrator
Это может быть полезно при установке или настройке некоторых программ, когда ОС ограничивает права обычного пользователя.
Творческое задание. Просмотрите в Википедии русскоязычную статью root и англоязычную статью Superuser. Выясните, какие плюсы и минусы могут быть у доступа с правами администратора.
Язык интерфейса
Windows 10 позволяет переключить язык интерфейса без переустановки ОС.
Это может быть полезно при работе с некоторыми программами. Например, автору приходилось переключаться на русскоязычный интерфейс для заполнения налоговой декларации с помощью официального приложения ФНС. Но технологии меняются очень быстро, и сейчас можно заполнить налоговую декларацию в облаке – через диалоговое окно веб-сайта – без установки программы.
Работа с англоязычным интерфейсом помогает освоить английский язык и привыкнуть к компьютерной терминологии. Как говорят программисты, «в английском языке все слова взяты из языка С++».
Кроме того, чтение справки на английском позволяет быстрее сообразить, что означают сокращённые названия команд и их параметров. Мы увидим, что это первые буквы или начало английских слов. Так будет гораздо легче освоить работу с компьютером – все названия становятся более понятными и даже очевидными.
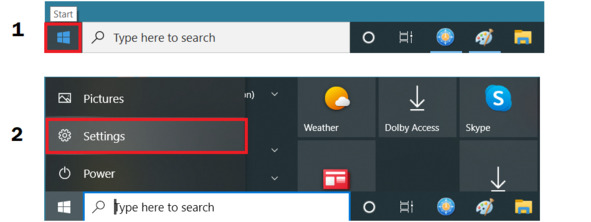
Чтобы переключить язык интерфейса ОС, вызываем настройки: Start – Settings, см. рис.
Рис. Вызов настроек ОС
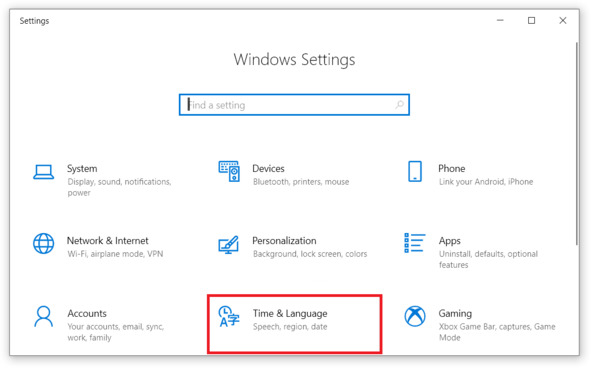
Далее в меню настроек ОС выбираем настройки языка: Time & Language, см. рис.
Рис. Меню настроек ОС
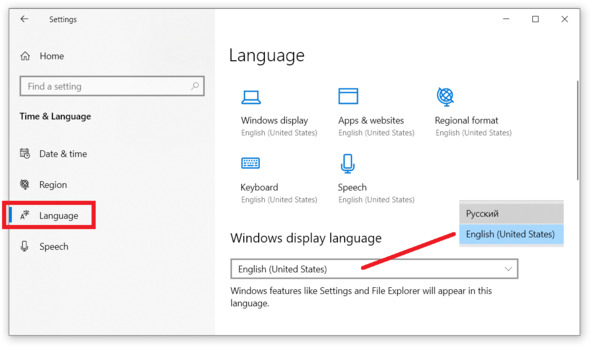
Переходим в раздел настройки языка Language и выбираем нужный язык, см. рис.
Рис. Выбор языка интерфейса ОС
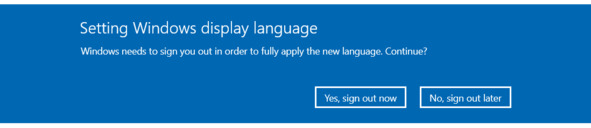
После переключения языка нас предупреждают, что придётся выйти из текущей учётной записи пользователя – Sign out, см. рис. Другими словами, сейчас нас «выйдут» из системы. Поэтому желательно сохранить файлы, которые мы редактируем, чтобы не потерять информацию.
Рис. Предупреждение системы
Соглашаемся и автоматически выходим из системы.
Снова входим со своим паролем и видим новый язык интерфейса. Теперь наше командное окно (командная строка) выводит сообщения на русском языке, см. рис.
Рис. Командная строка с русскоязычным интерфейсом
Все установленные программы живы, все настройки рабочего стола сохранились, никто не пострадал. В предыдущих версиях Windows для перехода на другой язык пришлось бы заново переустанавливать всю ОС, а потом и все прикладные программы. Теперь всё стало гораздо проще и быстрее.
Осталась одна небольшая проблема. Для изменения настроек компьютера может потребоваться участие системного администратора.
Дома это легко: пользователь чаще всего сам же и является администратором.
Если же на предприятии есть всего один сисадмин на три тысячи компьютеров, то работникам можно только посочувствовать.
Компьютер может в самый неподходящий момент сообщить, что для изменения настроек ОС нужны права администратора.
Задание. Переключитесь на английский язык интерфейса. Если у вас уже настроен английский, переключитесь на русский язык, ознакомьтесь с изменениями в интерфейсе, а потом переключитесь на английский.