Содержание
- Using SIMetrix/SIMPLIS in Altium NEXUS
- Getting Started
- A Quick Tour
- Applying Simulation Models to Components
- Setting Up Simulation
- SIMetrix/SIMPLIS Commands
- Running Simulations
- Differences Between Different Simulation Models
- Transient Analysis
- AC Small Signal Analysis and Periodic Operating Point Analysis
- Generating and Running Netlists
- Advanced Sim
- SIMetrix
- SIMPLIS
- Exporting to SIMetrix/SIMPLIS format
- Simulation Models
- Editing Simulation Model Parameters
- Using Model Files
- Model Compatibility
- Setting up New Simulation Models
- Using more than One Simulation Model
- Advanced Simulation with SIMPLIS
- SIMPLIS AC and Periodic Operating Point Analysis
- SIMPLIS Devices.IntLib
- Diode Reverse Recovery
- Self-Oscillating Converter
- Full-Bridge Converter
- Tips for Accurate Simulation
- Troubleshooting
Полное содержание
This document has been imported from the old
techdocs.altium.com
site. As such, its content is quite outdated. It has yet to be updated for the look, feel and possible functionality changes found in the latest version of the software.
Catena Software’s SIMetrix/SIMPLIS ® is a popular Circuit Simulation package. SIMetrix/SIMPLIS is a combination of two independent circuit simulators: SIMetrix, a SPICE-based simulator with numerous enhancements including custom models for power transistor devices; and SIMPLIS, a fast simulator that uses piecewise linear approximations and includes useful analysis modes for switching power supply circuits.
Using SIMetrix/SIMPLIS in Altium NEXUS
Circuit Simulation using SIMetrix and SIMPLIS in Altium NEXUS is similar to using Advanced Sim, Altium NEXUS’s built-in simulator. Altium NEXUS supports SIMetrix/SIMPLIS in three main ways:
- Direct Simulation from Altium NEXUS using SIMetrix/SIMPLIS
- Using models from the SIMetrix/SIMPLIS model library, not only in the native SIMetrix and SIMPLIS simulators but in also in Altium NEXUS’s built-in simulator
- Exporting Schematics containing simulation models to SIMetrix/SIMPLIS format.
To use any of these features, you need the SIMetrix/SIMPLIS application (release 5.3j or higher) and a valid license.
This document assumes some familiarity with SIMetrix/SIMPLIS. Refer to the following documentation for more detailed information about simulation:
Getting Started
To use the SIMetrix/SIMPLIS Circuit Simulator in Altium NEXUS, you must declare the location of SIMetrix/SIMPLIS application:
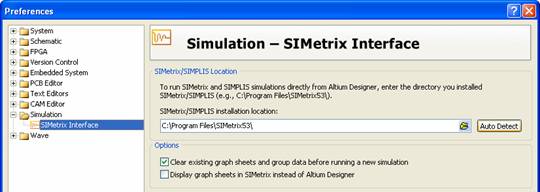
- Select the DXP » Preferences command which brings up the Preferences dialog
- Navigate to the SIMetrix Interface tab under the Simulation folder
Figure 1: Simulation — SIMetrix Interface options
- Type the installation path in the SIMetrix/SIMPLIS installation location field or click the Auto Detect button to automatically detect the location of the application
- The Clear existing graph sheets and group data before running a new simulation checkbox controls whether to clear results from the last execution of the SIMetrix/SIMPLIS waveform viewer, or to let these results display on top of each other. This checkbox is enabled by default
- The Display graph sheets in SIMetrix instead of Altium NEXUS checkbox gives you the option of using the SIMetrix waveform viewer instead of Altium NEXUS. Enable this option if you are generating SIMetrix or SIMPLIS netlists from Altium NEXUS, or the generated netlists won’t display anything when you run them in SIMetrix/SIMPLIS. This checkbox disabled by default.
The first time you use a SIMetrix/SIMPLIS simulator, Altium NEXUS will launch the SIMetrix/SIMPLIS application. You will see the small SIMetrix/SIMPLIS Command Shell dialog appear in the top left corner of your screen. The dialog can be minimized but not closed for SIMetrix/SIMPLIS features to function.
A Quick Tour
Once you have declared the installation location of your SIMetrix/SIMPLIS installation, you are ready to use this feature.
- Select File » Open Project, which brings up the Choose Project to Open dialog
- Navigate to ExamplesCircuit SimulationBoost Converter folder of your installation and open the Boost Converter.PrjPCB project. If you have installed Altium NEXUS in a custom location, navigate to this project accordingly
- In the Projects panel, open the Boost Converter.SchDoc Schematic Document. This is a simple DC—DC converter circuit
Note: There is a SIMetrix/SIMPLIS equivalent of this circuit in your SIMetrix/SIMPLIS installation under C:Program FilesSIMetrix53examplesSIMPLISBoost_ConverterStartup.sxsch. If you have installed the SIMextrix/SIMPLIS application in a custom location, navigate to this file accordingly. View this file to see how SIMetrix/SIMPLIS and Altium NEXUS concepts match up.
In order to run a simulation, you need to provide every component with a Simulation model. Many of the components have been placed from existing libraries such as Miscellaneous Devices.IntLib. If a library component has a Simulation model that works in Advanced Sim, then it is likely to work in SIMetrix and SIMPLIS without modification. The Model Compatibility section describes some exceptions in handling simulation models.
Some components have been placed from a library called SIMetrix Devices.IntLib which is part of the project and can be seen in the Projects Panel under LibrariesCompiled Libraries. This library contains Simulation models sourced from the SIMetrix/SIMPLIS model library.
As with Advanced SIM models, SIMetrix and SIMPLIS models can also be added to your project directly or compiled into your own integrated library. Refer to the document, Working with Integrated Libraries for more information about building your own libraries
Applying Simulation Models to Components
You may need or want to apply multiple Simulation models to a component. You would need to do this if you have a Simulation model that is incompatible with one of the simulators you want to use. Altium NEXUS can detect incompatibilities automatically in many cases and will inform you of these. You would want to apply multiple Simulation models if you have a Simulation model that performs better in one simulator than another.
There are two basic approaches for setting up Simulation models for multiple simulators. You can either:
- Use one Simulation model that is compatible for all simulators
- Use multiple Simulation models that have been configured for each simulator.
The approach you choose will depend on the complexity of the component, the availability of suitable models and the level of detail required in your simulation. Circuit simulation can sometimes be complex and the option to get a «second opinion» on a difficult circuit which has accuracy or convergence issues is a favourable capability.
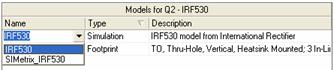
In the Boost Converter.SchDoc, examine the Component Properties of the two MOSFET components, Q1 and Q2. Each component has two Simulation models: IRF530 and SIMetrix_IRF530.
Figure 2: The IRF530 Simulation models for the component in the Component Properties dialog
The IRF530 Simulation model comes from the component manufacturer and is compatible with all three simulators. SIMetrix_IRF530 is from the SIMetrix/SIMPLIS model library and uses a proprietary SIMetrix feature to model the nonlinear capacitance between gate and drain terminals. This feature is said to improve accuracy and performance in SIMetrix but is not currently compatible with Advanced Sim.
Alternatively, examine the Component Properties of the UC3842 component, U1. This is a relatively complex component so it requires native models for each of the three simulators: UC3842B for Advanced Sim, SIMetrix_UC3842 for SIMetrix, and SIMPLIS_UC3842 for SIMPLIS. Refer to the Simulation Models section for more detailed information.
Setting Up Simulation
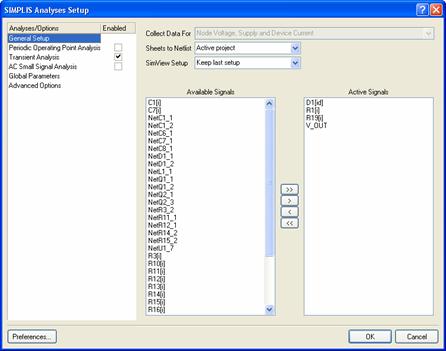
To setup the simulation in SIMPLIS, select the Design » Simulate » SIMPLIS command. The Analyses Setup dialog appears as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Choosing options in the Analyses Setup dialog for SIMPLIS simulator
This Analyses Setup dialog is split into two sections. The left hand side of the dialog allows you to configure your Analyses/Options. The right hand side of the dialog changes depending on the Analyses/Option selected. General Setup allows you to select the signals to display on the right hand side of the dialog. For this example we are interested in the output voltage V_OUT and the current through a few components.
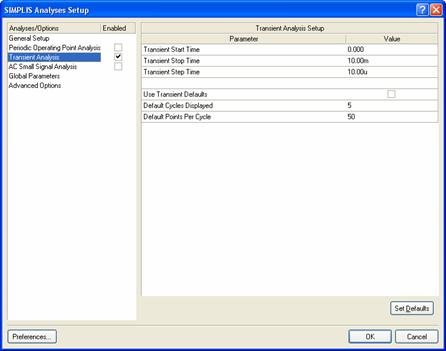
The set of analysis types in the left hand side of this dialog are different in each simulator. SIMPLIS supports three types: Periodic Operating Point Analysis, Transient Analysis and AC Small Signal Analysis. This simulation is a Transient Analysis. To view the analysis parameters, click on Transient Analysis.
Figure 4: Checking the analysis parameters for the Transient Analysis
The parameters that can be set for each analysis type are different in each simulator. Transient Analysis in SIMPLIS has three parameters: a Start Time, a Stop Time, and a Step Time. You can set a default Transient Start, Stop and Step Time by enabling the Use Transient Defaults checkbox. The defaults are calculated based on the time periods of the sources in your circuit.
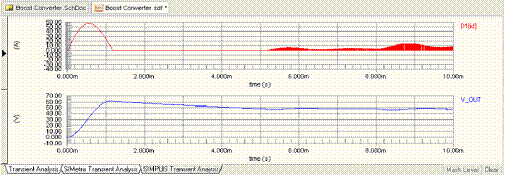
In this example, the last transition representing a sudden change in load occurs 8ms after the power up, so the default would be to run the simulation for over 8ms. To see the output voltage settling for a little while longer than this, populate the Stop Time with a value of 10ms manually.
Altium NEXUS remembers the settings you populate in the Analyses Setup dialog. Each time you run a simulation, the settings are remembered from your last simulation. This is true for parameters that the different simulators have in common, if you switch simulators, making it easy to run the same simulation in SIMPLIS and Advanced Sim and compare the results.
Note: Ensure that you always have the project file containing the schematic with simulation data open as any simulation settings you choose from Free Documents in the Projects panel will be lost when you close the file.
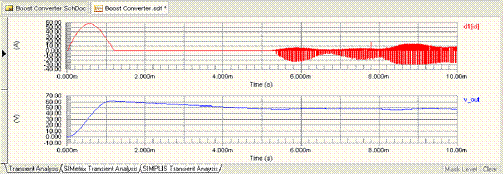
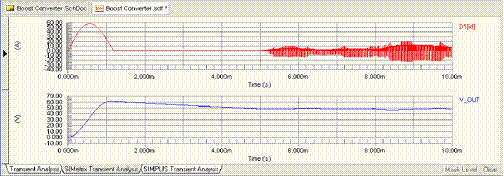
The Design » Simulate menu has two more options: Mixed Sim for running Advanced Sim, and SIMetrix for running SIMetrix. This example works with all three simulators. Due to the different approximations made by each simulator, the results are slightly different. This is most noticeable in the graph of the current through the diode D1 shown below. Fortunately in this example, these differences have little effect on the stability of the output voltage.
Figure 5: Advanced Sim Transient Analysis Results
Figure 6: SIMetrix Transient Analysis Results
Figure 7: SIMPLIS Transient Analysis Results
In Altium NEXUS, simulation results are displayed in a Simulation Data File with a *.sdf file extension.
It is important to understand the approximations made by your simulator. Remember that accuracy and simulation speed can sometimes be a delicate trade-off. You might like to experiment with the model for the D1 component and with the Advanced Options available in each simulator to get a feel for the different simulation models.
SIMetrix/SIMPLIS Commands
This section describes the SIMetrix and SIMPLIS specific commands available in Altium NEXUS. If these commands are missing, ensure you have declared the location of your SIMetrix/SIMPLIS installation, as described in the Getting Started section.
Running Simulations
To run simulations, choose from the following commands:
For Advanced Sim: Design » Simulate » Mixed Sim
For SIMetrix: Design » Simulate » SIMetrix
For SIMPLIS: Design » Simulate » SIMPLIS.
All commands bring up the same Analyses Setup dialog. In General Setup for SIMetrix and SIMPLIS, the Collect Data For field is locked for Node Voltages, Supply and Device Current.
In SIMetrix, the available analysis types are:
- Transient Analysis
- DC Sweep Analysis
- AC Small Signal Analysis
- Noise Analysis
- Pole-Zero Analysis
- Transfer Function Analysis.
In SIMPLIS, the available analysis types are:
- Periodic Operating Point Analysis
- Transient Analysis
- AC Small Signal Analysis.
Refer to your Catena documentation for detailed descriptions on these analysis types.
Differences Between Different Simulation Models
Transient Analysis
SIMPLIS’s Transient Analysis option does not have the Max Step Time, Use Initial Conditions or Fourier Analysis parameters. The Step Time is handled slightly differently by SIMPLIS, the minimum Step Time supported by SIMPLIS is 0.000125 times (Stop Time minus Start Time). If you set the Step Time any smaller than this, it will be silently clamped to the minimum value.
SIMetrix’s Transient Analysis includes some additional parameters for Real-time Noise. This feature can only be used if it is included in your SIMetrix/SIMPLIS licence.
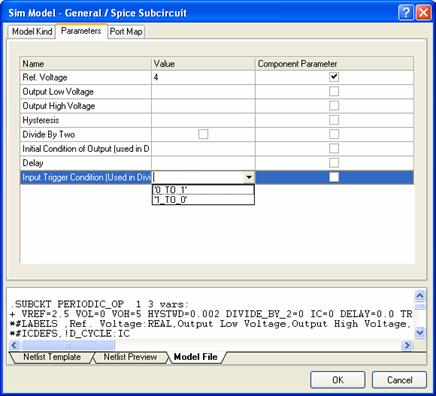
AC Small Signal Analysis and Periodic Operating Point Analysis
SIMPLIS’s AC Small Signal Analysis requires a special component to be placed on the Schematic. Place the Periodic Operating Point Trigger component and drive with a signal that goes high whenever a switching event occurs in your circuit. If you try to run AC Small Signal or Periodic Operating Point Analysis in SIMPLIS without this component, an error is generated. For more information on the Periodic Operating Point Trigger, refer to the Advanced Simulation with SIMPLIS section.
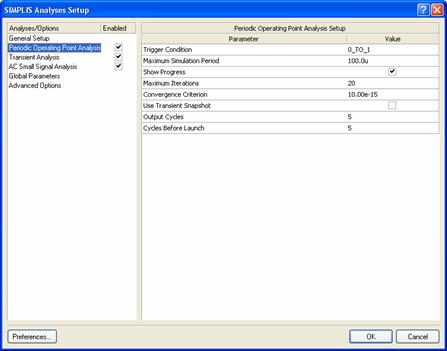
Periodic Operating Point Analysis is only available in SIMPLIS. Its main use is in conjunction with AC Small Signal Analysis but you can also see a graph of SIMPLIS finding the steady-state «operating point» by checking the Show Progress option.
Figure 8: SIMPLIS and Periodic Operating Point Analysis
Advanced Options for the three simulators are different. SIMPLIS has only a few advanced options. The only one you are likely to need is IGNORE_UNITS, which is enabled by default. SIMetrix and Advanced Sim, however, provide quite a few advanced options to control your simulation’s accuracy and convergence. Some Advanced Sim and SIMetrix options (like ABSTOL and VNTOL) are identical, and have much the same effect in both simulators. Settings for these options are shared between the two simulators. Others are similar but not identical so you have to set a differently-named option for each simulator. For example, the number of steps to use if you have to use the GMIN stepping algorithm is called GMINSTEP in Advanced Sim and GMINSTEPITERLIMIT in SIMetrix.
Refer to the Advanced Simulation with SIMPLIS section in this document and the SIMetrix and SIMPLIS documentation for each simulator for more information about Advanced Options.
SIMetrix’s multi-step analysis types (Device Sweep, Parameter Sweep, Model Parameter Sweep, Temperature Sweep, Frequency Sweep, Snapshot, and Monte Carlo) are not supported in this release of Altium NEXUS. To use these analysis types, you can export your Schematic to SIMetrix/SIMPLIS format (see below) and run them from the SIMetrix/SIMPLIS application.
Generating and Running Netlists
The netlist is a text file and can be edited in a text editor. You can generate a netlist for each of the three simulators which can be useful if you want to edit the netlist directly or examine the actual device statements given to the simulator.
To generate a SIMPLIS netlist, Altium NEXUS must communicate with the SIMetrix/SIMPLIS application so the SIMetrix/SIMPLIS Command Shell dialog may appear while you are waiting for your SIMPLIS netlist.
Advanced Sim
To generate an Advanced Sim Netlist in Altium NEXUS:
- Select the Design » Netlist For Project » XSpice command
To run the Advanced Sim Netlist in Altium NEXUS: - Open the netlist which is saved in a .nsx file, displayed under the GeneratedAdvanced Sim Netlists in the Projects Panel
- Select the Simulate » Run command to run this netlist.
SIMetrix
To generate a SIMetrix netlist in Altium NEXUS:
- Select the Design » Netlist For Project » SIMetrix command
To run the SIMetrix netlist, open the SIMetrix/SIMPLIS application: - Select the Simulator » Run Netlist command and navigate to find your file
SIMPLIS
To generate a SIMPLIS netlist in Altium NEXUS:
- Select the Design » Netlist For Project » SIMPLIS command
To run the SIMPLIS netlist, open the SIMetrix/SIMPLIS application - Select the SIMPLIS » Run Netlist command
- The file names for both SIMetrix and SIMPLIS netlists have the file extension *.net so be careful not to overwrite a netlist file with output from the two different simulators.
Remember to enable the Display graph sheets in SIMetrix instead of Altium NEXUS option in DXP » Preferences, or the generated netlists won’t actually display anything when you run them in SIMetrix/SIMPLIS.
Exporting to SIMetrix/SIMPLIS format
You can export your Altium NEXUS Schematic or project to SIMetrix format using the File » Export File to Simetrix or File » Export Project to Simetrix commands.
Exporting to SIMetrix requires Altium NEXUS to communicate with the SIMetrix/SIMPLIS application so the SIMetrix/SIMPLIS Command Shell dialog may appear during this operation.
In this release of Altium NEXUS, not all components on the exported schematic are editable in the SIMetrix application. As a work around, use the Edit Properties command in SIMetrix instead of Edit Part, or delete and re-place the component in SIMetrix.
Simulation Models
Until now, all the Simulation models you have seen were preloaded from integrated libraries. This is the easiest way to use Simulation models as all the work of setting up the models was done in the Library Editor. Eventually you will want to set up your own Simulation models, either because you can’t find a particular component in any library, or because you want to make your own integrated libraries. The method in both cases is the same. SIMetrix/SIMPLIS Simulation models are very similar to Altium NEXUS models so you will find a brief description here focusing on the SIMetrix/SIMPLIS-specific features.
Editing Simulation Model Parameters
Many Simulation models have editable parameters. SIMetrix/SIMPLIS models are no different to Altium NEXUS models in this respect. The appearance of some SIMetrix/SIMPLIS model parameters is slightly different making them look a little more like the Edit Part dialog in SIMetrix/SIMPLIS.
Double-click on a Simulation model in the bottom right of the Component Properties dialog, then click on the Parameters tab. The contents of the Parameters tab is different for each model Kind, and, in the case of General/Spice Subcircuit models, is different for each subcircuit.
The Component Parameter checkbox next to each parameter gives you the option of making the parameter a component parameter, where it can be seen and edited in the top right section of the Component Properties dialog. This is makes model parameters visible on the Schematic.
Differences exist in the Parameters tab of SIMetrix and SIMPLIS subcircuit models. Subcircuit model parameters usually have abbreviated names like VREF and VOL, but in the Name column, you will see that Altium NEXUS displays a longer name, such as Ref. Voltage and Output Low Voltage found in the SIMetrix/SIMPLIS model file. These longer names, however, are only visible in the Parameters tab. Everywhere else, such as in the model file itself and on the Schematic if you check the Component Parameter box, you will see only abbreviated names.
Figure 9: Parameters tab for the model file
In addition, the appearance of the Parameters tab for the common SIMetrix Electrolytic Capacitor and Lossy Inductor components is similar to those of the built-in model Kinds.
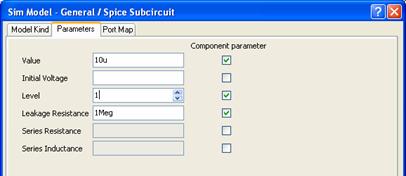
When you change the Level parameter, the parameters that are not used at that detail level are grayed out. The Initial Voltage and Initial Current parameters are especially important for SIMPLIS — remember that a blank initial condition is quite different from an initial condition of 0. Each initial condition field actually corresponds to two model parameters named IC and USE_IC. Again, you will only see these if you enable the Component Parameter option for an Initial Voltage or Initial Current.
Figure 10: Entering the values for the Initial Conditions manually
This release of Altium NEXUS does not automatically populate initial condition parameters from successful SIMPLIS simulations as it does with SIMetrix/SIMPLIS. If SIMPLIS fails to converge on an initial operating point, you may have to populate some initial conditions manually. Try using information from previous simulation runs, from other simulators, from exporting your Schematic to SIMetrix/SIMPLIS or from your own knowledge of the circuit.
Using Model Files
Most of the interesting model kinds (such as diodes, transistors, and subcircuits) require you to attach a model file. Model files come in several different types (Advanced Sim, SIMetrix, and SIMPLIS).
You can locate model files in Altium NEXUS’s Libraries, in the SIMetrix/SIMPLIS model library or download them from a manufacturer or other source. The SIMetrix/SIMPLIS model library is in the directory supportmodels under your installed SIMetrix/SIMPLIS application folder (usually C:Program FilesSIMetrix53supportmodels). SIMetrix/SIMPLIS model files can be used like Advanced Sim model files. They can be:
1. Added to your project in the Projects panel
2. Added to your installed libraries in the Libraries panel
3. Declared in the In File or Full Path fields of the Sim Model dialog accessed by double-clicking on your Simulation Model in the Component Properties dialog
4. Compiled into an integrated library.
Advanced Sim model files have file extensions *.ckt and *.mdl, and usually contain one model each. SIMetrix/SIMPLIS model files all have file extensions *.lb, and each one contains dozens or even hundreds of models. If you click on the Model File tab at the bottom of your SIM Model dialog, you will see where your model is in the file by scrolling the view down to the beginning of the model.
An important difference is that Altium NEXUS gives all SIMetrix and SIMPLIS models names beginning with SIMetrix_ or SIMPLIS_. This helps you recognize which models are intended for which simulator and also helps you tell your models apart. For example, the UC3842 component has two models in the SIMetrix/SIMPLIS model library: one called SIMetrix_UC3842 and another called SIMPLIS_UC3842. If the SIMetrix or SIMPLIS model name already begins with SIMetrix_ or SIMPLIS_ , then Altium NEXUS doesn’t add the prefix again. SIMPLIS_XOR is SIMPLIS_XOR in Altium NEXUS, not SIMPLIS_SIMPLIS_XOR which would be redundant.
Figure 11: Model File for the Spice Subcircuit.
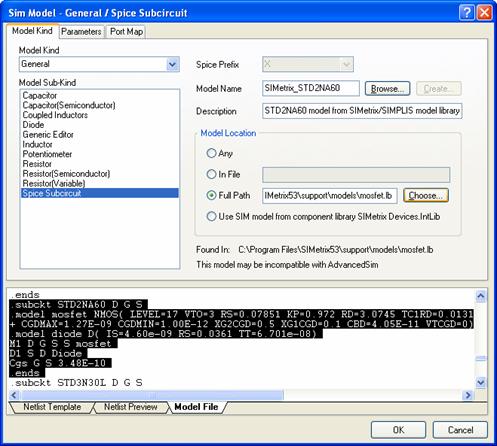
Model Compatibility
Finding models compatible with your simulator may be difficult. There are many different simulators available and if you try to use a model designed for a different simulator, your simulation may behave erratically. With three different simulators that you might want to use, the problem of finding models for every component (not to mention the time it would take to set them all up) could become time consuming.
Fortunately, if you are missing a native Advanced Sim, SIMetrix, or SIMPLIS model for a component, then Altium NEXUS will convert the best model you have available to your target simulator. This lets you mix and match Advanced Sim, SIMetrix, and SIMPLIS models. For many components, you will only need one model. For complex or critical components, you can attach specialized models that have been tuned for each simulator.
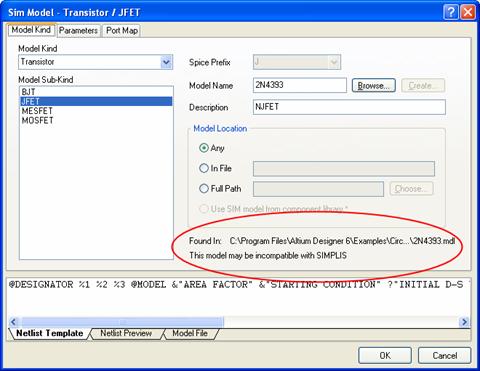
Altium NEXUS can convert many different kinds of models. There are still a few models that it cannot convert due to limitations in the simulator or because the feature has not been implemented yet. If you try to set up a model that is incompatible with one or more simulators, Altium NEXUS will warn you with the following message: This model may be incompatible with SIMPLIS in the Sim Model editor dialog, under the model location,
Figure 12: Incompatible Model Warning
Altium NEXUS does not prevent you from using the model in that simulator. You may experience errors either from Altium NEXUS’s model conversion process or from the target simulator.
The following model types are currently incompatible with Advanced Sim:
1. SIMetrix’s proprietary code models (ad_converter, adc_schmitt, da_converter, d_init, d_logic_block, d_open_c, and d_open_e).
2. SIMetrix’s proprietary MOSFET model (NMOS and PMOS LEVEL=17).
3. SIMetrix’s saturable inductor models (CORE and CORENH).
The following model types are currently incompatible with SIMetrix:
1. Uniform Distributed RC models (URC)
2. Altium NEXUS SimCode models (simcode, xadc, xdac, xdav, and xsimcode)
The following model types are currently incompatible with SIMPLIS:
1. Equation Voltage and Current Sources (B)
2. Single Frequency FM Voltage and Current Sources (SFFM)
3. JFETs (NJF and PJF)
4. MESFETs (NMF and PMF)
5. Lossless Transmission Lines (T)
6. Lossy Transmission Lines (LTRA)
7. Uniform Distributed RC models (URC)
8. SIMetrix’s saturable inductor models (CORE and CORENH).
The source of the incompatibility can be from the model file or the Netlist Template. For example, an Equation source won’t be compatible with SIMPLIS, whether have you explicitly selected the model Kind Voltage Source/Equation, or used a General/Spice Subcircuit or General/Generic Editor model file that contains a SPICE B statement.
Setting up New Simulation Models
Now we are finally ready to give a component a new Simulation model. You can do this whether or not the component already has an existing Simulation model
The basic steps in setting up a Simulation model are outlined below:
1. If the model requires a model file, ensure that the model file is available (for example, by adding it to your project or installed libraries)
2. In the bottom right of the component’s Component Properties dialog, under Models, click Add and then select Simulation
3. Set the Model Kind and Model Sub-Kind
4. Give the model a Name. If the model requires a model file, the Name must be that of a model in the model file. Remember that SIMetrix and SIMPLIS models always have names beginning with SIMetrix_ or SIMPLIS_ prefix
5. Give the model a Description. The Description is free form
6. On the Port Map tab, connect up the component pins and model pins.
SIMetrix models will generally have a Model Kind and Sub-Kind of General/Diode, General/Generic Editor, General/Spice Subcircuit , Transistor/BJT, Transistor/JFET, Transistor/MESFET, or Transistor/MOSFET.
Native SIMPLIS models do not have their own separate Kinds and SubKinds. The Model Kind and Sub-Kind of a SIMPLIS model will almost always be General/Spice Subcircuit.
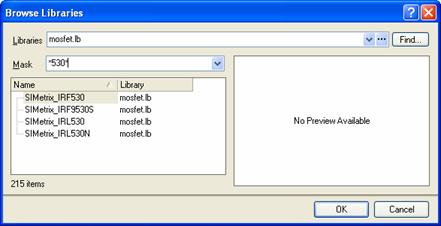
Altium NEXUS 6.8 has a new feature which can make steps 3, 4, and 5 much easier, especially if you have thousands of models to choose from. In the Sim Editor dialog, click the Browse button. The Browse Libraries dialog will appear.
Figure 13: Choosing which Model Library to use from the Browse Libraries dialog
Next to Libraries, select a model file or a library from the list box. Only model files and libraries in your project and your installed libraries are in the list, but you can also browse by clicking on … or Find buttons. Once you have selected a file, scroll down the list of models and click on the name of the model you want. To narrow your search, type part of the model name in the Mask field. Once you have found the model, click the OK button. Altium NEXUS will populate the model’s Name, Description, Kind, and Sub-Kind fields for you.
Using more than One Simulation Model
If a component has more than one Simulation model, how does Altium NEXUS decide which one to use in each simulator?
For Advanced Sim, one of the Simulation Models is distinguished as the «current» model — this is the one displayed on top in the Models panel of the Component Properties dialog. You can change which model is current by clicking the button next to the model name, and selecting a model from the drop-down list.
For SIMetrix,
1. If the component has a native SIMetrix model, then it is used by default
2. Alternatively, the current model is used.
For SIMPLIS, the rules are slightly different:
1. The first choice is the component’s native SIMPLIS model, if any
2. If there is no SIMPLIS model, the SIMetrix model is used instead. The reason for this is that SIMetrix models are generally better suited for conversion to SIMPLIS than average SPICE models
3. Alternatively, the current (Advanced Sim) model is used.
These rules have been designed to choose the best model for each simulator. If you find that you need to switch models on a component frequently, consider creating a library with multiple versions of that component, each with a different set of Simulation models.
Advanced Simulation with SIMPLIS
This section provides some additional information and resources for using SIMPLIS from Altium NEXUS. SIMPLIS is quite different in many respects from Advanced Sim and SIMetrix.
SIMPLIS AC and Periodic Operating Point Analysis
SIMPLIS AC Analysis looks similar to Advanced Sim and SIMetrix but functions quite differently. Time-varying DC sources run exactly as they do in Transient Analysis, instead of being stopped as they are in SPICE-based simulators. This difference is especially important in switching power supply circuits with oscillator devices, and most closely approximates the kind of frequency analysis that you could do with a breadboard on the bench.
SIMPLIS also has AC voltage and current sources similar to SPICE. From Altium NEXUS, there is no special «SIMPLIS AC Source» component. Use the AC Magnitude and AC Phase parameters of any independent source. At the SIMPLIS level, these parameters generate an extra AC source alongside the DC source. These sources effectively disappear in Transient Analysis, so they have no effect on the circuit except in AC Analysis.
SIMPLIS AC Analysis requires an initial Periodic Operating Point (POP) Analysis to run. This is why Altium NEXUS doesn’t let you turn AC Analysis on and POP Analysis off in the Analyses Setup dialog at the same time.
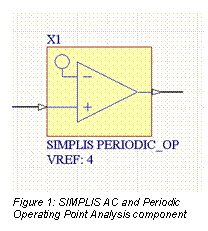
POP Analysis finds the steady-state «operating point» of a switching power supply circuit. To use it, you must place a SIMPLIS PERIODIC_OP component from SIMPLIS Devices.IntLib on your schematic. Whenever the output of this component goes high, it signals a POP switching event to SIMPLIS.
It is possible to use another component to trigger POP Analysis, but it is not as easy. In the Analyses Setup dialog, under Global Parameters, add a parameter named TRIG_GATE with the SIMPLIS name of an eligible device. SIMPLIS requires that the device must be a digital component and you must know how to get the SIMPLIS name that comes out of the netlist. So if you want to drive POP with the output of a T-type Flip-Flop called U2, set TRIG_GATE to XU2.!D_SIMPLIS_TFF.
Any PERIODIC_OP component on the schematic overrides the TRIG_GATE parameter and is the preferred method to drive POP Analysis.
For more information about SIMPLIS analysis modes, refer to your Catena documentation.
SIMPLIS Devices.IntLib
SIMPLIS Devices.IntLib is a library of components with primitive SIMPLIS models. «Primitive» in this case means that each component corresponds to exactly one of the model statements from Chapter 4 in the SIMPLIS Reference Manual.
SIMPLIS devices cannot be used in a real circuit, they are useful for modelling. You can use them in a circuit to model certain effects that you know how to approximate with piecewise linear functions. You can use them when drawing up a SIMPLIS model for a complex component as an Altium NEXUS Schematic.
SIMPLIS devices are of course designed for SIMPLIS and they are also compatible with other simulators. Altium NEXUS can automatically convert all SIMPLIS primitives into equivalent models for Advanced Sim and SIMetrix. The results you get in these simulators won’t be as fast or accurate as in SIMPLIS.
Diode Reverse Recovery
As an example of modelling with SIMPLIS devices, select File » Open Project and when the Choose Project to Open dialog appears, navigate to C:Program FilesAltium NEXUSExamplesCircuit SimulationDiode Reverse Recovery folder and open the Diode Reverse Recovery.PrjPCB project
This project contains two Schematic Documents: Diode Reverse Recovery Test Circuit.SchDoc which is a simple test circuit that applies a large reverse bias to a diode. Diode Model.SchDoc which models the diode itself in terms of simulation sources and a SIMPLIS piecewise linear resistor.
Run the simulation to see the reverse recovery effect. (Make sure you have Miscellaneous Devices.IntLib in your installed libraries first) When the reverse bias is suddenly applied, a small reverse current flows in the diode before it quickly recovers. Even though this circuit uses a SIMPLIS model, Altium NEXUS lets you run the simulation in all three simulators.
This simple example also illustrates another important point
— it is best practice, even for simple designs, to keep your test circuits and external stimuli on different schematic sheets from the circuit that you’re testing.
Self-Oscillating Converter
Open an example of a circuit using SIMPLIS devices and AC Analysis. select File » Open Project and when the Choose Project to Open dialog appears, navigate to C:Program FilesAltium NEXUSExamplesCircuit SimulationSelf-Oscillating Converter folder and open the Self-Oscillating Converter.PrjPCB project.
This is a DC—DC converter circuit. The Simulation models in this circuit have been set up with SIMPLIS in mind so you won’t get useful results in Advanced Sim or SIMetrix without some modification.
The SIMPLIS PERIODIC_OP component X1 is connected to the gate terminal of the MOSFET Q1. Whenever this voltage goes above VREF (2.5 V by default), it signals a switching event to SIMPLIS.
Run the simulation to see the result. The Show Progress option has been turned on so you can see the number of cycles it takes for the circuit to reach its periodic operating point.
The piecewise linear inductor component L2 models the saturation effect in the transformer TX2. This is a well-known property of real transformers where the inductance of the coils is not a constant, but falls off when the core starts to saturate. In this example, it has been placed as a component in parallel with the primary winding of the transformer, but it can almost as easily be incorporated into the transformer’s model file. The piecewise linear function itself has been approximated from knowledge of the core material’s permeability. SIMPLIS does not yet provide an automatic method for creating a piecewise linear approximation from this knowledge. The piecewise linear fit is a trade-off between simulation accuracy and performance.
The model file of the optocoupler component U1 may look a little strange because it was created by generating a netlist from the gen_opto Schematic used in several Transim circuit templates. There are many different ways to model this component, again trading off accuracy and performance.
Full-Bridge Converter
For another example of a circuit using AC Analysis, select File » Open Project and when the Choose Project to Open dialog appears, navigate to C:Program FilesAltium NEXUSExamplesCircuit Simulation Full-Bridge Converter folder and open the Full-Bridge Converter.PrjPCB project. This is another DC—DC converter circuit. This circuit has been set up with SIMPLIS in mind, so make sure you run this one in SIMPLIS.
The SIMPLIS PERIODIC_OP component X1 in this example is connected to the clock synch output of the UC1825 controller device U1. For this example we need to divide the clock down by two, so the signal has been fed through a Toggle Flip-Flop first (The PERIODIC_OP component also has a Divide By Two parameter that does the same thing)
Run the simulation to see the result. The signals in Transient Analysis might look erratic but this is because the default scale on the vertical axis shows the most detail. Try changing the scale by clicking on the axes or adding signals to the simulation and displaying multiple waves on the same plot by using Add Wave To Plot on the right-click menu.
The initial conditions on the capacitor and inductor components are essential for SIMPLIS to find the initial operating point. Try varying some of the initial conditions to see the effect this has on SIMPLIS.
Tips for Accurate Simulation
Different simulators function differently so they may sometimes vary greatly in performance or produce different results for the same circuit.
If you have problems with performance, accuracy or convergence, here are a few tips that should help you diagnose and rectify the problems:
- Ensure your circuit is physically accurate. The default capacitor, inductor and diode models especially can be a bit unrealistic as they do not include parasitic and leakage resistances that exist in real life. For diodes, ensure your model sets the RS parameter. For more realistic capacitor and inductor models, try the components Capacitor (Electrolytic, Simple), Capacitor (Electrolytic, Detailed), and Inductor (Lossy) from SIMetrix Devices.IntLib
- Ensure you are using high-quality models that do not generate large discontinuous changes in voltage or current
- Wherever possible, use native models in each simulator. SIMetrix and SIMPLIS models have generally been tuned for those simulators, so you should use them wherever available
- If you can’t find a native SIMPLIS model but you can find a SIMetrix one, use that. SIMetrix models are generally better suited for conversion to SIMPLIS than other SPICE models
- If SIMPLIS can’t find an initial operating point, set some initial conditions. You can set initial conditions on BJT, Capacitor, Diode, Inductor, and MOSFET models on the Parameters tab of the Sim Model dialog. Advanced Sim and SIMetrix both ignore these initial conditions unless you tick the Use Initial Conditions checkbox in Transient/Fourier Analysis Setup
- If Advanced Sim or SIMetrix can’t find an initial operating point, force one by using the Initial Condition and Node Set components (from Simulation Sources.IntLib). These components are ignored in SIMPLIS
- If SIMetrix or Advanced Sim transient analysis fails with a «time step too small» error, try using a different Integration method or relax the accuracy by increasing the value of ABSTOL in Advanced Options. Other options worth investigating are GMINSTEP (in Advanced Sim), and ABSTOLMAX and GMINSTEPITERLIMIT (in SIMetrix).
Refer to Transim’s and Catena’s documentation for more tips on using SIMetrix and SIMPLIS applications.
Troubleshooting
Catena Software has been most helpful in modifying SIMetrix/SIMPLIS to allow it to be driven directly from Altium NEXUS.
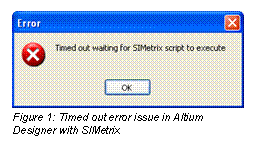
SIMetrix/SIMPLIS release 5.3j is still a new interface so you may experience occasional timeouts. For example, if you have a dialog open in SIMetrix/SIMPLIS, it may not respond to Altium NEXUS, and you will eventually see the Timed out message.
If you ever see this message, close any open dialogs in SIMetrix/SIMPLIS, and try the operation again.
Try SIMetrix/SIMPLIS Elements, our free demonstration version
Try the free demo
Online Documentation
Full documentation for both SIMetrix and SIMetrix/SIMPLIS is available online.
User Manual
SIMetrix Simulator Reference
SIMetrix Script Reference
SIMetrix Verilog A Reference
SIMPLIS Documentation Home
SIMPLIS Reference
DVM
SystemDesigner
PDF Manuals
We provide PDF versions of our core manuals, which may be printed for personal and internal-business use only.
User Manual
Simulator Reference
SIMPLIS Reference
Verilog-A Manual
Script Reference
Tutorials
Tutorials Index
Tutorial 1: Getting Started
Tutorial 2: Creating a Schematic and Running a Simulation
Tutorial 3: Using the Waveform Viewer
SIMPLIS Tutorials
Self-Training
SIMetrix Self-Training
SIMPLIS Self-Training
Previous Versions
SIMetrix Online Documentation for Version 9.0
SIMPLIS Online Documentation for Version 9.0
SIMetrix Online Documentation for Version 8.5
SIMPLIS Online Documentation for Version 8.5
Tutorials & Training
SIMPLIS Tutorial — The SIMPLIS tutorial is intended to help new users get started with the SIMPLIS simulator and to serve as a general reference for SIMPLIS. The tutorial follows the progression of a buck converter design from first constructs to a final, parametrized, hierarchical design.
Learning SIMPLIS — A structured experience in which a capable and willing engineer can come up to speed with SIMPLIS in four (full-time) weeks. At the conclusion of the experience, the engineer will be confident that they will be able to competently apply SIMPLIS to appropriate switching power supply modeling objectives.
DVM Tutorial — The DVM Tutorial guides a user through configuring a working schematic to run in the Design Verification Module, run built-in test plans and customize them. A host of other, more advanced, topics is covered as well, including schematic and component modification and test configuration.
MDM Tutorial — The MDM Tutorial introduces a user to the basics of the SIMPLIS Magnetics Design Module through the design of an inductor for a DC-to-DC Buck converter and a transformer for an isolated AC line self-oscillating flyback converter.
Advanced SIMPLIS Training Materials — This section of the documentation comes directly from the training course that SIMPLIS Technologies conducts several times per year in different locations. The course material is intended for those with some experience using SIMPLIS and covers a wide range of topics from the POP analysis to Parameterization to measuring Switching Losses and Efficiency.
Уникальный симулятор, созданный для высокоскоростного анализа линейных и смешанных цепей.
Приложение SIMPLIS (аббревиатура от «SIMulation for Piecewise LInear System») было создано с целью быстрого моделирования источников питания и импульсных стабилизаторов, а также исследования ключевых схем преобразователей напряжения. Оно, также как и программа SPICE, функционирует на уровне компонентов радиосхемы, однако анализы переходных процессов выполняет в 10-50 раз быстрее. Подобной скорости моделирования модуль SIMPLIS достигает благодаря применению кусочно-линейной аппроксимации взамен решения систем нелинейных уравнений, используемых в программе SPICE. Приложение выполняет следующие виды анализов: переходных процессов, ФЧХ/АЧХ с замкнутой петлей авторегулирования и в рабочей точке. Последний анализ представляет собой ускоренный расчет установившегося режима работы импульсного блока питания при постоянных нагрузке и питании. Для особо сложных в плане симуляции случаев предусмотрен еще один режим анализа – Multi-Tone AC, являющийся подобием двухчастотного метода определения интермодуляционных искажений. Кроме того в программе имеется функция автоматического преобразования SPICE-моделей в модели формата SIMPLIS.
Вторая программа SIMetrix является полноценным симулятором аналогово-цифровых схем. В ее основе лежат два распространенных продукта – XSPICE и SPIСE. Приложение имеет схемный редактор, симулятор и графический пост-процессор. В качестве основного метода итерации применяется решение Ньютона-Рэфсона, обеспечивающего быстроту расчетов режимов переходных процессов и по постоянному току. Для особо «каверзных» схем имеется алгоритм псевдопереходного анализа с изоляцией/фиксацией невычисляемых узловых потенциалов и адаптируемым шагом итерации. Программа SIMetrix выполняет поддержку моделей элементов спецификации MOS9, BSIM3/4, Mextram, VBIC и совместима с файлами HSPICE. Кроме того приложение имеет пробник Бодэ и калькулятор КПД, а также поддерживает создание произвольного логического блока, имитирующего работу цифрового устройства.
Пакет программ SIMetrix/SIMPLIS является платным. Бесплатная версия симулятора (SIMetrix/SIMPLIS Intro) имеет множество ограничений, среди которых стоит отметить: лимит на количество узлов в исследуемой схеме (не больше 140), отсутствие поддержки командной строки, пользовательских скриптов и Verilog-компилятора. Некоторые из отключенных функций могут быть активированы на срок в тридцать дней при использовании опции разблокировки. Скачать последнюю версию можно со страницы разработчиков по адресу http://www.simetrix.co.uk/site/demo.php или http://www.simplistechnologies.com/downloads/file/win32/simetrix-simplis (необходима регистрация). Дистрибутив с программами включает в себя подробный пользовательский мануал, файлы помощи и сотни примеров выполненных работ из различных направлений схемотехники.
Программы, входящие в данный комплект, были разработаны благодаря усилиям двух компаний-партнеров – SIMetrix Technologies (Великобритания, графство Беркшир, город Тэтчем) и SIMPLIS Technologies (США, штат Орегон, город Портленд).
Рассматриваемый комплект программ для симулирования электронных схем представлен на английском языке, русификатора для него не имеется.
Приложение SIMetrix/SIMPLIS создано для работы в операционной среде Microsoft Windows (8, 7, Vista и XP). Поддерживаются как 32-битные, так и 64-битные платформы.
Распространение программы: платная. Есть демо-версия с ограничениями на 140 узлов
Официальный сайт SIMetrix/SIMPLIS: http://www.simetrix.co.uk
Форматы файлов SIMetrix/SIMPLIS: SXSCH
Скачать SIMetrix/SIMPLIS
Обсуждение программы на форуме
Suggest us how to improve StudyLib
(For complaints, use
another form
)
Your e-mail
Input it if you want to receive answer
Rate us
1
2
3
4
5