vitalya abrosimov
1 неделя назад
Женя дай бог тебе здоровья ты просто император ремонта я еьусь месяц и ты показывал как надо четко ровно
Михаил Сергеев
3 недели назад
Круто!
Капитан
5 месяцев назад
Познавательно, поймёт даже чайник.👍
ЕгорPROO prooo
8 месяцев назад
Это что такое
Юрий Секненков
9 месяцев назад
Спасибо, очень полезная информация! Вы реально многих воспитали мастерством в мопедоремонтах!
сергей васюченков
10 месяцев назад
Нахрена я его смотрю. У меня дизель 12.7 литра!?
M micend
1 год назад
Шёл 2022 год, смотрю тёплые, ламповые видео. Интересно и познавательно. Сейчас Евгений заматерел, стал совсем бездушный в видео.
gtblack1988
1 год назад
Хрена колесо раздувает))
Виктор Ион Спидвагон
1 год назад
Я один думал что это эндуро с двигателем от скутера
NO STOP ENGINE!
1 год назад
Бло же время когда у тебя небыло не одного шуропаверта
роб стен
1 год назад
Доброго времени суток, подскажите пожалуйста в картере Сузуки стрит меджик между подшипником коленвала и приводом маслонасоса устанавливается сальник или нет ? При разборе двигателя под ремонт сальника не было ! Да и места под сальник вроде очень мало ! Смотрел ваши видео по ремонту мопедов Сузуки, везде сальники устанавливаются !
Оксана Гольцова
1 год назад
А скажи пожалуйста как регелировать поплавок , если он полностью плостмассовый ?
Кир Корнев
1 год назад
время рандомных реков из 2021
Александр Плахов
1 год назад
Пит Стоп!!!
Женя,
Спасибо…
Какой молодец,
Столько ньюансов
рассказал, показал,
Разжевал.
Беру на вооружение.
Ремонт… Твой…
Сражение или
Словно бой…
Бой победный…
Для этого у тебя всё
Есть… И
занятий и попыток тьма,
А
З Н А Н И Й
Просто не счесть.
Восхищаюсь и преклоняюсь.
Снимаю шляпу…
Иван Борисович
1 год назад
Сегодня купил такой здрочь
Saudi Nord
1 год назад
Ремонте мопЭда, главное терпение)))
Saudi Nord
1 год назад
КоррЭктной сделать)))
Saudi Nord
1 год назад
Когда ничего не знают, сразу почему то на Китай ссылаются))).
Гордый Перец
1 год назад
2021 на месте! Смотрим и наслаждаемся!
CHeeCHara
2 года назад
Много нового узнал, спасибо большое, на драгстере прям похожие симптомы, может теперь смогу победить проблему).
-
Page 1
FD110… -
Page 2
FOREWORD GROUP INDEX This manual contains an introductory description On SUZUKI FD 110 and procedures for Its inspec- GENERAL INFORMATION tion/service and overhaul of its main components. Other information considered as generally known is PERIODICAL MAINTENANCE not included. Read GENERAL INFORMATION sec-… -
Page 3
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL TO LOCATE WHAT YOU ARE LOOKING FOR : 1. The text of this manual is divided into sections. 2. As the title of these sections are listed on the previous page as GROUP INDEX, select the section where what you are looking for belong. -
Page 4
99000-32030 Specified torque. Apply oil, Use engine oil unless Apply THREAD LOCK “1342” otherwise specified. 99000-32050 Apply SUZUKI SUPER GREASE “A” Apply or use brake fluid. 99000-25010 Apply SUZUKI SILICONE GREASE. Measure in voltage range. 99000-25100 Apply SUZUKI MOLY PASTE. -
Page 6: Table Of Contents
GENERAL INFORMATION 1-1 GENERAL INFORMATION CONTENTS WARNING/CAUTION/NOTE…………….1-2 GENERAL PRECAUTIONS …………….1-2 SUZUKI FD 110 XC / XCS / XCD / XCSD…………1-4 SERIAL NUMBER LOCATION …………… 1-4 FUEL AND OIL RECOMMENDATIONS ……….1-4 FUEL ………………… 1-4 ENGINE OIL………………1-5 FRONT FORK OIL …………….
-
Page 7: Warning/Caution/Note
1-2 GENERAL INFORMATION WARNING/CAUTION/NOTE Please read this manual and follow its instructions carefully. To emphasize special information, the symbol and the words WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE have special meanings. Pay special attention to the mes- sages highlighted by these signal words. Indicates a potential hazard that could result in death or injury.
-
Page 8
GENERAL INFORMATION 1-3 * If parts replacement is necessary, replace the parts with Suzuki Genuine Parts or their equivalent. * When removing arts that are to be reused, keep them arranged in an orderly manner so that they may be reinstalled in the proper order and orientation. -
Page 9: Serial Number Location
1-4 GENERAL INFORMATION SUZUKI FD 110 XB517QD/XB517QSC • Difference between illustrations and actual motorcycles depends on the markets. SERIAL NUMBER LOCATION The frame serial number or V.I.N. (Vehicle Identification Number) is stamped on the left side of the steering head tube. The engine serial number is located on the upper right side of the crankcase. These numbers are required especially for registering the machine and ordering spare parts.
-
Page 10: Engine Oil
GENERAL INFORMATION 1-5 ENGINE OIL Be sure the engine oil you use comes under API classification of SF or SG and that its viscosity rating is SAE 40. If an SAE 40 motor oil is not available, select an alternate according to the right chart BRAKE FLUID Specification and classification: DOT 4…
-
Page 11: Specifications
1-6 GENERAL INFORMATION SPECIFICATIONS DIMENSIONS AND DRY MASS Overall length………….. 1,932 mm Overall width ………….. 650 mm Overall height …………. 1,062 mm Seat height …………..755 mm Wheel base …………..1,230 mm Ground clearance …………153 mm Dry mass …………..96 kg ENGINE Type …………….
-
Page 12
GENERAL INFORMATION 1-7 CHASSIS Frame …………….. SSRF (SUZUKI SINGLE RECTANGULAR FRAME) Front suspension …………Telescopic, coil spring, oil damped Rear suspension …………Swing arm type, coil spring Steering angle …………45° (right & left) Caster …………….. 27° Trail …………….65 mm Front brake ………….. -
Page 13
1-8 GENERAL INFORMATION… -
Page 14: Periodical Maintenance
PERIODICAL MAINTENANCE PERIODICAL MAINTENANCE CONTENTS PERIODICAL MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE ……….2-2 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE CHART…………2-2 LUBRICATION POINTS …………….2-3 MAINTENANCE AND TUNE-UP PROCEDURES ……… 2-4 BATTERY ………………..2-4 EXHAUST PIPE BOLTS…………….2-5 AIR CLEANER ………………2-5 VALVE CLEARANCE…………….2-6 SPARK PLUG………………2-8 ENGINE OIL ………………..
-
Page 15: Periodical Maintenance Schedule
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE PERIODICAL MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE The chart below lists the recommended intervals for all the required periodic service work necessary t keep the motorcycle operating at peak performance and economy. Mileages are expressed in terms of kilometers and time for your convenience. NOTE: More frequent servicing may be performed on motorcycles that are used under severe conditions.
-
Page 16: Lubrication Points
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE LUBRICATION POINTS Proper lubrication is important for smooth operation and long life of each working part of the motorcycle. Major lubrication points are indicated below. DRIVE CHAIN SPEEDOMETER GEARBOX SPEEDOMETER CENTER STAND PIVOT FRONT WHEEL CABLE AND SPRING HOOK BEARING SIDE STAND PIVOT AXLE SHAFT…
-
Page 17: Maintenance And Tune-Up Procedures
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE MAINTENANCE AND TUNE-UP PROCEDURES This section describes the servicing procedures for each item of the Periodic Maintenance requirements. BATTERY Inspect initially at 1,000 km (1 month) and Every 4,000 km (4 months) thereafter. • The battery must be removed to check the electrolyte level and specific gravity.
-
Page 18: Exhaust Pipe Bolts
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE When installing the battery lead wires fix the + Led first and — lead last. BATTERY • Make sure that the breather pipe is tightly secured and undamaged, and is routed as shown in the photograph. BATTERY BREATHER HOSE EXHAUST PIPE BOLTS Tighten Initially at 1,000 km (1 month) and Inspect Every 4,000 km (6 months) thereafter.
-
Page 19: Valve Clearance
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE • Loosen the four screw and remove the air cleaner cover. • Remove the air cleaner element. • Carefully use an air hose to blow the dust form the cleaner element inside. • Reinstall the cleaned or new cleaner element in the reverse order of removal.
-
Page 20
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE • Remove spark plug, valve inspection caps 1 and valve timing inspection plug 2. • Remove the magneto cover cap and rotate the magneto rotor with box wrench to set the piston at (TDC) of the compression stroke. (Rotate the rotor until the “T” line on the rotor is aligned with the center of hole on the magneto cover. -
Page 21: Spark Plug
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE SPARK PLUG Inspect at 4,000 km (6 month) Replace Every 8,000 km (12 months). • Carbon deposits on the spark plug will prevent good sparking and cause misfiring. Clean the deposits off periodically • If the center electrode is fairly worn down, the plug should be replaced and the plug gap set to the specified gap using a thickness gauge.
-
Page 22: Engine Oil
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE ENGINE OIL Replace Initially at 1,000 km (1 month) and Every 4,000 km thereafter. After a long period of use, the engine oil will deteriorate and quicken the wear of sliding and interlocking surfaces. Replace the transmission oil periodically following the procedure below. •…
-
Page 23: Fuel Hose
2-10 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE NECESSARY AMOUNT OF ENGINE OIL OIL CHANGE: 800 ml OIL FILTER CHANGE: 900 ml OVER HAUL: 1,000 ml FUEL HOSE Inspect at 4,000 km (6 month) Replace Every 4 years FUEL FILTER Clean Every 8,000 km (12 months). CARBURETOR Inspect Initially at 1,000 km (1 month) and Every 4,000 km (6 months) thereafter.
-
Page 24: Drive Chain
2. 19 20 21 1 2 3 The standard drive chain is DAIDO DID 428. SUZUKI recommends that this standard drive chain should be used for the replacement. • Count out 21 pins (20-pitch) on the chain measure the distance between the two.
-
Page 25
2-12 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE NOTE: When replacing the drive chain, replace the drive chain and sprockets as a set. CLEANING AND LUBRICATING Wash the drive chain in cleaning solvent and lubricate it with chain lube or motor oil. If the motorcycle operates under dusty conditions, frequent rapid acceleration or at sustained high speeds, the drive chain should be cleaned and lubricated more often. -
Page 26: Brake
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-13 BRAKE (BRAKE) Inspect Initially at 1,000 km (1 month) and Every 4,000 km (6 months) thereafter. (BRAKE HOSE AND BRAKE FLUID) Inspect Every 4,000 km (6 month) Replace houses Every 4 years. Replace Fluid Every 2 years. FRONT BRAKE (DISC TYPE) •…
-
Page 27: Disc Brake
2-14 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE AIR BLEEDING THE BRAKE FLUID CIRCUIT (DISC BRAKE) Air trapped in the fluid circuit acts like a cushion to absorb a large proportion of the pressure developed by the master cylin- der and thus interferes with the full braking performance of the brake caliper.
-
Page 28
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-15 REAR BRAKE ADJUSTING Adjust the free travel 1 to 15-25 mm. by turning the adjusting nut 2. REAR BRAKE SHOE WEAR This motorcycle is equipped with brake lining wear limit indica- tor. As shown in Fig., at the condition of normal lining wear, the extension line of the index mark on the brake camshaft should be within the range embossed on the brake panel with brake on. -
Page 29: Tire
The standard tire fitted on this motorcycle is 2.50-17 for front and 2.75-17 for rear. The use of tires other than those specified may cause instability. It is highly recommended to use a SUZUKI Genuine Tire. STEERING Inspect Initially at 1,000 km (1 month) and Every 8,000 km (12 months) thereafter.
-
Page 30: Front Fork
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-17 FRONT FORK Inspect Every 8,000 km (12 months). Inspect the front forks oil leakage, scoring or scratches on the outer surface of the inner tubes. Replace any defective parts, if necessary. (Refer to page 5-19) REAR SUSPENSION Inspect Every 8,000 km (12 months).
-
Page 31: Chassis Bolts And Nuts
2-18 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE CHASSIS BOLTS AND NUTS Tighten Initially at 1,000 km (1 month) and Every 4,000 km (6 months) thereafter. The nuts and bolts listed below are important safety related parts. They must be retightened when neces- sary to the specified torque with a torque wrench. (Refer to page 2-18 for the locations of the following nuts and bolts on the motorcycle.) ITEM kg/cm…
-
Page 32
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-19… -
Page 33: Compression Pressure Check
2-20 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE COMPRESSION PRESSURE CHECK (FD110XC / XCS / XCD / XCSD) The compression of a cylinder is a good indicator of its internal condition. The decision to overhaul the cylinder is often based on the results of a compression test. Periodic maintenance records kept at your dealership should include compression readings for each maintenance service.
-
Page 34: Oil Pressure Check
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE 2-21 OIL PRESSURE CHECK Check periodically the oil pressure in the engine to judge roughly the condition of the moving parts. OIL PRESSURE SPECIFICATION Above 0.1 kg/cm. at 3,000 r/min., Oil temp. at 60°C Below 0.3 kg/cm. If the oil pressure is lower or higher than the specification, the following causes may be considered. LOW OIL PRESSURE •…
-
Page 35: Automatic Clutch Inspection
2-22 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE AUTOMATIC CLUTCH INSPECTION This motorcycle is equipped with an automatic clutch. The engagement of the clutch is Gove med by engine RPM and centrifugal mechanism located in the clutch. To insure proper performance and longer lifetime of the clutch assembly it is essential that the clutch engages smoothly and gradually.
-
Page 36
ENGINE ENGINE CONTENTS ENGINE COMPONENTS REMOVABLE WITH THE ENGINE IN PLACE ………………….. 3-2 ENGINE REMOVAL AND REINSTALLATION……….3-3 ENGINE REMOVAL …………….3-3 ENGINE REINSTALLATION …………..3-5 ENGINE DISASSEMBLY …………….3-6 CYLINDER HEAD……………… 3-12 GEAR SHIFTING CLUTCH …………..3-14 CLUTCH COVER AND CLUTCH ADJUSTMENTS ……3-15 ENGINE COMPONENTS INSPECTION AND SERVICE…… -
Page 37: Engine Components Removable With The Engine In Place
ENGINE ENGINE COMPONENTS REMOVABLE WITH THE ENGINE IN PLACE The part listed below can be removed and reinstalled without removing the engine from the frame. Refer to the page listed in each section for removal and reinstallation instructions. ENGINE CENTER Exhaust pipe Carburetor Cam chain tensioned adjuster…
-
Page 38: Engine Removal And Reinstallation
ENGINE ENGINE REMOVAL AND REINSTALLATION ENGINE REMOVAL Before taking the engine out of the frame, wash the engine with a steam cleaner. The procedure of engine removal is sequen- tially explained in the following steps. • Support the motorcycle with the center stand. •…
-
Page 39
ENGINE • Remove the engine sprocket by loosen the bolt 1 and sprocket lock plate 2. • Remove the sprocket. • Disconnect the several lead wires. • Magneto lead wire coupler 3. • Gearshift indicator lead wire coupler 4. • Engine ground coupler •… -
Page 40: Engine Reinstallation
ENGINE ENGINE REINSTALLATION Reinstall the engine in the reverse of engine removal. • Install the engine mounting bolts and tighten the nuts to the specification. Engine mounting nut: 55 N-m (5.5 kg-m) • Install the drive chain. The drive chain joint clip should be attached in the way that the slit end will face opposite to the direction of rotation.
-
Page 41: Engine Disassembly
ENGINE ENGINE DISASSEMBLY The procedure for engine disassembly is sequentially explained in the following steps. • Remove the gearshift lever and kick starter lever. • Remove the cam pocket cover. • Remove the cap and insert the screwdriver into the slotted end of the cam chain tension adjuster and turn it clockwise to lock the spring tension.
-
Page 42
ENGINE • Remove the chain guide and gasket. • Loosen the cylinder nut and remove the cylinder. • Place a clean rag over the cylinder base to prevent piston pin circlip from dropping into the crankcase and then, remove the piston pin circlip with a long-nose pliers. -
Page 43
ENGINE • Loosen the nut by using the special tool. 09910-20115: Con-rod stopper • Remove the first clutch assembly, circlip and primary drive gear. • Remove the clutch bearing. • Loosen the nut by using the special tool. 09930-40113: Rotor holder •… -
Page 44
ENGINE • Remove the oil washer and oil pump drive gear. • Remove the shift cam stopper bolt 1. • Remove the shift cam pin bolt 2. • Remove the shift cam stopper plate, shift cam pin guide and pins. •… -
Page 45
3-10 ENGINE • Loosen the rotor nut by using the special tool. 09930-44550: Rotor holder • Loosen the rotor by using the special tool. 09930-34951: Rotor remover • Loosen the screw and remove the starter clutch plate • Remove the starter driven gear. •… -
Page 46
ENGINE 3-11 • Remove the crankcase screws. • Separate the right and left crankcase by using the special tool. 09920-13120: Crankcase/crank shaft separator • Remove the kick starter shaft by turning it. • Remove the gearshift fork shaft, gearshift fork and gearshift cam. -
Page 47: Cylinder Head
3-12 ENGINE • Remove the crankshaft by using a plastic mallet. • Remove the oil seals and bearings by using the special tools. 09914-79610: Bearing installer 09921-20210: Bearing puller 09930-30102: Sliding shaft 09913-76010: Bearing installer 09925-98221: Bearing installer 09913-75520: Bearing installer 09913-75821: Bearing installer CYLINDER HEAD •…
-
Page 48
ENGINE 3-13 • Remove the rocker arm shafts by using an 8 mm thread bolt. NOTE: Intake and exhaust rocker arm shafts differ in the length. • Remove the rocker arms • Remove the wave washer • Remove the spring valve by compress the valve springs with the special tools. -
Page 49: Gear Shifting Clutch
3-14 ENGINE • Remove the stem seal 1 with a long nose pliers. • Take out the spring seat 2. For installing the valve spring seat and valve stem seal, refer to pages 3-21 and 22. • Remove the valve guide by using the special tool. 09916-44310: Valve guide remover For servicing the valve guide, refer to page 3-21.
-
Page 50: Clutch Cover And Clutch Adjustments
ENGINE 3-15 CLUTCH COVER AND CLUTCH ADJUSTMENTS • Loosen the lock nut and remove clutch release arm. CLUTCH ADJUSTMENT • Loosen the lock nut 1. • First, turn the adjusting bolt clockwise by a one turn and turn it counterclockwise until resistance is felt, then turn it clockwise by a 1/8 turn.
-
Page 51: Gear Shifting Clutch
3-16 ENGINE • Clutch wheel-inspect visually the condition of the inner clutch wheel surface for scoring, cracks, or uneven wear. CLUTCH HOUSING INSPECTION Inspect the inner surface of clutch housing for deep scratches or discoloration caused by burning. If any defects are found, replace the clutch housing with a new one.
-
Page 52: Gear Shift Fork
ENGINE 3-17 Drive plate distortion Item Service Limit No. 1, 2 0.1 mm GEAR SHIFT FORK Using a thickness gauge, check the shifting fork clearance in the groove of its gear. this clearance for each of the two shifting forks plays an important role in the smoothness and positive ness of shifting action.
-
Page 53: Crankcase Bearing And Oil Seal
LEFT CRANKCASE BEARING REASSEMBLY • Install the oil seal into the crankcase using the special tool. 09913-75821: Bearing installer • Apply a small quantity of SUZUKI SUPER GREASE “A” TO THE LIP OF OIL SEAL. 99000-25010: SUZUKI SUPER GREASE “A”…
-
Page 54: Cylinder Head Related Parts
ENGINE 3-19 RIGHT CRANKCASE BEARING DISASSEMBLY • Remove the right crankcase bearing by using the special tool. 09913-75821: Bearing installer 09921-20210: Bearing puller 09930-30102: Sliding shaft RIGHT CRANKCASE BEARING REASSEMBLY • Install the right crankcase bearing into the crankcase by using the special tool.
-
Page 55: Valve And Valve Spring Disassembly
3-20 ENGINE Measure the diameter of rocker arm shaft with a micrometer Standard: 9.981 — 9.990 mm 09900-20205: Micrometer (0-25 mm) When checking the valve rocker arm, the inside diameter of the valve rocker arm and wear of the camshaft contacting surface should be checked.
-
Page 56: Valve
ENGINE 3-21 VALVE VALVE FACE WEAR Measure the thickness “T” and, if the thickness is found to have been reduced to the limit, replace the valve. NOTE: Visually in sport each valve for wear of its seating face, Replace any valve with an abnormally worm face. Service Limit : 0.05 mm VALVE STEM RUNOUT Support the valve with “V”…
-
Page 57
3-22 ENGINE VALVE GUIDE SERVICE • Remove the valve guide with the valve guide remover. 09916-44310: Valve guide remover • Re-finish the valve guide holes in cylinder head with a reamer 1 and handle 2. 09916-34580: Valve guide remover (10.8 mm) 09916-34542: Handle •… -
Page 58
ENGINE 3-23 • Lubricate valve stem seal with oil, and press-fit the seal into position with a finger tip. Do not reuse the stem seals. VALVE SEAT WIDTH • Coat the valve seat uniformly with Prussian blue. Fit the valve and tap the coated seat with the valve face in a rotating man- ner, in order to obtain a clear impression of the seating con- tact. -
Page 59
3-24 ENGINE • Insert the solid pilot with a slight rotation. Seat the pilot SOLID PILOT snugly. Install the 45° cutter, attachment and T-handle. • Using the 45° cutter, rescale and clean up the seat with one or row turns. •… -
Page 60
Valve spring tension Standard: 147 nm. HEIGHT 25.80 mm. VALVE AND VALVE SPRING REASSEMBLY • Insert the valves, with their stems coated with (SUZUKI MOLY PASTE) all around and along the full stem length with- out any break. Similarly oil the lip of the stem seal. -
Page 61: Camshaft
3-26 ENGINE • Fit a valve spring retainer, compress the springs with a valve spring compressor and fit the cotter halves to the stem end. 09916-14510: valve spring compressor 09916-14521: Attachment 09916-84511: Tweezers CAMSHAFT CAM WEAR Worn-down cams are often the cause of mistimed valve opera- tion resulting in reduced output power.
-
Page 62: Cylinder Distortion
ENGINE 3-27 NOTE: * Before reassembling the cam sprocket flange onto the camshaft, apply the internal face of the cam sprocket flange with THREAD LOCK SUPER “1303”. * This procedure may be performed only once before camshaft replacement is required. * Installation of the cam sprocket flange requires exact alignment to severe correction of the valve timing.
-
Page 63
3-28 ENGINE PISTON CYLINDER CLEARANCE As a result of the above measurement, if the piston to cylinder clearance exceeds the following Limit, overhaul the cylinder and use an oversize piston, or replace both cylinder and piston. Service Limit: 0.120 mm PISTON RING-GROOVE CLEARANCE Using a thickness gauge, measure the side clearance of the 1st and 2nd rings. -
Page 64: Piston Pin
ENGINE 3-29 OVERSIZE RINGS • Oversize piston ring The following two types of oversize pis- ton ring are used. They bear the following identification num- bers. Piston ring 1 st. and 2nd 0.5 mm: 50 1.0 mm: 100 • Oversize oil ring The following two types of oversize oil ring are used.
-
Page 65: Starter Clutch And Starter Driven Gear Bearing
3-30 ENGINE CONROD DEFLECTION AND CONROD BIG END SIDE CLEARANCE Wear on the big end of the con rod can be estimated by check- ing the movement of the small end of the rod. This method can also check the extent of wear on the parts of the con rod’s big end.
-
Page 66: Engine Reassembly
ENGINE 3-31 ENGINE REASSEMBLY The engine is reassembled by carrying out the steps of disassembly in the reversed order, but there are a number of steps which demand special description or precautionary measures. NOTE: Apply engine oil to each running and sliding part before reassembling. CRANKSHAFT •…
-
Page 67
3-32 ENGINE CRANKSHAFT SHIM SELECTION • Degrease the right crankshaft web, shim and inner race of the right crankshaft bearing. • Place the removed shim 1 on the right crankshaft. • Put the plastic-gauges (special tool) cut out about 10 mm. on the shim, as shown in the photograph at right. -
Page 68: Kick Starter
ENGINE 3-33 KICK STARTER *(A) : THREAD LOCK SUPER “1322” • Align the punch mark 1 of kick starter shaft with punch mark 2 of kick starter • Turn the kick starter shaft counter-clockwise and then lock the kick starter with kick starter guide.
-
Page 69
3-34 ENGINE TRANSMISSION • Seat the circlip in the groove and its ends A should be located as shown in the photo. • When mounting circlip, pay attention to the direc- tion of the circlip. Fit it to the rounded side against the gear surface GEAR CIRCILP… -
Page 70
• Apply engine oil to con rod big end and T/M. gears. • Apply BOND NO. 1215 to the mating surface of the left crankcase. 99000-31110: SUZUKI BOND NO.1215 • Assemble the crankcases within few minutes. NOTE: • After crankcase crews have been tightened, check if crank- shaft rotate smoothly. -
Page 71
3-36 ENGINE SHIFT CAM RETAINER • install the shift cam retainer after applying THREAD LOCK SUPER “1322” to the screws. 99000-32110: THREAD LOCK SUPER “1322” ROTOR AND STATOR • Install the stator magneto cover. STARTER CLUTCH • Apply a small quantity of THREAD LOCK SUPER “1303” to the starter clutch bolts and tighten them to the specified toque by holding the crankshaft. -
Page 72
ENGINE 3-37 • Wipe the tapered portion of the crankshaft and also the generator rotor with a cleaning solvent. • Install the key to the crankshaft. • Install the rotor assembly after resembling the rotor and starter gear. • Apply THREAD LOCK SUPER “1303” to the thread and tighten the nut by using the special tool. -
Page 73
3-38 ENGINE • When installing the gearshift lever, align the stopper bolt with gearshift lever relating part. NOTE: Install the bearing as shown in the photograph. • When install the shift cam pin bolt, apply THREAD LOCK SUPER “1322” to thread. 99000-32110: THREAD LOCK SUPER “1322”… -
Page 74
ENGINE 3-39 OIL PUMP • When Installing the oil pump, use dowel pin and new O-rings. • Apply THREAD LOCK “1342” to the oil pump securing screws. 99000-32050: THREAD LOCK SUPER “1342” GEAR SHIFTING CLUTCH • Install the gear shifting clutch by using the circlip. •… -
Page 75
3-40 ENGINE FIRST CLUTCH • When installing the clutch shoe in the clutch housing align the boss 1 of one way clutch inner with slit 2 of clutch shoes. • Fix the primary drive gear to clutch housing, circlip by using a special tool. -
Page 76
ENGINE 3-41 • Installing the first clutch to the crankshaft. • Tighten the first clutch shoe nut to specified torque by using the special tool. First clutch shoe nut: 5 N-m (5.0 kg-m) 9915-20115: Conrod holder NOTE: Clean the oil filter when reassembling it. CLUTCH ADJUSTMENT Refer to page 3-14. -
Page 77
The following are reminders for piston installation: • Rub a small quantity of SUZUKI MOLY PASTE on to the pis- ton pin. • Place a clean rag over the cylinder base to prevent piston pin circlip from dropping into crankcase, and then fit the piston pin circlip with long nose pliers. -
Page 78
ENGINE 3-43 CYLINDER Before mounting the cylinder block, oil the big end and small end of the conrod and the sliding surface of the piston. • Inspect the oil orifice for cragged. • Fit dowel pins to crankcase and then fit gasket. To prevent oil leakage. -
Page 79
3-44 ENGINE • Tighten the cylinder head nut to the specified torque. Cylinder head nut: 20 N.m (2.0 kg-m) Cylinder head nut: 10 N.m (1.0 kg-m) Cylinder base nut: 10 N.m (1.0 kg-m) IGNITION TIMING • Position “T” mark 1 on the magneto rotor with the center of magneto cover hole 2 keeping the camshaft drive chain pulled up ward. -
Page 80
ENGINE 3-45 CAM CHAIN TENSION ADJUSTER • Install a new gasket and the cam chain tension adjuster to the cylinder with the two bolts and tighten them to the specified torque. chain tension adjuster bolt : 1.2 kg-m NOTE: * Before installing the cam chain tension adjuster, lock the tension spring with a screwdriver. -
Page 81
3-46 ENGINE… -
Page 82
SHAFT DRIVE FUEL AND LUBRICATION SYSTEM CONTENTS FUEL SYSTEM ………………..4-2 FUEL TANK, FUEL VALVE, FUEL FILTER AND FUEL LEVEL GAUGE ..4-3 FUEL TANK AND FUEL VALVE REMOVAL ……… 4-3 FUEL FILTER REMOVAL …………… 4-3 INSPECTION AND CLEANING ………….. 4-4 CARBURETOR ……………….. -
Page 83: Fuel System
FUEL AND LUBRICATION SYSTEM FUEL SYSTEM When tuning the starter motor, a negative pressure is generated in the combustion chamber. This negative pressure draws on the fuel tap diaphragm, (through a passage way in the carburetor intake pipe) and vac- uum hose.
-
Page 84: Fuel Tank, Fuel Valve, Fuel Filter And Fuel Level Gauge
FUEL AND LUBRICATION SYSTEM FUEL TANK, FUEL VALVE, FUEL FILTER AND FUEL LEVEL GAUGE FUEL TANK AND FUEL VALVE REMOVAL • Remove the leg side shields/frame covers, left and right. (See page 5-1.) • Remove the seat by removing its mounting nuts 1. •…
-
Page 85: Inspection And Cleaning
FUEL AND LUBRICATION SYSTEM FUEL LEVEL GAUGE REMOVAL • Remove the right leg side shield/right frame cover. (See page 5-1.) • Disconnect the fuel level gauge lead wire coupler 1. • Remove the fuel level gauge 2 by removing the mounting screws.
-
Page 86: Carburetor
FUEL AND LUBRICATION SYSTEM CARBURETOR SPECIFICATIONS ITEM SERVICE LIMIT Carburetor type MIKUNI VM 17 Bore size 17 mm I.D. No. 09GF Idle r/min 1,500 100 r/min Float height 1.0 mm Main jet (M.J.) #92.5 Main air jet (M.A.J.) 1.65 mm. Jet needle (J.N.) 4 PA11-2 Needle jet (N.J.)
-
Page 87: Carburetor
FUEL AND LUBRICATION SYSTEM CARBURETOR JET NEEDLE THROTTLE VALVE NEEDLE JET MAIN JET PILOT JET FLOAT NEEDLE VALVE FLOAT PIN THROTTLE VALVE ADJUSTER SCREW 10) PLUNGER 11) OVERFLOW PIPE 12) PILOT AIR SCREW 13) JET NEEDLE LOCKER…
-
Page 88: Slow System
FUEL AND LUBRICATION SYSTEM SLOW SYSTEM This system supplies fuel to the engine operation with the piston valve 5 close or slightly opened. The fuel from the float chamber 6 is metered by the pilot jet 8. Where it mixes with air coming in the pilot air jet #1 and pilot air passage 9.
-
Page 89: Starter System
FUEL AND LUBRICATION SYSTEM STARTER SYSTEM When the starter plunger 1 is lifted, the fuel metered by the starter jet 2 is mixed with the air coming from the float chamber 3. The mixture, rich in fuel content, reaches plunger area and mixes again with air com- ing from the starter air passage 4.
-
Page 90: Transient Enrichment System
FUEL AND LUBRICATION SYSTEM TRANSIENT ENRICHMENT SYSTEM The transient enrichment system is a device which keeps fuel/air mixture ratio constant in order not to gen- erate unstable combustion when the throttle grip is returned suddenly during high speed driving. When the throttle valve is closed suddenly, large negative pressure generated on cylinder side works on to a dia- phragm 2.
-
Page 91: Carburetor Removal
4-10 FUEL AND LUBRICATION SYSTEM CARBURETOR REMOVAL • Remove the center leg shield. (See page 5-1.) • Remove the leg shields, left and right. (See page 5-1.) • Remove the carburetor intake pipe 1. • Disconnect the fuel hose 2 and 3 vacuum hose. •…
-
Page 92: Carburetor Jet Inspection
FUEL AND LUBRICATION SYSTEM 4-11 • Remove the float assembly 1 by removing the pin 2. Do not use a wire for cleaning of passage and jets. • Remove the main jet 3. • Remove the pilot jet 4. Do not use a wire for cleaning of passage and jets. •…
-
Page 93: Float Height Adjustment
4-12 FUEL AND LUBRICATION SYSTEM FLOAT HEIGHT ADJUSTMENT To check the float height, invert the carburetor body, with the float arm kept free, measure the height A while float arm is just in contact with needle valve by using calipers. Bend the tongue 1 as necessary to bring the height A to this value.
-
Page 94: Lubrication System
FUEL AND LUBRICATION SYSTEM 4-13 LUBRICATION SYSTEM OIL PRESSURE Refer to page 2-18 OIL FILTER Refer to page 2-8. OIL SUMP FILTER When you replace the engine oil, check to be sure that the oil sump filter is free from any sign of rupture, also wash the oil sump filter clean periodically.
-
Page 95: Engine Lubrication System Chart
4-14 FUEL AND LUBRICATION SYSTEM ENGINE LUBRICATION SYSTEM CHART…
-
Page 96: Lubrication System
FUEL AND LUBRICATION SYSTEM 4-15 LUBRICATION SYSTEM…
-
Page 97
CHASSIS CHASSIS CONTENTS EXTERIOR PARTS ………………5-3 REMOVAL ………………..5-5 REINSTALLATION……………… 5-6 REMOVAL AND DISASSEMBLY …………5-7 INSPECTION AND DISASSEMBLY …………5-8 REASSEMBLY AND REMOUNTING………… 5-10 FRONT WHEEL AND FRONT BRAKE (DISC BRAKE)……5-12 REMOVAL AND DISASSEMBLY …………5-12 INSPECTION AND DISASSEMNBLY……….. 5-12 REASSEMBLY AND REMOUNTING………… -
Page 98
FI SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS 5-2… -
Page 99: Exterior Parts
CHASSIS EXTERIOR PARTS…
-
Page 100
CHASSIS REAR HANDLEBAR’S COVER FRONT HANDLEBAR’S COVER… -
Page 101: Removal
CHASSIS REMOVAL COVER, FRAME HEAD • Remove the PLATE, FRONT LICENSE by removing the bolts 1 and 2. • Remove the frame head cover. REAR — VIEW MIRROR • Remove the rear-view mirrors, left and right, by loosening the lock nuts. HANDLEBAR’S COVER •…
-
Page 102: Reinstallation
CHASSIS • Remove the handlebar’s cover screws. • Remove the rear-side of the handlebar’s cover along with the speedometer by disconnecting the speedometer cable and speedometer lead wire couplers. REINSTALLATION • Reinstall the removed parts in the reverse order of removal. FRONT WHEEL AND FRONT BRAKE (DRUM BRAKE)
-
Page 103: Removal And Disassembly
CHASSIS REMOVAL AND DISASSEMBLY FRONT WHEEL Raise the front wheel of the ground with a jack or wooden block. • Remove the axle nut 1. • Disconnect the speedometer cable 2. • Disconnect the front brake cable 3. • Remove the axle and front wheel. FRONT BRAKE •…
-
Page 104: Inspection And Disassembly
CHASSIS • Remove the brake cam lever bolt/nut 1. • Remove the brake cam lever, brake lining wear indicator, washer, spring, O-ring and brake cam. (See page 5-4) INSPECTION AND DISASSEMBLY SPEEDOMETER GEARBOX Turn the speedometer gear 3 and check to see that gear turns smoothly together with the speedometer pinion 4.
-
Page 105
CHASSIS AXLE: SHAFT Using a dial gauge, check the axle shaft for run out and replace it if run out exceeds the limit. 09900-20606: Dial gauge (1/100 mm) 09900-20701: Magnetic stand 09900-21304: V-block set (100 mm) Service Limit: 0.25 mm WHEEL Inspect the wheel run out. -
Page 106: Reassembly And Remounting
Pay attention to the following points: WHEEL BEARING • Apply SUZUKI SUPER GREASE «A» to the bearings before installing. 99000-25010: SUZUKI SUPER GREASE «A” • Using the bearing installer set 1, press fit the bearing to the wheel.
-
Page 107
5-11 CHASSIS BRAKE CAM/SHAFT • Apply SUZUKI SUPER GREASE «A» to the brake cam/shaft and pin before installing the brake shoes. 99000-25010 SUZUKI SUPER GREASE «A» Be careful not to apply too much grease to the cam/shaft and pin. If grease gets on the lining, brake effectiveness will be lost. -
Page 108: Front Wheel And Front Brake (Disc Brake)
CHASSIS 5-12 FRONT WHEEL AND FRONT BRAKE (DISC BRAKE) REMOVAL AND DISASSEMBLY FRONT WHEEL Remove the front wheel in the same manner of the drum brake type. (See page 5-5.) FRONT BRAKE • Flatten the lock portions of the lock washers. •…
-
Page 109: Reassembly And Remounting
5-13 CHASSIS Measure the run out with a dial gauge. Replace the disc if the run out exceeds the service limit. Service Limit Brake disc run out: 0.3 mm 09900-20606: Dial gauge (1/100 mm) 09900-20701: Magnetic stand REASSEMBLY AND REMOUNTING WHEEL BEARING ……………………..
-
Page 110: Brake Pad Replacement
CHASSIS 5-14 SPEEDOMETER GEARBOX AND FRONT WHEEL Refer to page 5-9. BRAKE PAD REPLACEMENT • Loosen the brake pad pins 1. Remove the brake caliper by removing the caliper mounting bolts 2. Hang the brake caliper on the frame with a string etc., taking care not to bend the brake hose.
-
Page 111: Caliper Inspection
5-15 CHASSIS • Remove the caliper bracket 6. • Place a rag over the piston to prevent its popping out and push out the piston with an air gun. Do not use high pressure air to prevent piston damage. • Remove the dust seal 7 and piston seal 8. Do not reuse the piston seal and dust seal to prevent fluid leakage..
-
Page 112
• Install the pistons seal 2 and dust seals 1. • Install the pistons 3. • Apply SUZUKI SILICONE GREASE to the caliper axles. 99000:25100: SUZUKI SILICONE GREASE • Install the break pads. • Tighten the caliper mounting bolts 4 to the specified torque. -
Page 113: Master Cylinder Inspection
5-17 CHASSIS • Break lever 4. • Break light switch 5. • Remove the reservoir cap 6 and diaphragm 7. • Drain break fluid. • Remove the dust seal 8. • Remove the circlip 9 by using the special too. 09900-06108: Snap ring pliers •…
-
Page 114
CHASSIS 5-18 NOTE: When fitting the circlip, make sure that the sharp edge of the circlip faces outside. • When remounting the master cylinder on the handlebar, align the master cylinder holder’s mating surface “A” with punched mark “B” on the handlebar and tighten the upper clamp bolt first as shown. -
Page 115: Handlebar
5-19 CHASSIS HANDLEBAR REMOVAL 1) handle bar 3) bolt 4) nut • Remove the rear-view mirrors. (See page 5-3.) • Remove the front and rear handlebar’s covers. (See pages 5-3 and 5-4.) • Disconnect the speedometer cable and speedometer lead wire couplers.
-
Page 116: Reassembly
SUZUKI SUPER GREASE «A» to the front brake lever pivot. • Install the front brake cable. (For drum brake) NOTE: Apply a small quantity of SUZUKI SUPER GREASE “A” o the front brake cable end. (For drum brake) 99000-25010: SUZUKI SUPER GREASE “A”…
-
Page 117: Front Fork And Steering
5-21 CHASSIS • Connect each lead wire. • Connect the speedometer cable. • Install the front and rear handlebar’s covers. FRONT FORK AND STEERING…
-
Page 118: Removal And Disassembly
CHASSIS 5-22 REMOVAL AND DISASSEMBLY • Remove the rear-view mirror. (See page 5-3.) • Remove the left and right leg shields. (See page 5-1.) • Remove the handle bar • Remove the front fender 1. • Remove the front fender by remove the screw 2. •…
-
Page 119
5-23 CHASSIS • Loosen the speedometer cable/front brake cable 1 (For drum brake clamp bolt.) • Remove the steering stem lock nut 2 by using universal clamp wrench. 09910-60611: Universal clamp wrench • Remove the washer. • Remove the steering stem nut 3. 9910-60611: Universal clamp wrench •… -
Page 120
CHASSIS 5-24 • Remove the outer lower race with a thin chisel or screw driver. • The outer lower race is pressed to the steering stem. If the lower race is removed, replace it with a new one. • It is not necessary to remove the outer lower race if corrosion, dents or damage on the race have not occurred. -
Page 121: Inspection
5-25 CHASSIS • Remove the damper rod 1 from the inner tube. • Remove the oil seal 2. INSPECTION STEERING RACE AND BALL • Inspect the upper race, lower race and balls for corrosion, dents or damage. If dents are noticed on the race, replace the balls and races as a set.
-
Page 122: Reassembly And Remounting
09940-34561: Attachment “D” • Install the oil seal with the special tool. NOTE: * Before installing the oil seal apply a small quantity of SUZUKI SUPER GREASE “A” to the lip of oil seal. 09900-25010: SUZUKI SUPER GREASE “A” 09940-52860: Front fork oil seal installer •…
-
Page 123
• Pour specified fork oil into the inner tube. Fork oil type : Fork oil # 10 9000-99044-10 G: SUZUKI FORK OIL # 10 Capacity (each leg): 70 ml • hold the front fork vertical and adjust the fork oil level with the special tool. -
Page 124
CHASSIS 5-28 • Apply SUZUKI SUPER GREASE “A” to the upper and lower races sufficiently and place the balls to the specified quantity. (Upper): 22 pcs Number of balls (Lower): 28 pcs 99000-25010: SUZUKI SUPER GREASE “A” • Install the steering stem bracket 2. -
Page 125: Rear Wheel And Rear Brake
5-29 CHASSIS REAR WHEEL AND REAR BRAKE REMOVAL AND DISASSEMBLY REAR WHEEL • Support the motorcycle with the center stand. • Remove the rear brake adjusting nut 1. • Remove the cotter pin and torque link nut 2. • Remove the chain case 1 by removing the bolts and screw.
-
Page 126
CHASSIS 5-30 • Remove the rear axle nut 1. • Loosen the drive chain adjusting nuts 2, left and right. • Draw out the axle shaft. • Disengage the drive chain from the rear sprocket. • Remove the rear wheel. REAR SPROCKET •… -
Page 127: Rear Brake
5-31 CHASSIS • Flatten the lock portions of the lock washers. • Remove the rear sprocket by removing the nuts. • Remove the spacer out of the sprocket 1 mounting drum. • Remove the oil seal with the special tool. 09913-50121: Oil seal remover The removed oil seal should be replaced with a new one.
-
Page 128: Inspection And Disassembly
CHASSIS 5-32 • Remove the brake cam lever bolt/nut 1. • Remove the brake cam lever, brake lining wear indicator, washer, O-ring and brake cam. (See page 5-27.) INSPECTION AND DISASSEMBLY. WHEEL BEARING ……… Refer to page 5-6. AXLE SHAFT ……… Refer to page 5-7. WHEEL ……….
-
Page 129: Reassembly And Remounting
Pay attention to the following points: WHEEL BEARING • Apply SUZUKI SUPER GREASE «A» to the bearings before installing. 99000-25010 : SUZUKI SUPER GREASE «A» • Using the bearing installer set, press fit the bearing to the wheel.
-
Page 130
NOTE: Face the stamped mark on the sprocket to outside. BRAKE CAM/SHAFT • Apply SUZUKI SUPER GREASE “A” to the brake cam/shaft and pin before installing the brake shoes. 99000-25010 : SUZUKI SUPER GREASE «A» Be careful not to apply too much grease to the cam/shaft and pin. -
Page 131: Rear Suspension
5-35 CHASSIS REAR SUSPENSION SWING ARM AND SHOCK ABSORBER REMOVAL • Remove the rear wheel.(see page 5-27) • Remove the shock absorber mounting lower bolts 1, left and right…
-
Page 132: Inspection And Disassembly
CHASSIS 5-36 • Remove the swing arm pivot nut 1. • Remove the swing arm by removing its pivot shaft. INSPECTION AND DISASSEMBLY SWINGARM BUSHING/SWINGARM Inspect the swing arm bushing for wear or damage. Inspect the swinger for distortion. If any defects are found, replace the swing arm bushings and swing arm with new ones.
-
Page 133: Reassembly And Remounting
5-37 CHASSIS • Remove the bushing from the swing arm by using a suitable hand-press. The removed bushing should be replaced with a new one. REASSEMBLY AND REMOUNTING Reassemble and remount the swing arm and shock absorber in the reverse order of removal and disassembly, and also carry out the following steps: SWINGARM BUSHING •…
-
Page 134
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM ELECTRICAL SYSTEM CONTENTS CAUTIONS IN SERVICING…………….6-2 LOCATION OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS ……….6-4 CHARGING AND LIGHTING SYSTEM …………6-5 DESCRIPTION………………6-5 TROUBLESHOOTING…………….6-6 STARTER SYSTEM ………………6-9 DESCRIPTION………………6-9 TROUBLESHOOTING…………….6-10 STARTER MOTOR REMOVAL AND DISASSEMBLE ……6-11 STARTER MOTOR INSPECTION………… -
Page 135: Fuse
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM CAUTIONS IN SERVICING CONNECTOR • When connecting a connector, be sure to push it in until a CLICK click is felt. • Inspect the connector for corrosion, contamination and break- age in its cover. COUPLER • With a lock type coupler, be sure to release the lock before CLICK disconnecting it and push it in fully till the lock works when connecting.
-
Page 136
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM CONNECTING BATTERY • When disconnecting terminals from the battery for disassembly or servicing, be sure to disconnect the negative — terminal first, • When connecting terminals to the battery, be sureto connect the positive + terminal first. • If the terminal is found corroded, remove the battery, pour warm water over it and clean with a wire brush. -
Page 137: Location Of Electrical Components
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM LOCATION OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS 1) Battery 7) Ignition coil 2) Fuse
Generator 3) Fuel level gauge 9) Starter motor 4) Turn signal relay 10) Horn 5) Regulator / rectifier 11) CDI unit 6) Starter relay…
-
Page 138: Turn Signal Light
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM CHARGING AND LIGHTING SYSTEM DESCRIPTION The circuit of the charging and lighting system is indicated in the figure, which is composed of an AC gener- ator, regulator / rectifier unit and battery. The AC current generated from AC generator is converted by rectifier and is turned into DC current, then it charges the battery.
-
Page 139: Troubleshooting
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM TROUBLESHOOTING • Remove accessories. Installed Battery runs down quickly. Check accessories which excessively • Short circuit of wire harness. leak waste electric power. • Loose or disconnected wires. • Faulty battery. Not installed Inspect battery leak current. • Faulty battery. Correct (Refer to page 6-6.) •…
-
Page 140
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM INSPECTION BATTERY LEAK CURRENT INSPECTION • Open the seat. • Turn the ignition switch to the OFF position. • Disconnect the battery — lead wire. Note that leakage is indicated if the needle swings even a little when the milliampare meter of the pocket tester is connected between a — terminal and lead wire of the battery as shown. -
Page 141
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM GENERATOR (CHARGING/LIGHTING) COIL INSPECTION • Remove the center leg shield, leg shields and leg side shields/frame covers. (See page 5-1) • Disconnect the generator lead wire coupler. Using the pocket tester, measure the resistance between the lead wires and ground. If the resistance checked is incorrect, replace the charg- ing/Lighting coil with a new one. -
Page 142: Starter System
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM REGULATOR/RECTIFIER INSPECTION • Remove the right leg side shield/right frame cover. (See page 5-1). • Disconnect the regulator/rectifier coupler. Using a pocket tester (x1 kΩ range), measure the resistance between the terminals in the following table. 09900-25002: Pocket tester Tester knob indication : x1 kΩ…
-
Page 143: Troubleshooting
6-10 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM TROUBLESHOOTING c t i t i s Starter motor will not . s i Check whether to run the starter Check Whether to hear the click motor when connect the starter noise from the starter relay when Clicks the starter button is pushed.
-
Page 144: Starter Motor Removal And Disassemble
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM 6-11 STARTER MOTOR REMOVAL AND DISASSEMBLE • Remove the center leg shield and leg shields. • Disconnect the starter motor lead wire and remove the starter motor by removing the mounting screws. (Refer to page 3-15) • Disassemble the starter motor as shown in the illustration. 1) BOLT (2PCS) 2) O-RING 3) STARTER MOTER CASE…
-
Page 145: Starter Motor Reassembly
Replace the O-rings with new ones to prevent oil leakage and moisture. • Apply SUZUKI SUPER GREASE A to the lip of the oil seal. 99000-25010: SUZUKI SUPER GREASE A • Apply a small quantity of MOLY PASTE to the armature shaft.
-
Page 146: Starter Relay Inspection
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM 6-13 • Apply a small quantity of THREAD LOCK SUPER “1322” to the starter motor housing screws. 9000-32110: THREAD LOCK SUPER “1322” STARTER RELAY INSPECTION • Remove the right leg side shield/right frame cover. (See page 5-1.) • Disconnect the lead wire coupler from the starter relay. •…
-
Page 147: Ignition System
6-14 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM IGNITION SYSTEM Ignition switch Fuse Ignition Transformer coil Magneto Switen Pick-up circuit coil Battery Spark plug CDI unit Ignition timing control circuit DESCRIPTION The FD110 XC / XCS / XCD / XCSD engine is equipped with a new type ignition system. This new system minimizes timing fluctuations.
-
Page 148: Troubleshooting
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM 6-15 TROUBLESHOOTING *Check : Ignition switch is ON Position. : Fuse is not blown before the diagnosis. No spark at plug Check the CDI unit coupler for poor • Poor contact of coupler Looseness contact. Correct Inspect the resistance of charging coil •…
-
Page 149: Inspection
6-16 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM INSPECTION IGNITION COIL PRIMARY PEAK VOLTAGE • Remove the spark plug cap. • Connect a new spark plug to the spark plug and ground it to the cylinder head. NOTE: Make sure that the spark plug cap and spark plug are connected properly.
-
Page 150
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM 6-17 IGNITION COIL RESISTANCE • Disconnect the ignition coil lead wires and spark plug cap. Measure the ignition coil resistance in both the primary and sec- Terminal ondary windings using the multi circuit tester. If the resistance in both the primary and secondary windings is close to the speci- fied values, the windings are in sound condition. -
Page 151
6-18 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM If the peak voltage measured on the CDI unit coupler is lower then the standard value, measure the peak voltage on the pickup coil coupler as follows. • Disconnect the pickup coil coupler • Connect the multi circuit tester (DM 200) with the peak volt adaptor as follows. -
Page 152
NOTE: As capacitor, thyristors, diodes, etc. are used inside this CDI unit, the resistance values will differ when an ohmmeter other than SUZUKI pocket tester is used. 09900-25002 : Pocket tester Tester knob indication: X1 kΩ range Unit: Approx. KΩ… -
Page 153
6-20 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM SPARK PLUG • Remove the spark plug. 09930-10121: Spark plug socket wrench set Carbon Deposit Check to see the carbon deposit on the plug. If the carbon is deposited, remove it with a spark plug cleaner machine or carefully using a tool with a pointed end. Spark Plug Gap Measure the plug gap with a thickness gauge if it is correct. -
Page 154: Fuel Meter
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM 6-21 FUEL METER FUEL METER CIRCUIT Fuel level gauge Fuel tank : Orange B/W: Black with White tracer Y/B : Yellow with Black tracer INSPECTION FUEL LEVEL GAUGE • Remove the fuel level gauge. (See page 4-3). Check the resistance of each float position with a pocket tester. If the resistance measured is incorrect, replace the fuel gauge assembly with new one.
-
Page 155: Combination Meter
6-22 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM FUEL METER • Disconnect the fuel level gauge lead wire coupler. (See page 4-3). To test the fuel meter two different checks may be used. The first connect a jumper wire between B/W and Y/B wires coming from the main wiring harness.
-
Page 156: Inspection
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM 6-23 G/L : GREEN WITH BLUE TRACER Y/L : YELLOW WITH BLUE TRACER : WHITE Y/W : YELLOW WITH WHITE TRACER Y/B : YELLOW WITH BLACK TRACER B/W : BLACK WITH WHITE TRACER Y/G : YELLOW WITH GREEN TRACER : LIGHT BLUE INSPECTION INDICATOR…
-
Page 157: Lamps
6-24 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM LAMPS HEADLIGHT AND TURN SIGNAL LIGHT HEADLIGHT BULB REPLACEMENT • Remove the front handlebar’s cover. • Push in on the bulb socket, turn it to the left, and pull it out • Remove the headlight bulb. When replacing the headlight bulb , do not touch the glass.
-
Page 158: Tail/Brake Light And Turn Signal Light
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM 6-25 TAIL/BRAKE LIGHT AND TURN SIGNAL LIGHT TAIL / BRAKE LIGHT BULB AND TURN SIGNAL LIGHT BULB REPLACEMENT • Remove the tail/brake light lens and turn signal lens. • Push in on the bulb, turn it to the left, and pull it out. Do not over tighten the lens fitting screws.
-
Page 159: Switches
6-26 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM SWITCHES Inspect each switch for continuity with the pocket tester. If any abnormality is found, replace the respective switch assemblies with new ones. 09900-25002: Pocket tester Tester knob indication: X 1Ω range IGNITION SWITCH HORN BUTTON Color Color Position Position…
-
Page 160: Battery
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM 6-27 BATTERY SPECIFICATIONS Electric starter Kick starter Item with kick starter type type Type designation YB 5L-B GM3 –3B 12V 15kC 12V 10.8 kC Capacity (5Ah/10 HR) (3Ah/10HR) Standard 1.28 at 20 °C 1.26 at 20 °C Electrolyte S.G. In fitting the battery to the motorcycle, connect the breather Pipe to the battery vent.
-
Page 161: Recharging Operation
6-28 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM Check the electrolyte level and add distilled water, as necessary to raise the electrolyte to each cell’s UPPER level. Check the battery for proper charge by taking an electrolyte S.G. reading. If the reading is 1.22 (YB5L-B) or less/1.20 (GM3-3B) or less, as corrected to 20 °C, it means that the battery is still a run-down condition and needs recharging.
-
Page 162: Service Life
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM 6-29 SERVICE LIFE Lead oxide is applied to the pole plates of the battery which will come off gradually during the service. When will come off gradually during the sediment, the battery can not be used any more. If the battery is not charged for a long time, lead sulfate is generated on the surface of the pole plates and will deteriorate the performance (suifation).
-
Page 163
6-30 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM… -
Page 164: Wiring Diagram
SERVICING INFORMATION SERVICING INFORMATION CONTENTS TROUBLESHOOTING ………………7-2 ENGINE ………………..7-2 CARBURETOR ………………7-5 CHASSIS ………………..7-6 BRAKES ………………..7-7 ELECTRICAL ………………. 7-8 BATTERY ………………..7-9 WIRING DIAGRAM FD 110 (XB517QSC/XB517QD)……..7-10 WIRE HARNESS, CABLE AND HOSE ROUTING……..7-11 WIRE HARNESS ROUTING …………..7-11 CABLE ROUTING ……………..
-
Page 165: Troubleshooting
SERVICING INFORMATION TROUBLESHOOTING ENGINE Complaint Symptom and possible causes Remedy Engine will not start, or Compression too low is hard to start. 1. Out of adjustment valve clearance. Adjust. 2. Worn valve guides or poor seating of valves. Repair or replace. 3.
-
Page 166
SERVICING INFORMATION Noise seems to come from clutch 1. Worn or slipping clutch shoe. Replace. 2. Worn or slipping clutch drive plate. Replace. Noise seems to come from crankshaft 1. Due to wear ratting bearings. Replace. 2. Worn and burnt big-end bearing. Replace. -
Page 167
SERVICING INFORMATION 9. Spark plug too cold. Replace by hot type Plug. 10. Clogged jets in carburetor. Clean. 11. Deflective magneto. Replace. Engine runs poorly in 1. Weakened valve springs. Replace. high speed rage. 2. Worn camshaft or rocker arms. Adjust. -
Page 168: Carburetor
SERVICING INFORMATION Complaint Symptom and possible causes Remedy Engine overheats. 1. Heavy carbon deposit on piston crown. Clean. 2. Not enough oil in the engine. Add oil. 3. Defective oil pump or clogged oil circuit. Replace or clean. 4. Too low in float chambers fuel level. Adjust.
-
Page 169: Chassis
SERVICING INFORMATION Complaint Symptom and possible causes Remedy Medium-or high 1. Clogged main jet or main air jet. Check and clean. Speed trouble. 2. Clogged needle jet. Check and clean. 3. Not operating properly throttle valve. Check throttle valve For operation.
-
Page 170: Brakes
SERVICING INFORMATION Complaint Symptom and possible causes Remedy Rear suspension too soft. 1. Weakened shock absorber spring. Replace. 2. Leakage oil of shock absorber. Replace. Noisy rear suspension 1. Loose bolts on shock absorber. Retighten. 2. Worn swing arm bushing. Replace.
-
Page 171: Electrical
SERVICING INFORMATION ELECTRICAL Complaint Symptom and possible causes Remedy 4. Loose connection of lead wire. Connect/tighten. Spark plug soon become 1. Mixture too rich. Adjust carburetor. fouled with carbon. 2. Idling speed set too high. Adjust carburetor. 3. Incorrect gasoline. Change.
-
Page 172: Battery
SERVICING INFORMATION BATTERY Complaint Symptom and possible causes Remedy “Sulfation”, acidic white 1. Not enough electrolyte. Add distilled water, if the powdery substance or 2. Battery case is cracked. battery has not bee n spots on surfaces of cell 3. Battery has been left in a run down condi- damaged and “sulfation”…
-
Page 173: Wiring Diagram Fd 110 (Xb517Qsc/Xb517Qd)
7-10 SERVICING INFORMATION WIRING DIAGRAM FD 110 (XB517QSC/XB517QD)
-
Page 174: Wire Harness, Cable And Hose Routing
SERVICING INFORMATION 7-11 WIRE HARNESS, CABLE AND HOSE ROUTING WIRE HARNESS ROUTING PASS THE WIRINGUNDER T HE F UE L HOS E IG NIT ION S WIT C H C LAMP R E AR B R AK E LIG HT S WIT C H F UE L G AUG E B AT T E R Y ( + ) T E R MINAL C OV E R…
-
Page 175
7-12 SERVICING INFORMATION MAGNETO LEAD WIRE ROUTING PICK-UP COIL GROMMET MAGNETO LEAD WIRE ENGINE GROUND WIRE GEAR POSITION INDICATOR GROMMET CLAMP MAGNETO STATOR 8.0 KG-M… -
Page 176: Cable Routing
SERVICING INFORMATION 7-13 CABLE ROUTING S T AR T E R C AB LE S T AR T E R LE V E R VIEW A S T AR T E R C AB LE C LAMP C LAMP S P E E DOME T E R C AB LE F R ONT B R AK E C AB LE F R ONT B R AK E C AB LE VIEW B…
-
Page 177: Front Brake Hose Routing
7-14 SERVICING INFORMATION FRONT BRAKE HOSE ROUTING T HR OT T LE C AB LE S T AR T E R C AB LE C LAMP S T AR T E R C AB LE S P E E DOME T E R C AB LE C LAMP F R ONT B R AK E C AB LE S T AR T E R C AB LE…
-
Page 178: Fuel Hose Routing
SERVICING INFORMATION 7-15 FUEL HOSE ROUTING FUEL TANK CLAMP…
-
Page 179
7-16 SERVICING INFORMATION BATTERY FUEL TANK BATTERY BREATHER HOSE… -
Page 180: Front Wheel Set Up (Drum Type)
SERVICING INFORMATION 7-17 FRONT WHEEL SET UP (DRUM TYPE)
-
Page 181: Front Wheel Set Up (Disk Type)
7-18 SERVICING INFORMATION FRONT WHEEL SET UP (DISK TYPE)
-
Page 182: Rear Wheel Set Up
SERVICING INFORMATION 7-19 REAR WHEEL SET UP 114.8 mm.
-
Page 183: Special Tools
7-20 SERVICING INFORMATION SPECIAL TOOLS 09900-00401 “L” type haxagon 09900-00410 09900-06107 09900-06108 09900-09003 wrench set Hexagon wrench set Snap ring pliers Snap ring pliers Impact driver set 09900-20202 09900-20203 09900-20205 09900-20508 09900-20101 Micrometer Micrometer Micrometer Cylinder gauge set Vernier calipers (1/100 mm, (1/100 mm, (1/1000 mm,…
-
Page 184
SERVICING INFORMATION 7-21 09915-64510 09913-76010 09915-44531 Compression gauge 09913-84510 09914-79610 09915-74510 Oil pressure gauge 09915-63310 (Adaptor) Bearing installer Bearinginstaller Oil pressure gauge adaptor 09916-14510 09916-14521 09916-20630 09916-24311 Valve spring Valve lifter attach- 09916-21110 Valve seat cutter Solid pilot compressor ment Valve seat cutter set head (n-126) (N-100-5.0) -
Page 185
7-22 SERVICING INFORMATION 09940-14920 09940-52860 09940-51710 09941-34513 Steering stem nut Front fork oil seal Steering race 09940-60113 Steering outer race wrench installer set installer Spoke nipple wrench installer 09941-74910 09943-74111 09941-50111 Steering bearing Front fork oil level 09951-16080 Bearing remover installer gauge Bearing installer… -
Page 186: Tightening Torque
SERVICING INFORMATION 7-23 TIGHTENING TORQUE ENGINE ITEM Kg-m Cylinder head nut 18.0-22.0 1.8-2.2 Cylinder head bolt 8.0-12.0 0.8-1.2 Cam sprocket bolt 9.0-11.0 0.9-1.1 Cam chain tensioner bolt 8.0-12.0 0.8-1.2 Starter clutch bolt 14.0-16.0 1.4-1.6 Spark plug 10.0-12.0 1.0-1.2 Valve clearance inspection cap bolt Cylinder head right cover bolt 8.0-12.0 0.8-1.2…
-
Page 187
7-24 SERVICING INFORMATION CHASSIS ITEM Kg-m Front axle/nut 30.0-47.0 3.0-4.7 Steering stem lock nut 25.0-35.0 2.5-3.5 Handlebar clamp bolt 50.0-60.0 5.0-6.0 Handlebar mounting nut Front fork cap bolt Front fork clamp bolt 25.0-40.0 2.5-4.0 Front brake master cylinder bolt 8.0-12.0 0.8-1.2 Front brake hose union bolt Front brake caliper mounting bolt… -
Page 188
SERVICING INFORMATION 7-25 TIGHTENING TORQUE CHART Conventional or W4W marked bolt “7” marked bolt Bolt Diameter A (mm) Kg-m Kg-m 0.15 13.5 10.5 21.0 16.0 24.0 “7” marked bolt “4” marked bolt Conventional bolt… -
Page 189: Service Data
7-26 SERVICING INFORMATION SERVICE DATA VALVE + GUIDE Unit: mm ITEM STANDARD LIMIT ————— Valve diam. ————— 0.04-0.07 ————— Valve clearance (when cold) 0.04-0.07 ————— Valve guide to valve stem 0.010-0.037 ————— Clearance 0.030-0.057 ————— Valve stem deflection IN.&EX. ————— 0.350 Valve guide I.D.
-
Page 190
SERVICING INFORMATION 7-27 Unit: mm ITEM STANDARD LIMIT 1 st 0.10 – 0.25 0.500 Piston ring end gap 2 nd 0.10 – 0.25 0.500 Piston ring to groove clearance 1 st ————- 0.180 2 nd ————- 0.150 Piston ring groove width 1 st 1.01-1.03 ————-… -
Page 191
7-28 SERVICING INFORMATION TRANSMISSION + DRIVE CHAIN Unit: mm ITEM STANDARD LIMIT Primary reduction ratio 3.666 (77/21) ————— Final reduction ratio 2.428 (34/14) ————— Gear ratios 3.000 (33/11) ————— 2 nd 1.875 (30/16) ————— 3 rd 1.368 (26/19) ————— 1.052 (20/19) ————— Shift fork to groove clearance No. -
Page 192: Speedometer Light
SERVICING INFORMATION 7-29 ITEM STANDARD LIMIT Primary peak voltage Morn then 130 V (+)ground , (-)white/blue Pickup coil peak voltage Morn then 4 V (+)green/white , (-)blue/yellow Magneto coil resistance Lighting Y/W – B/W 0.3 — 1.5 Ω Charging W/R – B/W 0.5 – 2.0 Ω Pick-up G/W-L/Y 180 –…
-
Page 193: Fuel Tank
7-30 SERVICING INFORMATION BRAKE + WHEEL ITEM STANDARD LIMIT Master cylinder bore 12.700-12.743 ————— Master cylinder piston diam. 12.657-12.684 ————— Brake caliper cylinder bore 27.00-27.050 ————— Brake caliper piston diam. 2.930-26.50 ————— Brake drum I.D. Front ————— 110.7 Rear ————— 110.7 Wheel axle run out Axle…
- Особенности 110-кубовой модели
- Отличия Street Magic 110 и 110II
- Технические характеристики
- Плюсы и минусы в целом
- Оценки и отзывы владельцев
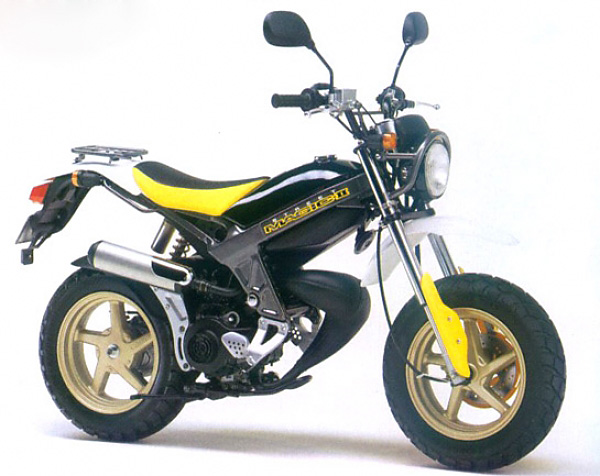
Стодесятикубовая версия Street Magic в целом копирует «базовый полтинник», за исключением чуть удлинённой базы и, разумеется, более производительного двигателя. Внешность и посадка у этого минибайка – мотоциклетные, но по технической части он полностью аналогичен более популярному классическому скутеру Suzuki Address 110.
В отличие от пятидесятикубовой модели, Street Magic 110 выпускался лишь в двух основных модификациях – «начальной» и «топовой». Но в данном случае первой вышла «топовая» TR110SDW (в июне 1998 года) и только через пару месяцев было запущено производство «начальной» TR110SW.
Особенности 110-го
Старшая модель «уличной магии» отличается взрывным и, даже можно сказать, злым нравом – для новичков этот скутер-байк однозначно не рекомендуется, а для подростков так и вовсе опасен!
Внешне отличить 110-кубовую модель от 50-кубовом можно по соответствующей надписи на боку. Упомянутую же уже, удлинённую (примерно на 5 см) базу «глазом» отметить сложно, но на ходу это отличие более чем очевидно – выражаясь в заметно лучшей устойчивости «по прямой».
Благодаря более мощному двигателю, конечно Street Magic 110 отличается лучшей динамикой, максимальной скоростью и, соответственно, бо́льшим расходом топлива.
Технические характеристики
- Двигатель – F131 (одноцилиндровый двухтактный):
- рабочий объём – 113 см³
- максимальная мощность – 10 л.с. при 6500 об/мин
- охлаждение – воздушное
- Трансмиссия – вариатор
- Подвеска:
- передняя – телескопическая вилка
- задняя – маятниковая с одним амортизатором
- Тормоз:
- передний – дисковый
- задний – барабанный
- Шины:
- передняя – 120/80-12
- задняя – 120/80-12
- Размеры
- высота (полная) – 975 мм
- высота (по сиденью) – 720 мм
- длина – 1700 мм
- ширина – 710 мм
- колёсная база – 1135 мм
- дорожный просвет – 120 мм
- Сухой вес – 85 кг
- Снаряженная масса – 91 кг
- Грузоподъёмность – 150 кг
- Максимальная скорость – более 90 км/час
- Расход топлива – 2,5-3,5 литра на 100 км (в зависимости от условий движения)
- Объём бензобака – 6,4 литра
Плюсы и минусы
Главный плюс модели – это мощность двигателя. Цифры, сами по себе, не выглядят впечатляюще, но «10 лошадок в 113 кубиках» для такого «малыша» это гораздо больше чем достаточно. Второе преимущество – необычная, но привлекательная внешность.
Ну и нельзя забывать о скутерной сущности модели – она вариаторная, так что никакой классической КПП тут нет, просто жми на газ и всё!
Минусов у Suzuki Street Magic 110 немного – разве что её редкость и, соответственно, трудности с поиском запчастей (особенно кузовных).
Найти запчасти в России можно только через специализированные форумы и группы в соцсетях. Часто приходится заказывать детали напрямую из Японии. Спасает родство этой модели по двигателю и вариатору с Suzuki Address 110.
Итоговые оценки и отзывы
дизайн и эргономика
ходовые качества
обслуживание и ремонт
качество и надёжность
Уникальный скутер с мотоциклетной компоновкой, мощным двигателем и хорошей проходимостью – отличный вариант индивидуального транспорта для сельской местности… да и не только для сельской.
Народный рейтинг: 4.17 ( 3 голосов)
Кнопка «Наверх»
Схема скутера Suzuki Street Magic
Схема скутера Suzuki Street Magic
Мануалы и
схемы скутеров
Suzuki мопедов мотоциклов все схемы можно скачать в одном архиве. ремонт следующих элементов скутера:
Правильная чистка карбюратора, замена троса управления, дисковые тормоза скутера, опережение зажигания, робота двигателя
перегревается.
Также вы можете сравнить скутера по техническим данным что лучше
выбрать обзор двигателей и ходовой части мотто
техники.
|
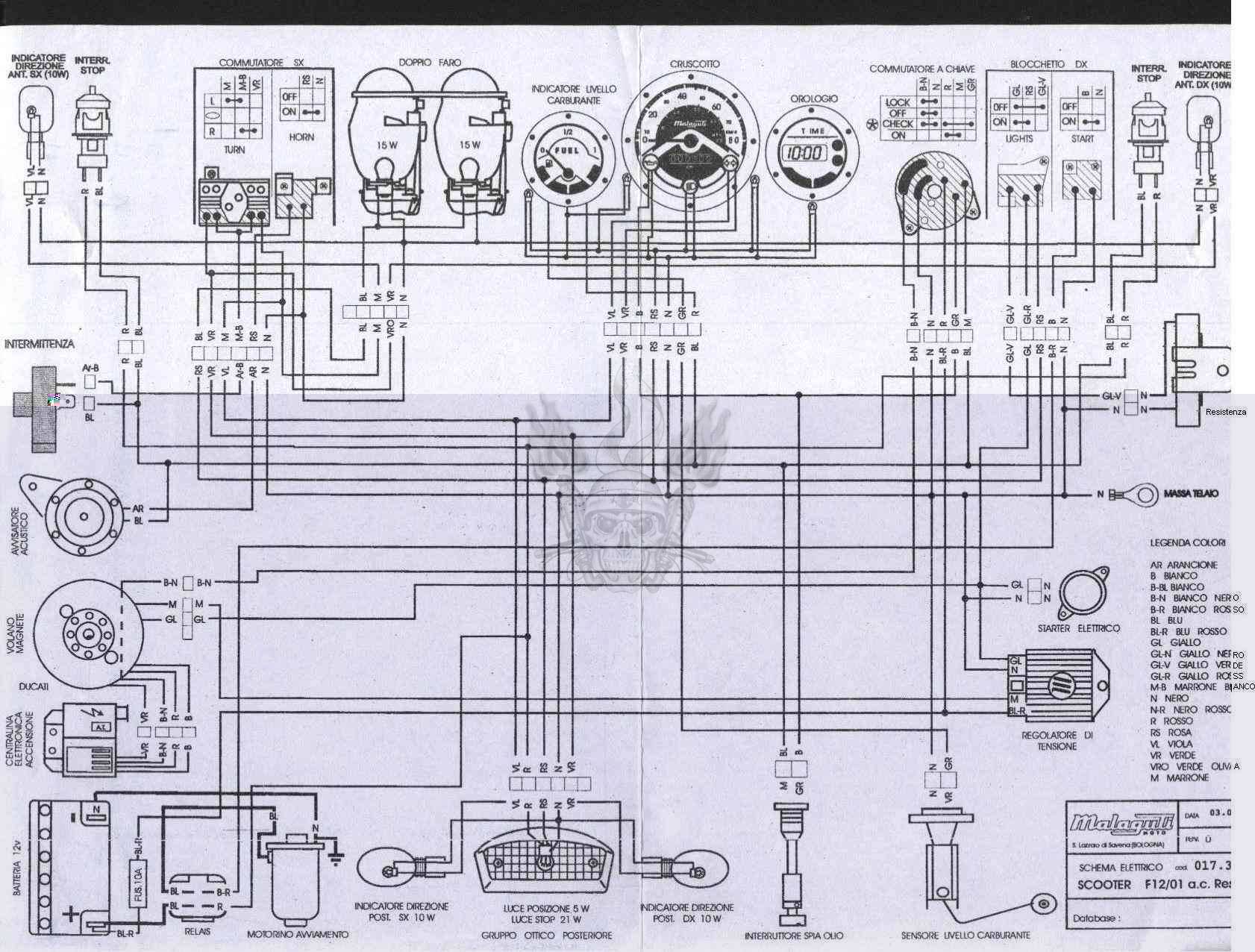
Схема скутера Malaguti F12 Phantom AC BJ01
|
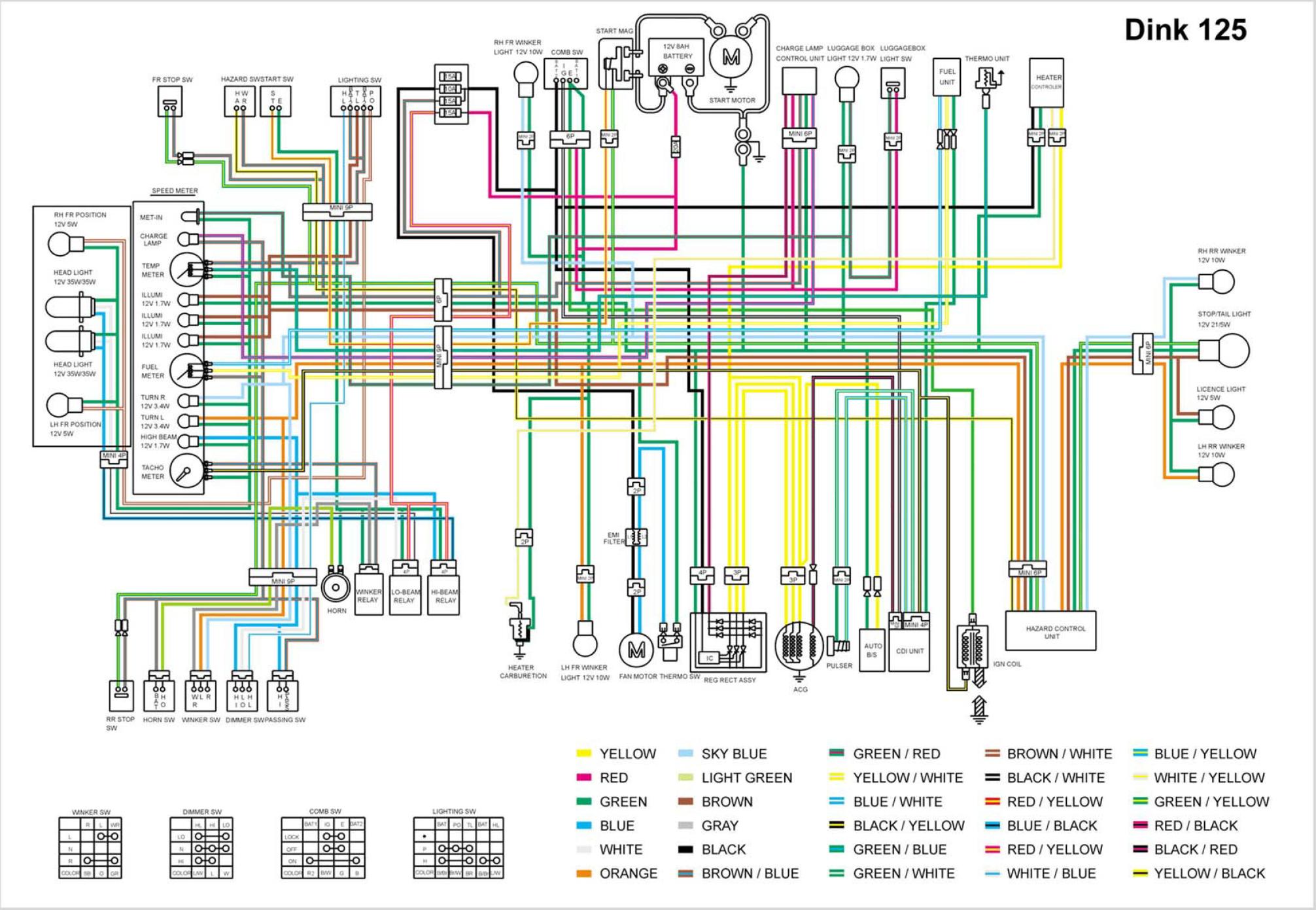
Схема проводки скутера Kymco Dink 125 D125
|
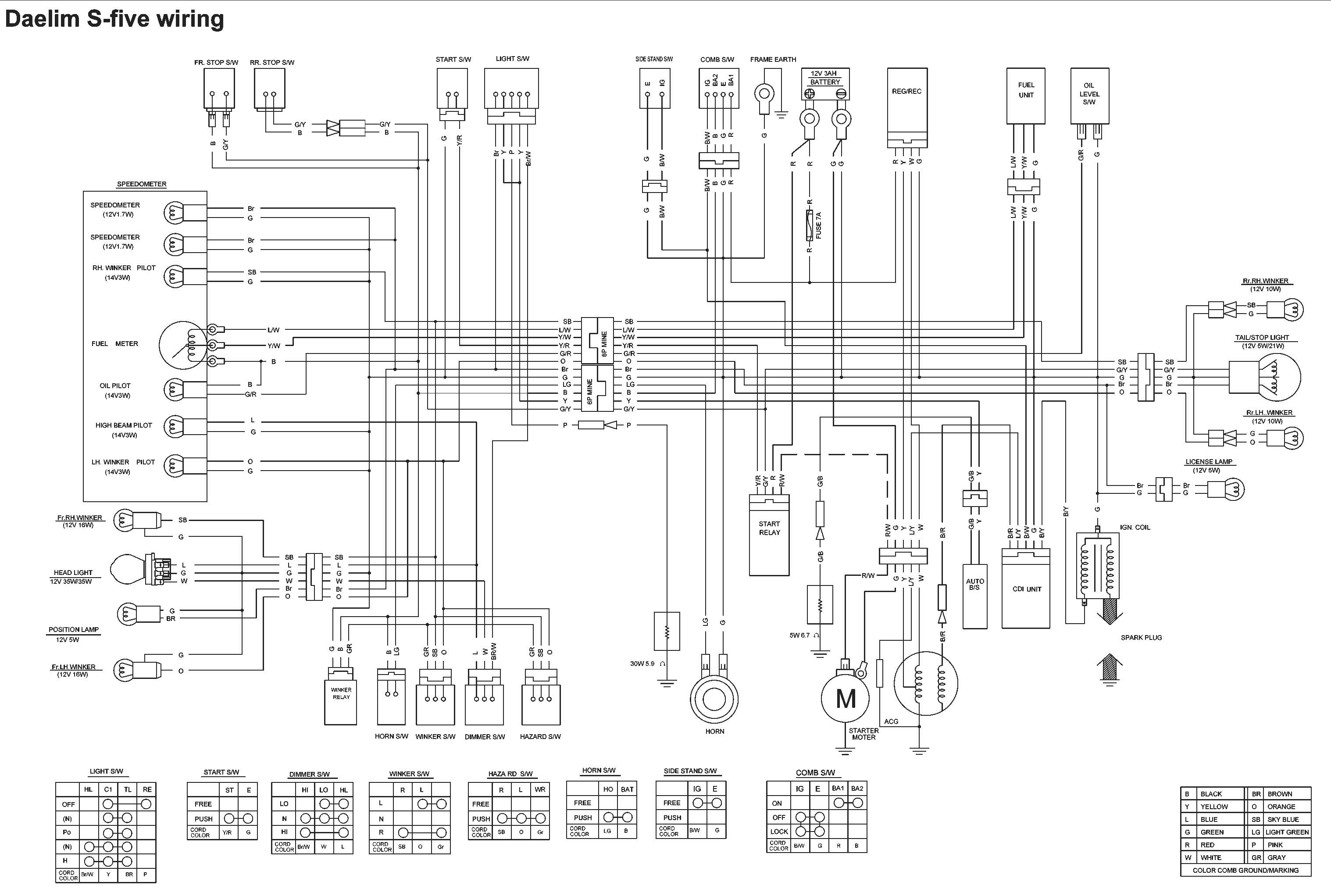
Электрическая схема Daelim S-Five
|
Сигнализация на скутер
|
Скутер Street Magic Suzuki — отличный пример японского качества по доступной цене. Мини-байк отличается высокой проходимостью и привлекательным внешним видом. Множество положительных отзывов мотолюбителей говорят о надежности, мощности и управляемости модели.
Описание производителя
Компания «Сузуки» основана в 1909 году японцем Митио Сузуки. Производство велось в трёх направлениях — мотоциклостроение, создание велосипедов с двигателем, изготовление ткацких станков. Спустя десятилетия компания приобрела значение одного из крупнейших поставщиков мототехники в США. В 1967 году корпорация открывает свой завод в Таиланде. В 2009 году руководство компании объединило усилия с Wolkswagen для разработки экологических автомобилей.
В профессиональном мотоспорте модели «Сузуки» стали участвовать с 1953 года, после выпуска модели Diamond Free. Благодаря ей был выигран кубок серьезного моточемпионата. Не боялись японские конструкторы и необычных экспериментов. Таковым оказалось создание модели Suzuki RE5 с роторным двигателем.
Отличительной чертой мотоцикла стал итальянский дизайн. Резкое ускорение — приятная особенность работы двигателя, которую по достоинству оценили многие мотолюбители. К 80-м годам Suzuki зарекомендовала себя как производитель надежных, мощных и скоростных мотоциклов.
Сегодня компания является крупным производителем автомобилей, мотоциклов, легких мопедов и скутеров.
Скутеры Suzuki
Все современные скутеры Suzuki имеют технические характеристики, которые стали особенностью продукции японской фирмы. В связи с этим заливаемый бензин рекомендуется покупать с октановым числом не ниже 93, а масло – только двухтактное для мототехники. Приблизительный расход топлива для скутеров японского производства равен 3 литрам.
Современные мопеды оснащаются вариатором, способным, в зависимости от нагрузки, регулировать передаточное число. Привод осуществляется при помощи ременной передачи. Все электрооборудование имеет напряжение 12 V.
На всех мопедах предусмотрен как ножной, так и электростартер. В процессе эксплуатации следует особое внимание уделять воздушному фильтру – при износе его частиц дорожная пыль попадает в карбюратор, засоряются жиклеры. Вследствие этого быстро изнашиваются поршень и цилиндр. Остальные детали и механизмы практически не требуют ремонта.
При правильной эксплуатации мини-байк Suzuki может служить в условиях российских дорог около двух лет. По истечении этого срока мощность двигателя заметно падает.
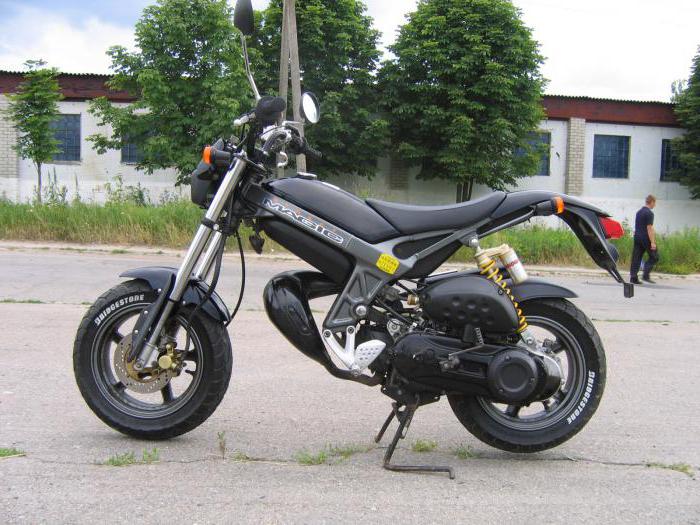
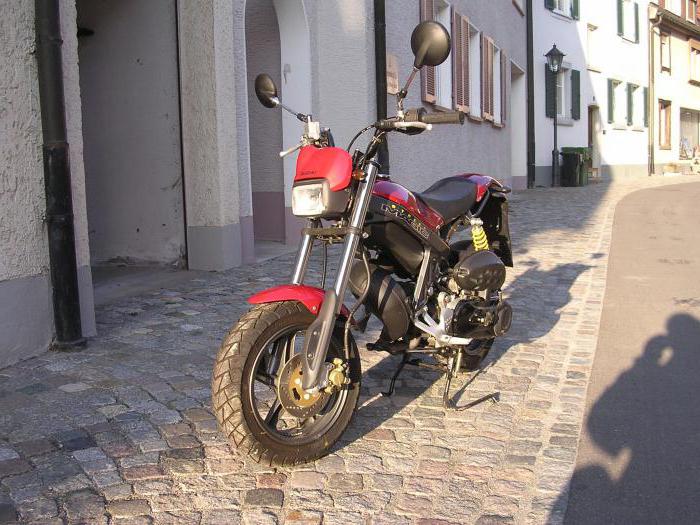
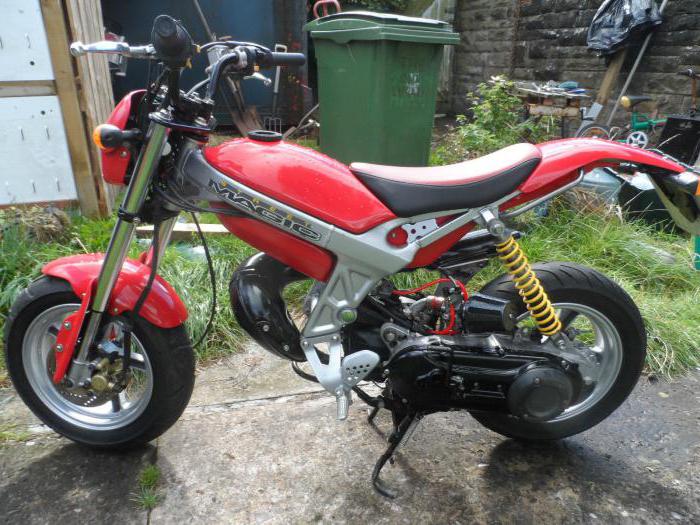
Скутер Suzuki Street Magic
Мини-байк поставляется в Европу в комплектации, обладающей меньшей мощностью, нежели продаваемый в Азии. Также на «европейца» устанавливается другая выхлопная система, коммутатор зажигания и шестерни редуктора. Чтобы снять ограничения, обусловленные работой этих деталей, многие мотолюбители заменяют их более совершенными. Это повышает мощность двигателя, значительно увеличивает максимальную скорость, придает бодрости разгонной динамике Suzuki Street Magic 50.
В большинстве случаев детали меняются на азиатские комплектующие Suzuki. Предпочтителен и выбор других фирм запчастей для этой модели.
Скутер представляет собой надежную машину для бездорожья и повседневной езды. Он отлично чувствует себя на проселочной дороге и в грязи, что достигается благодаря увеличенному клиренсу и широким колесам.
Особенности
Мини-байк имеет жесткую мотоциклетную раму и автоматическую трансмиссию. Он обладает небольшими размерами, за счет чего увеличивается маневренность и проходимость. Вариатор и воздушное охлаждение, а также некоторые элементы конструкции позаимствованы у скутера, что снижает стоимость модели и обеспечивает отличные ходовые качества.
Мини-байк более приспособлен к неровностям дороги, чем обычный скутер. Это объясняется его большими и широкими колесами. От мотоцикла он взял вынесенный вперед бак и ярко выраженный спортивный дизайн. Не имеет багажника, оборудован одноместным сиденьем.
Широкая цветовая гамма порадует любого мотолюбителя. Она представлена множеством оттенков – от серебристого до бордового. Вынесенные поворотники, большая фара и жесткая передняя вилка – вот основные привлекающие внимание особенности внешнего вида «уличного волшебника». Благодаря широкой области применения модель стала популярной как в Японии, так и в Европе.
Suzuki Street Magic: технические характеристики
Судя по отзывам, скутер легок в управлении, обладает отличными тормозами, уверенно держится на городской дороге. Такие особенности обусловлены параметрами Suzuki Street Magic.
Характеристики его следующие:
- объем двигателя равен 49 см3;
- двухтактный мотор;
- единственный цилиндр выдает мощность 7,2 л. с.;
- двигатель запускается как при помощи электрозапуска, так и кикстартером;
- задний тормоз-барабан обеспечивает минимальное время снижения скорости;
- диски представлены литым алюминием;
- объем топливного бака равен 6,2 литра;
- сухой вес — 78 кг.
Мини-байк обладает многими положительными характеристиками, в частности, у него отличная мотоциклетная рама и качественные элементы, взятые от обычного скутера. Некоторые пользователи отмечают небольшой объем топливного бака, однако модель и не предназначалась для длительных путешествий. Suzuki Street Magic 2 — усовершенствованный скутер с объемом двигателя 110 куб. см. Этот мини-байк можно назвать эксклюзивной моделью. Он оборудован своеобразной светотехникой и приподнятыми дисковыми тормозами. Также на шинах скутера выполнены грунтозацепы, что позволяет без проблем совершать путешествия по дорогам с различным покрытием.
Преимущества и недостатки
Скутер обладает множеством особенностей, которые можно причислить как к достоинствам, так и к недостаткам модели. Однако существует ряд неоспоримых преимуществ мини-байка перед другими представителями своего класса:
- стильный дизайн;
- комфортная посадка;
- отличный вариант для начинающего мотолюбителя или подростка;
- простота обслуживания и ремонта;
- японское качество сборки.
Несмотря на большое количество плюсов модели, можно выделить и ряд отрицательных моментов:
- слабые задние тормоза;
- отсутствие бардачка;
- сложность поиска некоторых запчастей.
Отзывы
По мнению опытных мотолюбителей, «Сузуки» при первом осмотре сразу привлекает внимание. Он намного жестче «скутера-табуретки». Меньший угол поворота руля позволяет легко контролировать движение мини-байка всем телом. Залитого бака объемом 6,2 литра хватает на 250-300 километров.
Неудобно ездить на нем только людям высокого роста. Благодаря небольшим размерам скутер можно носить буквально «на руках». Большие и широкие колеса, по словам владельцев, отлично справляются с неровными российскими дорогами.
Как отмечают опытные мотолюбители, Street Magic Suzuki грузится до 150 кг живого веса. Его можно назвать дачно-овощным внедорожником, который без труда справляется с поездками «город — деревня». Если поставить коммутатор без ограничений, мини-байк сможет развить скорость до 60 км/ч.
К сиденью, по мнению пользователей, надо привыкнуть. Оно отличается большой жесткостью. Сам мини-байк в силу своих габаритов и особенностей конструкции больше подходит для людей маленького и среднего роста. Высокие мотолюбители будут чувствовать себя на нем некомфортно.
Положительные отзывы о скутере Street Magic Suzuki в большинстве случаев отмечают удобство перемещения по ухабистой дороге. Он справляется с большинством препятствий, чувствуя себя уверенно даже в условиях отсутствия оборудованного дорожного полотна.
Цена
Японское качество и высокая проходимость мини-байка повысили его стоимость в сравнении с обычными скутерами от «Сузуки». Однако модель все равно можно причислить к недорогим (от 50 тысяч рублей в зависимости от комплектации). Множество представителей линейки продается в подержанном виде. Цены на б/у Street Magic Suzuki начинаются от 30 и заканчиваются 45 тыс. рублей.