Комментарии
8
Войдите или зарегистрируйтесь, чтобы писать комментарии, задавать вопросы и участвовать в обсуждении.
Войти
Зарегистрироваться
s500-47rus
Без машины
Спасибо тебе дружище! Будь счастлив!
11 месяцев
Jermaine
Я езжу на Toyota Auris (1G)
Вдруг кому пригодится в эл. виде (pdf):
Hilux / Hilux Surf / 4Runner (1988-1999) — t.me/Car_Guide/1576
Hilux Surf / 4Runner (1995-2002) — t.me/Car_Guide/1578
Hillux (2011) — t.me/Car_Guide/943
А так же большой выбор:
📚 Руководство по ремонту и эксплуатации авто
📘 Руководство по ремонту двигателей
⚠️ Электрические схемы
⚡️ Схемы предохранителей и реле
t.me/Car_Guide/1174
1 год
ROMAN111ENJINE
Без машины
🤝 огромное спасибо!
3 недели
Vitaliy670
Я езжу на LADA 4×4 3D
Спасибо огромное !
2 года
kolchasik
Я езжу на Ford C-Max I
Здоровья тебе! Спасибо
2 года
Sega-Niver
Я езжу на Suzuki Escudo (1G)
От спасибо мил человек
6 лет
KRSone
Я езжу на Mitsubishi Challenger
Благодарю 👍
6 лет
tourer28
Автор
Я езжу на Land Rover Freelander 2
юзайте на здоровье)
6 лет
- Симпатии
- 121
- Авто
-
Toyota Hilux 8 (Revo)
- Симпатии
- 121
- Авто
-
Toyota Hilux 8 (Revo)
Последнее редактирование: 19 дек 2020
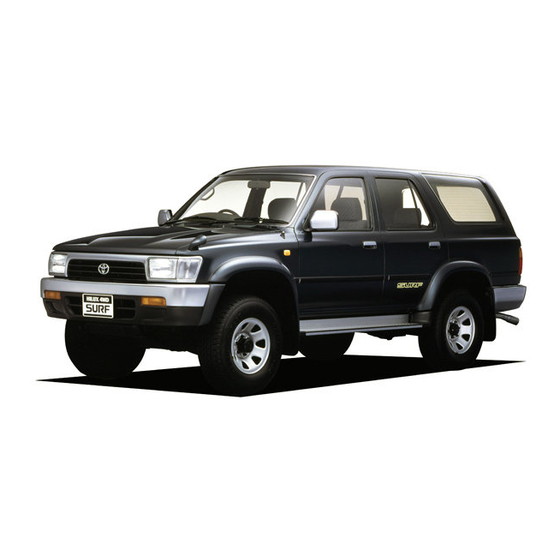
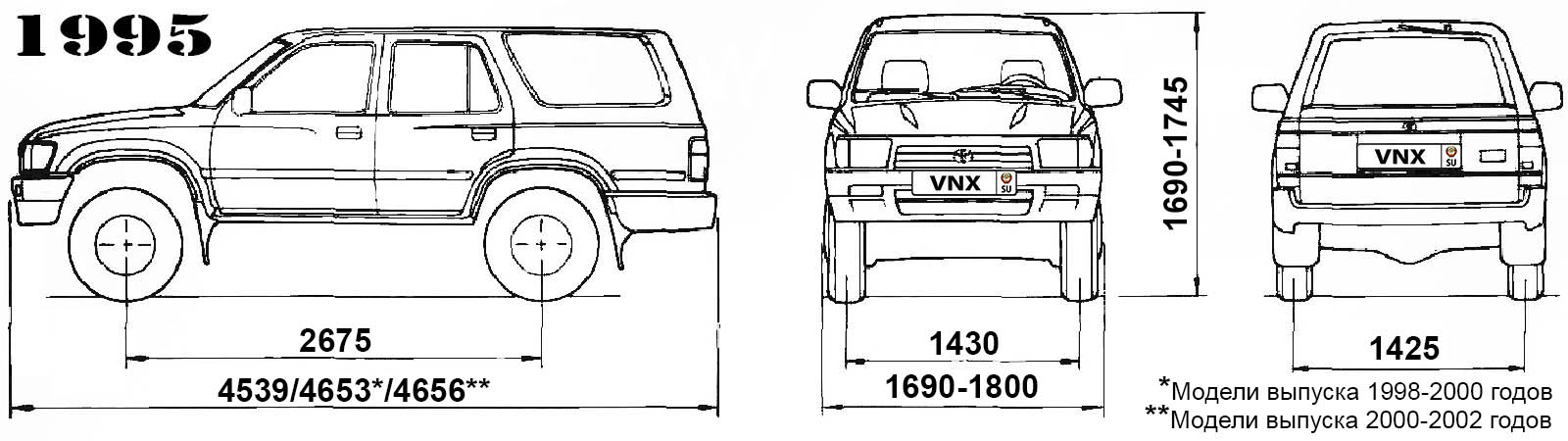
SUV Toyota Hilux Surf / 4Runner (Mark III, N180, SW4, Zhongxing Admiral) с бензиновыми двигателями: 3RZ-FE 2.7 л (2693 см³) 150-152 л.с./110-112 кВт 5VZ-FE 3.4 л (3378 см³) 175-186 л.с./129-136 кВт и дизельными 1KZ-TE 3.0 л (2982 см³) 132-140 л.с./97-103 кВт; Руководство по эксплуатации, техническому обслуживанию и ремонту. Технические характеристики, электросхемы, контрольные размеры кузова, устройство, диагностика, особенности конструкции. Производственно-практическое издание легковой автомобиль повышенной проходимости J-класса Тойота ФоРаннер (Хайлюкс Сёрф Н180) среднеразмерный рамный внедорожник с цельнометаллическими кузовами пятидверный универсал повышенной вместимости задне- и полноприводные модели третьего поколения выпуска с августа 1995 по 2002 год
ЕСЛИ ВЫ ВИДИТЕ ОШИБКУ 406 Not Acceptable и не видите документ, то скорей всего у Вас IP РФ и его надо сменить, на любой другой страны, с помощью VPN ( Scribd и SlideShare блокируют посетителей с Российским IP).
Видео Toyota Hilux Surf, 4Runner замена рулевой рейки (Тойота ФоРаннер, Хайлюкс Сёрф 95-02)
Toyota Hilux Surf, 4Runner Mark III общая информация (Тойота 4Раннер, Хайлюкс Серф 1995-2002)
РУЛЕВОЙ МЕХАНИЗМ
Снятие
1. Установите передние колеса в направлении движения по прямой.
2. Поддомкратьте автомобиль и снимите передние колеса.
3. Снимите нижний кожух защиты двигателя.
4. Отсоедините наконечники рулевых
тяг от поворотных кулаков.
а) Снимите шплинт и отверните гайку.
б) Используя специнструмент, отсоедините наконечники рулевых тяг от поворотных кулаков.
5. Отсоедините универсальный шарнир от червяка.
а) Нанесите метки на универсальный шарнир и вал червяка.
б) Отверните болт крепления универсального шарнира к червяку.
6. Отсоедините возвратный и нагнетательный трубопроводы от рулевого механизма.
7. Отверните болт и отсоедините возвратный и нагнетательный трубопровод от кронштейна крепления рулевого механизма.
8. Отверните болты и гайку и снимите кронштейн крепления рулевого механизма, втулку и кронштейн крепления трубопроводов.
9. Отверните два болта и снимите рулевой механизм в сборе, заказать на ebay amazon.
Примечание: будьте осторожны, чтобы не повредить трубопроводы системы усилителя рулевого управления.
Установка
1. Установка производится в порядке, обратном снятию.
2. Моменты затяжки болтов и гаек крепления деталей смотрите на сборочном рисунке.
3. Устанавливая рулевой механизм, совместите сделанные при снятии метки.
4. При установке шплинта на гайку крепления наконечников рулевых тяг к рычагам поворотного кулака возможен доворот гайки на угол не более 60°.
5. После установки рулевого механизма:
а) Стабилизируйте подвеску.
б) Долейте рабочую жидкость гидроусилителя рулевого управления.
в) Прокачайте систему усилителя рулевого управления.
г) Убедитесь в отсутствии утечек в системе гидроусилителя рулевого управления.
д) Проверьте углы установки и углы поворота передних колес.
| № | Спецификация / Specs | Данные |
| Габариты (мм/mm) и масса (кг/kg) / Dimensions and Weight | ||
| 1 | Длина / Length | 4539 |
| 2 | Ширина (без/с зеркалами) / Width | 1690 |
| 3 | Высота (загружен/пустой) / Height | 1690 |
| 4 | Колёсная база / Wheelbase | 2675 |
| 5 | Дорожный просвет (клиренс) / Ground clearance | 220 |
| 6 | Снаряжённая масса / Total (curb) weight | 1780 |
| Полная масса / Gross (max.) weight | 2430 | |
|
Двигатель / Engine |
||
| 7 | Тип / Engine Type, Code | Бензиновый, жидкостного охлаждения, четырехтактный, 5VZ-FE |
| 8 | Количество цилиндров / Cylinder arrangement: Total number of cylinders, of valves | 6-цилиндровый, V-образный, 24V, DOHC с верхним расположением двух распределительных валов |
| 9 | Диаметр цилиндра / Bore | 93.5 мм |
| 10 | Ход поршня / Stroke | 82.0 мм |
| 11 | Объём / Engine displacement | 3378 см³ |
| 12 | Система питания / Fuel supply, Aspiration | Распределенный впрыск топлива EFI |
| Атмосферный | ||
| 13 | Степень сжатия / Compression ratio | 9.6:1 |
| 14 | Максимальная мощность / Max. output power kW (HP) at rpm | 129 кВт (175 л.с.) при 4600 об/мин |
| 15 | Максимальный крутящий момент / Max. torque N·m at rpm | 303 Нм при 3600 об/мин |
|
Трансмиссия / Transmission |
||
| 16 | Сцепление / Clutch type | Гидротрансформатор с блокировкой / Torque Converter |
| 17 | КПП / Transmission type | АКПП 4 Автоматическая, четырёхступенчатая, гидромеханическая |
О Книге
- Название: Toyota HILUX SURF 4RUNNER Устройство, техническое обслуживание и ремонт
- Бензиновые двигатели: 3RZ-FE 2.7 л (2693 см³) 150-152 л.с./110-112 кВт 5VZ-FE 3.4 л (3378 см³) 175-186 л.с./129-136 кВт и дизельными 1KZ-TE 3.0 л (2982 см³) 132-140 л.с./97-103 кВт
- Выпуск с 1995 года
- Серия: «Профессионал»
- Год издания: 2003
- Автор: Коллектив авторов
- Издательство: «Ассоциация независимых издателей»
- Формат: PDF
- Страниц в книге: 410
- Размер: 131.33 МБ
- Язык: Русский
- Количество электросхем: 67
-
nekesha
- Администратор
- Сообщения: 1668
- Зарегистрирован: 17 дек 2014, 03:43
- Благодарил (а): 2 раза
- Поблагодарили: 6 раз
Toyota Hilux Surf 1988-1999 / Тайота Хайлюкс Сурф 1988-1999
Руководство по эксплуатации, техобслуживанию и ремонту Toyota Hilux Surf / Тайота Хайлюкс Сурф
Operation, Maintenance and Repair Manual Toyota Hilux Surf
- Года выпуска: 1988-1999
Year of release: 1988-1999
Дизельные двигатели: 2L, 3L, 2L-T, 2L-TE, 1KZ-T, 1KZ-TE
Diesel engines: 2L, 3L, 2L-T, 2L-TE, 1KZ-T, 1KZ-TE
- Язык: Русский
Формат: PDF
Размер: 127,1 Мб
Russian language
Format: PDF
Size: 127.1 MB
Скачать документацию Toyota Hilux Surf / Тайота Хайлюкс Сурф
Download the documentation of Toyota Hilux Surf
для распаковки используйте пароль — avtoproblem-net.ru
use the password to unpack — avtoproblem-net.ru
- Manuals
- Brands
- Toyota Manuals
- Automobile
- Hilux Surf 1993
- Owner’s manual
-
Contents
-
Table of Contents
-
Troubleshooting
-
Bookmarks
Quick Links
IN–1
INTRODUCTION
–
INTRODUCTION
Troubleshooting
-
Clutch troubleshooting
18 -
Manual transmission — precautions
35 -
W55 and W56 manual transmission troubleshooting
144 -
Automatic transmission troubleshooting
208 -
Overdrive Control System — Troubleshooting Flow-Chart
214 -
A340E Automatic Transmission Troubleshooting
248 -
A340E Automatic Transmission — Troubleshooting Flow-Chart
254 -
Electronic Control System — Troubleshooting Flow-Chart
262 -
A340H transmission troubleshooting
303 -
Troubleshooting flow-chart (A340H)
309 -
A340F Automatic Transmission Troubleshooting
370 -
Troubleshooting flow-chart (A340F)
376 -
A340F troubleshooting flow-chart
383 -
Transfer precautions
415 -
Propeller shaft troubleshooting
486 -
Suspension and axle troubleshooting
506 -
Brake system troubleshooting
665 -
Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System Troubleshooting
711 -
Steering troubleshooting
736 -
Progressive Power Steering (PPS) Troubleshooting
820 -
Lighting System Troubleshooting
847 -
Wiper and Washer System Troubleshooting
858 -
Combination Meter Troubleshooting
865 -
Power Window Control System Troubleshooting
877 -
Power Door Lock Control System Troubleshooting
882 -
Power Mirror Control System Troubleshooting
887 -
Cruise Control System Troubleshooting
896 -
Audio System Troubleshooting
924 -
Anti-theft system troubleshooting
925 -
Antenna troubleshooting
938 -
Clock Troubleshooting
943 -
Air conditioning system troubleshooting
1015 -
Heater troubleshooting
1040
Related Manuals for Toyota Hilux Surf 1993
Summary of Contents for Toyota Hilux Surf 1993
-
Page 1
IN–1 INTRODUCTION – INTRODUCTION… -
Page 2: How To Use This Manual
IN–2 INTRODUCTION – HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL INDEX An INDEX is provided on the first page of each section to guide you to the item to be repaired. To assist you in finding your way through the manual, the Section Title and major heading are given at the top of every page.
-
Page 3
IN–3 INTRODUCTION – HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL The procedures are presented in a step–by–step format: Example: • The illustration shows what to do and where to do it. • The task heading tells what to do. • The detailed text tells how to perform the task and gives other information such as specifications and warnings. -
Page 4: Identification Information
IN–4 INTRODUCTION – IDENTIFICATION INFORMATION CAUTIONS, NOTICES, HINTS: • CAUTIONS are presented in bold type, and indicate there is a possibility of injury to you or other people. • NOTICES are also presented in bold type, and indicate the possibility of damage to the components being repaired.
-
Page 5: General Repair Instructions
IN–5 INTRODUCTION – GENERAL REPAIR INSTRUCTIONS GENERAL REPAIR INSTRUCTIONS 1. Use fender, seat and floor covers to keep the vehicle clean and prevent damage. 2. During disassembly, keep parts in the appropriate order to facilitate reassembly. 3. Observe the following: (a) Before performing electrical work, disconnect.
-
Page 6
IN–6 INTRODUCTION – GENERAL REPAIR INSTRUCTIONS (b) When reusing precoated parts, clean off the old adhesive and dry with compressed air. Then apply the specified seal lock adhesive to the bolt, nut or threads. (c) Precoated parts are indicated in the component illustrations by the ”*”… -
Page 7
IN–7 INTRODUCTION – GENERAL REPAIR INSTRUCTIONS 11. Care must be taken when jacking up and supporting the vehicle. Be sure to lift and support the vehicle at the proper locations (See page IN–9). (a) If the vehicle is to be jacked up only at the front or rear end, be sure to block the wheels at the opposite end in order to ensure safety. -
Page 8
IN–8 INTRODUCTION – PRECAUTION PRECAUTION FOR VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH A CATALYTIC CONVERTER CAUTION: If large amounts of unburned gasoline flow into the converter, it may overheat and create a fire hazard. To prevent this, observe the following precautions and explain them to your customer. 1. -
Page 9
IN–9 INTRODUCTION – VEHICLE LIFT AND SUPPORT LOCATIONS VEHICLE LIFT AND SUPPORT LOCATIONS… -
Page 10
IN–10 INTRODUCTION – ABBREVIATIONS USED IN THIS MANUAL ABBREVIATIONS USED IN THIS MANUAL Automatic Disconnecting Differential Automatic Locking Retractor Automatic Transmission Automatic Transmission Fluid Before Top Dead Center BTDC California Calif. Circuit Breaker Cab and Chassis C&C Dash Pot Double Rear Wheel Electronic Control Unit Emergency Locking Retractor Electronic Spark Advance… -
Page 11
IN–11 INTRODUCTION – ABBREVIATIONS USED IN THIS MANUAL Toyota Computer Controlled System TCCS Top Dead Center TEMP. Temperature Transmission Undersize Vacuum Control Valve Vacuum Switching Valve Vacuum Transmitting Valve With Without Two Wheel Drive Vehicles (4 x 2) Four Wheel Drive Vehicles (4 x 4) -
Page 12
GLOSSARY OF SAE AND TOYOTA TERMS GLOSSARY OF SAE AND TOYOTA TERMS M076–03 This glossary lists all SAE–J 1930 terms and abbreviations used in this manual in compliance with SAE recommendations, as well as their Toyota equivalents. TOYOTA TERMS SAE ABBRE– SAE TERMS ( )––ABBREVIATIONS… -
Page 13
IN–13 INTRODUCTION – GLOSSARY OF SAE AND TOYOTA TERMS Idle Speed Control (ISC) Idle Air Control Intake or Inlet Air Temperature Intake Air Temperature I AT Ignition Control Module Indirect injection Indirect Fuel Injection Inertia Fuel–Shutoff Idle Speed Control Knock Sensor… -
Page 14
IN–14 INTRODUCTION – GLOSSARY OF SAE AND TOYOTA TERMS Bimetal Vacuum Switching Valve (BVSV) Thermal Vacuum Valve Thermostatic Vacuum Switching Valve (TVSV) Three–Way Catalyst (TWC) Three–Way Catalytic Converter CCRO Three–Way + Oxidation Catalytic Converter TWC+OC + CCo Volume Air Flow… -
Page 15
IN–15 INTRODUCTION – STANDARD BOLT TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS STANDARD BOLT TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS HOW TO DETERMINE BOLT STRENGTH Class Class Mark Mark Stud bolt 4– Hexagon 5– head bolt 6– 8– 9– 10– 11– No mark Hexagon flange bolt w/ washer No mark hexagon bolt Hexagon head bolt… -
Page 16
IN–16 INTRODUCTION – STANDARD BOLT TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS SPECIFIED TORQUE FOR STANDARD BOLTS Specified torque Diameter Pitch Class 1 OT… -
Page 17
CL–1 CLUTCH – CLUTCH… -
Page 18
CL–2 CLUTCH – Troubleshooting TROUBLESHOOTING Problem Possible cause Remedy Page Hard to shift or will Clutch pedal freeplay excessive Adjust pedal freeplay CL–3 not shift Air in clutch lines Bleed clutch system CL–4 Clutch release cylinder faulty Repair release cylinder CL–10 Clutch master cylinder faulty Repair master cylinder… -
Page 19: Clutch Pedal
CL–3 CLUTCH – Check and Adjustment of Clutch Pedal CHECK AND ADJUSTMENT OF CLUTCH PEDAL 1. CHECK THAT PEDAL HEIGHT AND PUSH ROD PLAY ARE CORRECT Pedal height (from asphalt sheet): 2WD 154.5 mm (6.0827 in.) 4WD 151.5 mm (5.9646 in.) (from floor panel): 157.5 mm (6.201 in.) Push rod play at pedal top: 1.0 –…
-
Page 20
CL–4 Bleeding of Clutch System, Inspection of Clutch Start System CLUTCH – BLEEDING OF CLUTCH SYSTEM HINT: If any work is done on the clutch system or if air is suspected in the clutch lines, bleed the system of air. NOTICE: Do not let brake fluid remain on a painted sur–… -
Page 21
CL–5 CLUTCH – Inspection of Clutch Start System 2. ADJUST CLUTCH START SWITCH (a) Measure the pedal stroke, and check the switch clearance ”A” using the chart left. (b) Loosen and adjust the switch position. (c) Recheck that the engine does not start when the clutch pedal is released. -
Page 22
CL–6 CLUTCH – Inspection of Clutch Start System (c) When pushing the switch, check that the indicator light comes on and there is continuity between ter– minals 1 and 2. (d) Check that there is no continuity between terminals 1 and 2 when disconnect the battery lead. If operation is not as specified, replace the clutch start cancel switch. -
Page 23: Clutch Master Cylinder
CL–7 CLUTCH – Clutch Master Cylinder CLUTCH MASTER CYLINDER COMPONENTS REMOVAL OF MASTER CYLINDER 1. REMOVE PUSH ROD PIN 2. DISCONNECT CLUTCH LINE UNION Using SST, disconnect the union nut. SST 09751–36011 3. REMOVE MASTER CYLINDER (a) Remove the mounting nut. (b) Pull out the master cylinder.
-
Page 24
CL–8 CLUTCH – Clutch Master Cylinder 2. REMOVE PUSH ROD (a) Pull back the boot and, using snap ring pliers, re– move the snap ring. (b) Pull out the push rod and washer. (c) Remove the piston from the cylinder. INSPECTION OF MASTER CYLINDER HINT: Clean the disassembled parts with compressed air. -
Page 25
CL–9 CLUTCH – Clutch Master Cylinder 4. INSTALL RESERVOIR TANK (a) Install reservoir tank and new grommet. (b) Using a pin punch and a hammer, drive in the slotted spring pin. INSTALLATION OF MASTER CYLINDER (See page CL–7) 1. INSTALL MASTER CYLINDER Install the mounting nut, and torque them. -
Page 26: Clutch Release Cylinder
CL–10 CLUTCH – Clutch Release Cylinder CLUTCH RELEASE CYLINDER COMPONENTS REMOVAL OF RELEASE CYLINDER 1. DISCONNECT CLUTCH LINE UNION Using SST, disconnect the union. SST 09751–36011 2. REMOVE TWO BOLTS AND PULL OFF RELEASE CYLINDER DISASSEMBLY OF RELEASE CYLINDER 1. PULL OUT PUSH ROD 2.
-
Page 27
CL–11 CLUTCH – Clutch Release Cylinder INSPECTION OF RELEASE CYLINDER HINT: Clean the disassembled parts with compressed air. 1. INSPECT RELEASE CYLINDER BORE FOR SCORING OR CORROSION If a problem is found, clean or replace the cylinder. 2. INSPECT PISTON AND CUPS FOR WEAR, SCORING, CRACKS OR SWELLING If either one requires replacement, use the parts from the cylinder kit. -
Page 28: Clutch Unit
CL–12 CLUTCH – Clutch Unit CLUTCH UNIT COMPONENTS REMOVAL OF CLUTCH UNIT 1. REMOVE TRANSMISSION (See pages MT–4, TF–5) HINT: Do not drain the transmission oil. 2. REMOVE CLUTCH COVER AND DISC (a) Put matchmarks on the clutch cover and flywheel. (b) Loosen the set bolts one turn at a time until spring tension is released.
-
Page 29
CL–13 CLUTCH – Clutch Unit 3. REMOVE BEARING,HUB AND FORK FROM TRANSMISSION (a) Remove the retaining clip pull off the bearing. (b) Remove the fork and boot. INSPECTION OF CLUTCH PARTS 1. INSPECT CLUTCH DISC FOR WEAR OR DAMAGE Using calipers, measure the rivet head depth. Minimum rivet depth: 0.3 mm (0.012 in.) If a problem is found, repair or replace the clutch disc. -
Page 30
CL–14 CLUTCH – Clutch Unit 5. IF NECESSARY, REPLACE PILOT BEARING (a) Using SST, remove the pilot bearing. SST 09303–35011 (b) Using SST, install the pilot bearing. SST 09304–30012 HINT: After assembling the pilot bearing to the hud, in– sure that it rotates smoothly. 6. -
Page 31
CL–15 CLUTCH – Clutch Unit 2. INSTALL CLUTCH COVER (a) Align the matchmarks on the clutch cover and fly– wheel. (b) Torque the bolts on the clutch cover in the order shown. Torque: 19 N–m (195 kgf–cm, 14 ft–lbf) HINT: Temporarily tighten the No. 1 and No. 2 bolts. 3. -
Page 32: Manual Transmission
MT1–1 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – G58, R150 and R150F MANUAL TRANSMISSION…
-
Page 33
MT1–2 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Description DESCRIPTION • Transmission types, G58, W55, W56, R150 and R1 50F are constant mesh synchronizers for forward gears and a sliding mesh reverse gear. • The illustrations below show the engagements of transmission gears. -
Page 34
MT1–3 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Description… -
Page 35
MT1–4 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Precautions, Troubleshooting PRECAUTIONS When working with FIPG material, you must be observe the following. • Using a razor blade and gasket scraper, remove all the old packing (FIPG) material from the gasket sur– faces. • Thoroughly clean all components to remove all the loose material. •… -
Page 36
MT1–5 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Removal and Installation of Transmission (2WD) REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION OF TRANSMISSION (2WD) Remove and install the parts as shown HINT: For the transmission with a transfer (4WD) refer to REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION OF TRANSMISSION WITH TRANSFER on Page MT1–14. -
Page 37
MT1–6 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Removal of Transmission REMOVAL OF TRANSMISSION HINT: For the transmission with a transfer (4WD) refer to REMOVAL OF TRANSMISSION WITH TRANSFER on page MT1– 16. 1. DISCONNECT BATTERY CABLE FROM NEGATIVE TER– MINAL 2. REMOVE FAN SHROUD SET BOLTS Remove the four bolts. -
Page 38
MT1–7 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Removal of Transmission 7.–2 (3VZ–E) REMOVE EXHAUST PIPE CLAMP AND EXHAUST PIPE (a) Remove the exhaust pipe clamp from the bracket. (b) Remove the exhaust pipe bracket from the clutch housing. (c) Remove the exhaust pipe from the manifold. (d) Disconnect exhaust pipe from catalytic converter front side. -
Page 39
MT1–8 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Removal of Transmission 11. REMOVE ENGINE REAR MOUNTING AND BRACKET (a) Remove the four bolts from the engine rear mount– ing. (b) Raise the transmission slightly by raising the engine with a jack. (c) Remove the four bolts from the support member and remove the mounting bracket. -
Page 40
MT1–9 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Removal of Transmission 17. REMOVE TRANSMISSION (a) Draw out the transmission toward the rear. (b) Lower the transmission front and remove the trans– mission from the vehicle. HINT: Be careful not to damage the extension housing dust deflector. -
Page 41
MT1–10 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Installation of Transmission INSTALLATION OF TRANSMISSION HINT: For the transmission with a transfer (4WD) refer to IN– STALLATION OF TRANSMISSION WITH TRANSFER on page MT1–20. 1. PLACE TRANSMISSION AT INSTALLATION POSITION Insert the extension housing between the member and floor and then slide the transmission forward. -
Page 42
MT1–11 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Installation of Transmission (c) Install the engine rear mounting bracket to the sup– port member. Torque the bolts. Torque: 59 N – m ( 590 kgf – cm, 43 ft – Ibf) (d) Lower the transmission and rest it on the extension housing. -
Page 43
MT1–12 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Installation of Transmission 6.–1 (22R–E) INSTALL STARTER LOWER MOUNTING BOLT AND CLUTCH RELEASE CYLINDER AND BRACKET Torque: Starter 39 N–m (400 kgf–cm, 29 ft – Ibf ) Tube Bracket 72 N–m (730 kgf–cm, 53 ft–lbf ) Clutch Release Cylinder 12 N–m (120 kgf–cm, 9 ft–Ibf) 6.–2(3VZ–E) -
Page 44
MT1–13 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Installation of Transmission 12. LOWER VEHICLE 13. INSTALL SHIFT LEVER (a) Apply MP grease to the shift lever. (b) Align the groove of the shift lever cap and the pin part of case cover. (c) Cover the shift lever cap with a cloth. (d) Then, pressing down on the shift lever cap, rotate it clockwise to install. -
Page 45
MT1–14 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Removal and Installation of Transmission with Transfer (4WD) REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION OF TRANSMISSION WITH TRANSFER (4WD) REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION OF TRANSMISSION WITH TRANSFER Remove and install the parts as shown. -
Page 46
MT1–15 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Removal and Installation of Transmission with Transfer (4WD) REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION OF TRANSMISSION WITH TRANSFER (Cont’d) Remove and install the parts as shown. -
Page 47
MT1–16 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Removal of Transmission with Transfer REMOVAL OF TRANSMISSION WITH TRANSFER 1. DISCONNECT BATTERY CABLE FROM NEGATIVE TER– MINAL 2. REMOVE FAN SHROUD SET BOLTS Remove the four bolts. 3. ( 3 VZ–E ) REMOVE HEATER HOSE CLAMP (a) Loosen clamp bolt. -
Page 48
MT1–17 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Removal of Transmission with Transfer 8. DISCONNECT PROPELLER SHAFT (See page PR–5) 9. DISCONNECT SPEEDOMETER CABLE, BACK–UP LIGHT SWITCH CONNECTOR AND TRANSFER INDICATOR SWITCH CONNECTOR 10.–1(3VZ–E) REMOVE EXHAUST PIPE, BRACKET AND CLAMP (a) Remove exhaust pipe clamp. (b) Remove exhaust pipe bracket from clutch housing. -
Page 49
MT1–18 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Removal of Transmission with Transfer 11.–2 (22R–E) REMOVE CLUTCH RELEASE CYLINDER, TUBE BRACKET Remove the mounting bolts and lay the cylinder alongside the engine. HINT: Do not disconnect the clutch line. 12. (3VZ–E) REMOVE THE FRONT DIFFERENTIAL SET BOLTS (a) Remove the three bolts. -
Page 50
MT1–19 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Removal of Transmission with Transfer 21. (22R–E/G58) REMOVE BREATHER HOSE Disconnect the breather hose from transfer upper cover and transmission control retainer. 22. REMOVE ENGINE REAR MOUNTING 23. (Regular Cab w/ Planetary Gear Type Transfer) REMOVE DYNAMIC DAMPER 24. -
Page 51
MT1–20 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Installation of Transmission with Transfer INSTALLATION OF TRANSMISSION WITH TRANSFER 1. INSTALL TRANSFER AND PROPELLER SHAFT UPPER DUST COVER TO TRANSMISSION WITH NEW GASKET (a) Shift the two shift fork shafts to the high–four posi– tion. (b) Apply MP grease to the adaptor oil seal. -
Page 52
MT1–21 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Installation of Transmission with Transfer 2. INSTALL ENGINE REAR MOUNTING Torque: 25 N–m (260 kgf–cm, 19 ft–lbf) 3. (Regular Cab w/ Planetary Gear Type Transfer) INSTALL DYNAMIC DAMPER Torque: 37 N–m (380 kgf–cm, 27 ft–lbf) 4. ( 22R–E/G 58) INSTALL BREATHER HOSE Connect the breather hose for transfer upper cover and transmission control retainer as shown. -
Page 53
MT1–22 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Installation of Transmission with Transfer 6.–2(22R–E) INSTALL TRANSMISSION BOLTS AND STIFFENER BOLTS Torque: (A) Transmission bolt 72 N–m (730 kgf–cm, 53 ft–lbf ) (B) Stiffener plate bolt 37 N–m (380 kgf–cm, 27 ft–Ibf) (C) Starter bolt 39 N–m (400 kgf–cm, 29 ft–Ibf) 7. -
Page 54
MT1–23 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Installation of Transmission with Transfer (d) Connect the exhaust pipe to the catalytic converter front side, and torque the bolts. Torque: 39 N . m (400 kgf–cm, 29 ft–lbf) 11.–2(22R–E) INSTALL EXHAUST PIPE, BRACKET AND CLAMP (a) Install the exhaust pipe to the manifold. -
Page 55
MT1–24 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Installation of Transmission with Transfer 14. CONNECT SPEEDOMETER CABLE, BACK–UP LIGHT SWITCH CONNECTOR AND TRANSFER INDICATOR SWITCH CONNECTOR 15. CONNECT PROPELLER SHAFT (See page PR–15) 16. FILL TRANSMISSION AND TRANSFER WITH OIL (Transmission oil) R150F (Engine) (3VZ–E) (22R–E) (22R–E) -
Page 56
MT1–25 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Installation of Transmission with Transfer 18.–2(W56) INSTALL TRANSFER SHIFT LEVER (a) Apply MP grease to the transfer shift lever. (b) Using pliers, install the shift lever and snap ring. 19. INSTALL TRANSMISSION SHIFT LEVER (a) Apply MP grease to the transmission shift lever. (b) Align the groove of the shift lever cap and the pin part of the case cover. -
Page 57
MT1–26 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Disassembly of Transmission (Components) DISASSEMBLY OF TRANSMISSION (G58 TRANSMISSION) Components… -
Page 58
MT1–27 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Disassembly of Transmission (Components) Components (Cont’d) -
Page 59
MT1–28 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Disassembly of Transmission (Components) Components (Cont’d) -
Page 60
MT1–29 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Disassembly of Transmission Disassembly of Transmission (See pages MT1–26 to 28) 1. REMOVE RELEASE FORK AND BEARING 2. REMOVE BACK–UP LIGHT SWITCH 3. REMOVE CLUTCH HOUSING FROM TRANSMISSION CASE Remove the nine bolts and clutch housing. 4. -
Page 61
MT1–30 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Disassembly of Transmission 7. REMOVE TRANSFER ADAPTOR (a) Using SST, remove the plug from the transfer adap– tor. SST 09923–00010 (b) Remove the shift lever housing set bolt. (c) Remove the shift lever shaft and housing. (d) Remove the eight bolts. -
Page 62
MT1–31 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Disassembly of Transmission 10. SEPARATE INTERMEDIATE PLATE FROM TRANSMISSION CASE (a) Stand the transmission as shown. (b) Using a plastic hammer, carefully tap off the trans– mission case. (c) Remove the transmission case from the intermedi– ate plate as shown. -
Page 63
MT1–32 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Disassembly of Transmission 13. REMOVE SHIFT FORK SHAFT SNAP RINGS Using two screwdrivers and a hammer drive out the three snap rings. 14. REMOVE SHIFT FORK SHAFT NO.5 (a) Using a pin punch and hammer, drive out the slotted spring pin. -
Page 64
MT1–33 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Disassembly of Transmission 16. REMOVE REVERSE SHIFT ARM, REVERSE SHIFT FORK AND SHIFT FORK SHAFT NO–3 (a) Using a magnetic finger–, remove the interlock pin from shift fork shaft No.3. (b) Using a pin punch and hammer, drive out the slotted spring pin. -
Page 65
MT1–34 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Disassembly of Transmission (b) Remove the shift fork No. 1 set bolt. (c) Remove the shift fork shaft No. 1. (d) Remove the interlock pin No. 1. (e) Remove the shift fork No. 2 set bolt. (f) Remove the shift fork No.1, No.2 and shift fork shaft No.2. -
Page 66
MT1–35 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Disassembly of Transmission (b) Using SST, remove the gear spline piece No. 5. SST 09213–60017 (09213–00020, 09213–00030, 09213–00060) (c) Remove the synchronizer ring, needle roller bearing and counter 5th gear. 20. REMOVE SPACER AND BALL (a) Remove the spacer. (b) Using a magnetic finger, remove the ball. -
Page 67
MT1–36 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Disassembly of Transmission 23. REMOVE REAR BEARING RETAINER Using a torx socket wrench, remove the four bolts. (Torx socket wrench T40 09042–00020) 24. REMOVE COUNTER GEAR (a) Using a snap ring expander, remove the counter gear rear bearing snap ring. (b) Using SST and 12 mm socket wrench, remove the counter gear rear bearing. -
Page 68
MT1–37 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Disassembly of Transmission (b) Remove the output shaft, from the intermediate plate by pulling on the output shaft and tapping on the intermediate plate with plastic hammer. 27. INSPECT BACK–UP LIGHT SWITCH Check that there is continuity between terminals as shown. -
Page 69
MT1–38 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Component Parts (Input Shaft Assembly) COMPONENT PARTS Input Shaft Assembly COMPONENTS INSPECTION OF INPUT SHAFT ASSEMBLY INSPECT SYNCHRONIZER RING (a) Turn the ring and push it into check braking action. (b) Using a feeler gauge, measure the clearance be– tween the synchronizer ring back and gear spline end. -
Page 70
MT1–39 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Component Parts (Input Shaft Assembly) (b) Using a press, remove the bearing. (c) Using SST and a press, install a new bearing. SST 09506–35010 (d) Select a snap ring that will allow minimum axial play. mm (in.) Thickness Mark (e) Using a snap ring expander, install the snap ring. -
Page 71
MT1–40 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Component Parts (Output Shaft Assembly Output Shaft Assembly COMPONENTS DISASSEMBLY OF OUTPUT SHAFT ASSEMBLY 1. REMOVE SLEEVE FROM OUTPUT SHAFT Using SST, remove the sleeve from the output shaft. SST 09950–20017… -
Page 72
MT1–41 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Component Parts (Output Shaft Assembly) 2. REMOVE FIFTH GEAR, REAR BEARING, FIRST GEAR, INNER RACE AND NEEDLE ROLLER BEARING (a) Using two screwdrivers and a hammer, tap out the snap ring. (b) Using a press, remove the 5th gear, rear bearing, 1st gear and inner race. -
Page 73
MT1–42 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Component Parts (Output Shaft Assembly 8. REMOVE HUB SLEEVE NO.2, SHIFTING KEYS AND SPRINGS FROM CLUTCH HUB NO.2 Using a screwdriver, remove the three shifting keys and springs from clutch hub No.2. -
Page 74
MT1–43 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Component Parts (Output Shaft Assembly INSPECTION OF OUTPUT SHAFT ASSEMBLY 1. INSPECT EACH GEAR THRUST CLEARANCE Using a feeler gauge, measure the thrust clearance of each gear. Standard clearance: 0.10 – 0.25 mm (0.0039 – 0.0098 in.) Maximum clearance: 0.25 mm (0.0098 in.) 2. -
Page 75
MT1–44 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Component Parts (Output Shaft Assembly) (d) Using a micrometer, measure the outer diameter of the inner race. Minimum diameter: 38.985 mm (1.5348 in.) If the outer diameter exceeds the minimum, replace the inner race. (e) Using a dial indicator, check the shaft runout. Maximum runout: 0.05 mm (0.0020 in.) If the runout exceeds the maximum, replace the output shaft. -
Page 76
MT1–45 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Component Parts (Output Shaft Assembly) ASSEMBLY OF OUTPUT SHAFT ASSEMBLY 1. INSTALL CLUTCH HUB NO.1 AND NO.2 INTO HUB SLEEVE HINT: Coat all of the sliding and rotating surface with gear oil before assembly. (a) Install the clutch hub and shifting keys to the hub sleeve. -
Page 77
MT1–46 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Component Parts (Output Shaft Assembly) 4. INSPECT THIRD GEAR THRUST CLEARANCE Using a feeler gauge, measure the 3rd gear thrust clear– ance. Standard clearance: 0.10 – 0.25 mm (0.0039 – 0.0098 in.) Maximum clearance: 0.25 mm (0.0098 in.) 5. -
Page 78
MT1–47 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Component Parts (Output Shaft Assembly (b) Apply gear oil to the needle roller bearing. (c) Assemble the 1st gear, synchronizer ring, needle roller bearing and bearing inner race. (d) Install the assembly on the output shaft with the synchronizer ring slots aligned with shifting keys. -
Page 79
MT1–48 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Component Parts (Output Shaft Assembly) 11. MEASURE FIRST GEAR THRUST CLEARANCE Using a feeler gauge, measure the 1 st gear thrust clearance. Standard clearance: 0.10 – 0.25 mm (0.0039 – 0.0098 in.) Maximum clearance: 0.25 mm (0.0098 in.) 12. -
Page 80
MT1–49 Component Parts (Counter Gear Assembly and Reverse Idler Gear) MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Counter Gear Assembly and Reverse Idler Gear COMPONENT DISASSEMBLY OF COUNTER GEAR ASSEMBLY REMOVE HUB SLEEVE NO.3 SHIFTING KEYS AND SPRINGS Using a screwdriver, remove the hub sleeve No.3, three shifting keys and two springs. -
Page 81
MT1–50 Component Parts (Counter Gear MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Assembly and Reverse Idler Gear) 2. INSPECT COUNTER GEAR Using a micrometer, measure the outer diameter of nee– dle roller bearing race. Standard clearance: 25.98 – 26.00 mm (1.0228 – 1.0236 in.) Maximum clearance: 25.86 mm (1.0181 in.) If the outer diameter exceeds the maximum, replace the counter gear. -
Page 82
MT1–51 Component Parts (Counter Gear Assembly and Reverse Idler Gear) MANUAL TRANSMISSION – (b) Using SST and a press, remove the bear- ing. SST 09950–00020 (c) Replace the side race. (d) Using a socket wrench and press, install the bear– ing, side race and innerrece. -
Page 83
MT1–52 Component Parts (Counter Gear MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Assembly and Reverse Idler Gear) INSPECTION OF REVERSE IDLER GEAR 1. INSPECT REVERSE IDLER GEAR OIL CLEARANCE Using a dial indicator measure reverse idler gear oil clear– ance . Standard clearance: 0.04 – 0.08 mm (0.0016 –… -
Page 84
MT1–53 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Component Parts (Transfer Adaptor) Transfer Adaptor COMPONENTS REPLACEMENT OF OIL SEAL IF NECESSARY, REPLACE TRANSFER ADAPTOR OIL SEAL (a) Using a screwdriver, pry out the oil seal. (b) Using SST and a hammer, drive in new oil seal. SST 09325–12010 INSPECTION AND REPLACEMENT OF REVERSE RESTRICT PIN… -
Page 85
MT1–54 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Component Parts (Transfer Adaptor) (b) Using a pin punch and hammer, drive out the slotted spring pin. (c) Remove the reverse restrict pin. 2. INSPECTION OF REVERSE RESTRICT PIN Turn and push the reverse restrict pin by hand while ap– plying force in axial direction. -
Page 86
MT1–55 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Component Parts (Front Bearing Retainer) Front Bearing Retainer COMPONENTS REPLACEMENT OF OIL SEAL IF NECESSARY, REPLACE FRONT BEARING RETAINER SEAL (a) Using a screwdriver, pry out the oil seal. (b) Using SST and a press, install a new oil seal. SST 09223–50010 Oil seal depth: 12.2 –… -
Page 87
MT1–56 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Assembly of Transmission ASSEMBLY OF TRANSMISSION (See pages MT1–26 to 28) HINT: Coat all of the sliding and rotating surface with gear oil before assembly. 1. INSTALL OUTPUT SHAFT TO INTERMEDIATE PLATE (a) Install the output shaft into the intermediate plate by pushing on the output shaft and tapping on the in–… -
Page 88
MT1–57 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Assembly of Transmission (b) Install the counter gear into the intermediate plate while holding the counter gear and install the counter break bearing with SST. SST 09316–60010 4. INSTALL REAR BEARING RETAINER Using a torx socket wrench, install and torque the screws. -
Page 89
MT1–58 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Assembly of Transmission 7. INSTALL BALL AND SPACER 8. INSTALL COUNTER FIFTH GEAR WITH HUB SLEEVE NO.3 ASSEMBLY AND NEEDLE ROLLER BEARINGS (a) Apply gear oil to the needle roller bearings. (b) Install the counter 5th gear with hub sleeve No.3 and needle roller bearings. -
Page 90
MT1–59 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Assembly of Transmission 10. INSTALL SNAP RING (a) Select snap ring that will allow minimum axial play. Thickness mm (in.) Mark (b) Using a brass bar and hammer, install the snap ring. 11. MEASURE COUNTER FIFTH GEAR THRUST CLEAR- ANCE Using a feeler gauge, measure the counter 5th gear thrust clearance. -
Page 91
MT1–60 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Assembly of Transmission 13. INSTALL SHIFT FORK SHAFT NO. 1 AND SHIFT FORK NO. 1 (a) Apply MP grease to the interlock pin No. 2 and install them into the shift fork shaft No. 1. (b) Using a magnetic finger, install the interlock pin No–1 to intermediate plate. -
Page 92
MT1–61 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Assembly of Transmission (d) Using a magnetic finger, install the interlock pin No. 1 to the intermediate plate. (e) Install the shift fork shaft No.3 through the interme– diate and reverse shift fork. (f) Using a pin punch and hammer, drive in the slotted spring pin. -
Page 93
MT1–62 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Assembly of Transmission (g) Using a pin punch and hammer, drive in the slotted spring pin to the shift fork RIo.3. (h) Install the shift fork shaft No.5 through the reverse shift head and intermediate plate. (i) Using a pin punch and hammer, drive in the slotted spring pin to the reverse shift head. -
Page 94
MT1–63 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Assembly of Transmission 17. INSTALL LOCKING BALLS, SPRINGS AND SCREW PLUGS (a) Install the four locking balls and four springs. HINT: Install the short spring into the bottom of the in– termediate plate. (b) Apply liquid sealer to the plug threads. Sealant: Part No. -
Page 95
MT1–64 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Assembly of Transmission 20. INSTALL FRONT BEARING RETAINER (a) Using a snap ring expander, install the two snap rings to input shaft bearing and counter gear front bearing. (b) Install the bearing retainer with a new gasket. (c) Apply liquid sealer to the bolt threads. -
Page 96
MT1–65 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Assembly of Transmission (e) Install the shift lever shaft to the transfer adaptor and shift lever housing. (f) Install and torque the shift lever housing bolt. Torque: 38 N–m (390 kgf–cm, 28 ft–lbf) (g) Using SST, install and torque the plug. SST 09923–00010 Torque: 37 N–m (380 kgf–cm, 27 ft–lbf) 22. -
Page 97
MT1–66 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Assembly of. Transmission 24. INSTALL RESTRICT PINS (a) Install the black pin on the reverse gear/5th gear side. (b) Install another pin and torque the pins. Torque: 27 N–m (280 kgf–cm, 20 ft–lbf) 25. INSTALL TRANSMISSION SHIFT LEVER CONTROL RETAINER (a) Install shift lever control retainer and new gasket. -
Page 98
MT1–67 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Disassembly of Transmission (Components) DISASSEMBLY OF TRANSMISSION (R150 AND R 150F TRANSMISSIONS) Components… -
Page 99
MT1–68 Disassembly of Transmission (Disassembly of Transmission) MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Disassembly of Transmission (See pages MT1–67, 68) 1. REMOVE RELEASE FORK AND BEARING 2. REMOVE BACK–UP LIGHT SWITCH, SPEEDOMETER DRIVEN GEAR (2WD). SHIFT LEVER RETAINER AND RESTRICT PINS 3. REMOVE CLUTCH HOUSING FROM TRANSMISSION CASE 4. -
Page 100
MT1–69 Disassembly of Transmission (Disassembly of Transmission) MANUAL TRANSMISSION – 5.–1 (2WD) REMOVE EXTENSION HOUSING (a) Remove the ten bolts. (b) Remove the shift lever housing set bolt. (c) Using a plastic hammer, tap the extension housing and remove the shift lever housing and shift and select lever. -
Page 101
MT1–70 Disassembly of Transmission MANUAL TRANSMISSION – (Disassembly of Transmission) 7. REMOVE BEARING SNAP RINGS Using a snap ring expander, remove the two snap rings. 8. SEPARATE INTERMEDIATE PLATE FROM TRANSMIS– SION CASE (a) Using a brass bar and hammer, carefully tap off the transmission case. -
Page 102
MT1–71 Disassembly of Transmission MANUAL TRANSMISSION – (Disassembly of Transmission) (b) Using a magnetic finger, remove the four springs and balls. 12. REMOVE SHIFT FORK SET BOLTS Remove the three bolts. 13. REMOVE SNAP RINGS Using two screwdrivers and a hammer, tap out the three snap rings. -
Page 103
MT1–72 Disassembly of Transmission MANUAL TRANSMISSION – (Disassembly of Transmission) 16. REMOVE SHIFT FORK SHAFT NO.2 AND SHIFT FORK (a) Pull out the shift fork shaft No. 2 from the intermedi– ate plate. (b) Remove the shift fork No.2. (c) Using a magnetic finger, remove the interlock pin from the intermediate plate. -
Page 104
MT1–73 Disassembly of Transmission (Disassembly of Transmission) MANUAL TRANSMISSION – 21. REMOVE REVERSE SHIFT ARM BRACKET Remove the two bolts and the reverse shift arm bracket. 22.–1 (2WD) REMOVE SPEEDOMETER DRIVE GEAR (a) Using two screwdrivers and a hammer, tap out the rear snap ring. -
Page 105
MT1–74 Disassembly of Transmission MANUAL TRANSMISSION – (Disassembly of Transmission) 24. REMOVE SPACER 25. MEASURE COUNTER FIFTH GEAR THRUST CLEAR- ANCE Using a feeler gauge, measure the counter 5th gear thrust clearance. Standard clearance: 0.10 – 0.35 mm (0.0039 – 0.0138 in.) Maximum clearance: 0.40 mm (0.0157 in.) 26. -
Page 106
MT1–75 Disassembly of Transmission (Disassembly of Transmission) MANUAL TRANSMISSION – 27. REMOVE THE SHIFTING KEYS AND SPRINGS FROM FIFTH GEAR AND HUB SLEEVE NO.3 Using a screwdriver, remove the three shifting keys and two rings. 28. REMOVE THRUST WASHER AND BALL 29. -
Page 107
MT1–76 Disassembly of Transmission MANUAL TRANSMISSION – (Disassembly of Transmission) 32. REMOVE OUTPUT SHAFT, COUNTER GEAR AND INPUT SHAFT AS A UNIT FROM INTERMEDIATE PLATE (a) Remove the output shaft, counter gear and input shaft as a unit from the intermediate plate by pulling on the counter gear and tapping on the intermediate plate with a plastic hammer. -
Page 108
MT1–78 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Component Parts (Input Shaft Assembly) COMPONENT PARTS Input Shaft Assembly COMPONENTS INSPECTION OF INPUT SHAFT INSPECT SYNCHRONIZER RING (a) Turn the ring and push it in to check the breaking ac– tion. (b) Using a feeler gauge, measure the clearance be– tween the synchronizer ring back and the gear spline end. -
Page 109
MT1–79 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Component Parts (Input Shaft Assembly (b) Using a press, remove the bearing. (c) Using SST and a press, install a new bearing. SST 09506–35010 (d) Select a snap ring that will allow minimum axial play and install it on the shaft. Thickness mm (in.) Mark… -
Page 110
MT1–80 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Component Parts (Output Shaft Assembly) Output Shaft Assembly COMPONENTS DISASSEMBLY OF OUTPUT SHAFT ASSEMBLY 1. REMOVE FIFTH GEAR, CENTER BEARING AND FIRST GEAR ASSEMBLY (a) Using a press, remove the 5th gear, center bearing, thrust washer and 1 st gear. (b) Remove the synchronizer ring. -
Page 111
MT1–81 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Component Parts (Output Shaft Assembly) 2. REMOVE HUB SLEEVE NO.1 ASSEMBLY AND SECOND GEAR ASSEMBLY (a) Using two screwdrivers and a hammer, tap out the snap ring. (b) Using a press, remove the hub sleeve No. 1, syn– chronizer ring and 2nd gear. -
Page 112
MT1–82 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Component Parts (Output Shaft Assembly) INSPECT OF OUTPUT SHAFT ASSEMBLY 1. INSPECT EACH GEAR THRUST CLEARANCE (a) Using a feeler gauge, measure the thrust clearance of 1 st gear and 3rd gear. (b) Using a dial indicator, measure the thrust clearance of 2nd gear. -
Page 113
MT1–83 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Component Parts (Output Shaft Assembly) (c) Using a dial indicator, check the shaft runout. Maximum runout: 0.06 mm (0.0024 in.) If the runout exceeds the maximum, replace the output shaft. 4. INSPECT SYNCHRONIZER RINGS (a) Turn the ring and push it in to check the braking ac– tion. -
Page 114
MT1–84 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Component Parts (Output Shaft Assembly) ASSEMBLY OF OUTPUT SHAFT ASSEMBLY 1. INSERT CLUTCH HUB NO. 1 AND NO.2 INTO HUB SLEEVE (a) Install the clutch hub and shifting keys to the hub sleeve. (b) Install the shifting key springs under the shifting keys. -
Page 115
MT1–85 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Component Parts (Output Shaft Assembly) 4. INSPECT THIRD GEAR THRUST CLEARANCE Using a feeler gauge, measure the 3rd gear thrust clear– ance. Standard clearance: 0.10 – 0.25 mm (0.0039 – 0.0098 in.) 5. INSTALL SECOND GEAR AND HUB SLEEVE NO. 1 (a) Apply gear oil to the shaft and needle roller bearing. -
Page 116
MT1–86 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Component Parts (Output Shaft Assembly) 7. INSTALL SPACER AND FIRST GEAR ASSEMBLY (a) Install the spacer on the output shaft. (b) Apply gear oil to the needle roller bearing. (c) Assemble the 1 st gear, synchronizer ring and needle roller bearing. -
Page 117
MT1–87 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Component Parts (Output Shaft Assembly) 11. INSPECT SECOND GEAR THRUST CLEARANCE Using a dial indicator, measure the 2nd gear thrust clear– ance. Standard clearance: 2nd gear 0.10 – 0.25 mm (0.0039 – 0.0098 in. ) 12. INSTALL FIFTH GEAR Using SST and a press, install the 5th gear. -
Page 118
MT1–88 Component Parts (Counter Gear Assembly and Reverse Idler Gear) MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Counter Gear Assembly and Reverse Idler Gear COMPONENTS INSPECTION OF COUNTER GEAR 1. INSPECT FIFTH GEAR OIL CLEARANCE (a) Install the spacer, counter 5th gear and needle roller bearings. -
Page 119
MT1–89 Component Parts (Counter Gear Assembly MANUAL TRANSMISSION – and Reverse Idler Gear) 3. INSPECT COUNTER GEAR Using a micrometer, measure the outer diameter of the counter gear journal. Minimum diameter: 27.860 mm (1.0968 in.) If the outer diameter exceeds the minimum, replace the counter gear. -
Page 120
MT1–90 Component Parts (Counter Gear Assembly MANUAL TRANSMISSION – and Reverse Idler Gear) INSPECTION OF REVERSE IDLER GEAR 1. INSPECT CLEARANCE OF REVERSE IDLER GEAR AND SHIFT ARM SHOE Using a feeler gauge, measure the clearance between the reverse idler gear and shift arm shoe. Standard clearance: 0.05 –… -
Page 121
MT1–91 Component Parts MANUAL TRANSMISSION – (Extension Housing and Transfer Adaptor) Extension Housing and Transfer Adaptor COMPONENTS REPLACEMENT OF OIL SEAL 1. (2WD) IF NECESSARY, REPLACE EXTENSION HOUSING OIL SEAL (a) Remove the dust deflector. (b) Using a screwdriver, pry out the oil seal. (c) Using SST and a hammer, drive in a new oil seal. -
Page 122
MT1–92 Component Parts MANUAL TRANSMISSION – (Extension Housing and Transfer Adaptor) 2. (4WD) IF NECESSARY, REPLACE TRANSFER ADAPTOR OIL SEAL (a) Using a screwdriver, pry out the oil seal. (b) Using SST and a hammer, drive in a new oil seal. SST 09325–12010 INSPECTION AND REPLACEMENT OF REVERSE RESTRICT PIN… -
Page 123
MT1–93 Component Parts MANUAL TRANSMISSION – (Extension Housing and Transfer Adaptor) 2. INSPECTION OF REVERSE RESTRICT PIN Turn and push the reverse restrict pin by hand while ap– plying force in axial direction. 3. INSTALL THE REVERSE RESTRICT PIN (a) Install the reverse restrict pin to the extension hous– ing or transfer adaptor. -
Page 124
MT1–94 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Component Parts (Front Bearing Retainer) Front Bearing Retainer COMPONENTS REPLACEMENT OF OIL SEAL IF NECESSARY, REPLACE FRONT BEARING RETAINER SEAL (a) Using a screwdriver, pry out the oil seal. (b) Using SST and a hammer, drive in a new oil seal. SST 09608–35014 (09608–06020, 09608–06090) Drive in depth: 11.2 –… -
Page 125
MT1–95 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Assembly of Transmission ASSEMBLY OF TRANSMISSION (See pages MT1–67, 68) 1. INSTALL OUTPUT SHAFT TO INTERMEDIATE PLATE (a) Install the output shaft into the intermediate plate by pushing on the output shaft and tapping on the in– termediate plate. -
Page 126
MT1–96 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Assembly of Transmission 5. INSTALL REVERSE SHIFT ARM TO REVERSE SHIFT ARM BRACKET Install the reverse shift arm to the pivot of the reverse shift arm bracket. 6. INSTALL REVERSE IDLER GEAR AND SHAFT Align the reverse shift arm shoe to the reverse idler gear groove and insert the reverse idler gear shaft to the inter–… -
Page 127
MT1–97 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Assembly of Transmission 10. INSTALL SYNCHRONIZER RING AND GEAR SPLINE PIECE NO.5 (a) Install the synchronizer ring on gear spline piece No. 5. (b) Using SST and a hammer, drive in gear spline piece No. 5 with the synchronizer ring slots aligned with the shifting keys. -
Page 128
MT1–98 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Assembly of Transmission 13. INSTALL SPACER 14. INSTALL OUTPUT SHAFT REAR BEARING Using SST and a hammer, drive in the rear bearing. SST (2WD) 09309–35010 (4WD) 09316–60010 (09316–00010, 09316–00070) 15. INSTALL SNAP RING (a) Select a snap ring that will allow minimum axial play. -
Page 129
MT1–99 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Assembly of Transmission 16.–1(2WD) INSTALL SPEEDOMETER DRIVE GEAR (a) Using a screwdriver and hammer, install the front snap ring. (b) Install the ball and drive gear. (c) Using a screwdriver and hammer, install the rear snap ring. 16.–2(4WD) INSTALL SLEEVE TO OUTPUT SHAFT Using a plastic hammer, drive in the sleeve onto the out–… -
Page 130
MT1–100 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Assembly of Transmission (c) Place the shift fork No.1 into the groove of hub sleeve No. 1. (d) Install the fork shaft No.3 to the reverse shift fork and shift head through the intermediate plate. 19. INSTALL SHIFT FORK SHAFT NO. 1 (a) Using a magnetic finger and screwdriver, install the interlock pin into the intermediate plate. -
Page 131
MT1–101 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Assembly of Transmission (b) Place the shift fork No.2 into the groove of hub sleeve No.2. (c) Install fork shaft No.2 to shift fork No.1 and No.2 through the intermediate plate. 21. INSTALL SHIFT FORK SHAFT NO.5 Install the shift fork shaft No.5 to reverse shift head through the intermediate plate. -
Page 132
MT1–102 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Assembly of Transmission 25. INSTALL SET BOLTS Install and torque the three bolts. Torque: 20 N–m (200 kgf–cm, 14 ft–lbf) 26. INSTALL LOCKING BALLS, SPRINGS AND SCREW PLUGS (a) Apply liquid sealer to the plug threads. Sealant: Part No. -
Page 133
MT1–103 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Assembly of Transmission (c) Align the each bearing outer race, each fork shaft end and reverse idler gear shaft end with the case in– stallation holes, and install the case. If necessary, tap on the case with a plastic hammer. 30. -
Page 134
MT1–104 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Assembly of Transmission (c) Install the shift and select lever into the extension housing. (d) Connect the shift and select lever to the fork shaft and put in the shift lever housing. (e) Align the fork shaft No.5 to the extension housing installation hole and push in the extension hous- ing. -
Page 135
MT1–105 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Assembly of Transmission (f) Install and torque the bolts. Torque: 37 N–m (380 kgf–cm, 27 ft–lbf ) (g) Install and torque the shift lever housing bolt. Torque: 38 N–m (390 kgf–cm, 28 ft–Ibf) (h) Apply liquid sealer to the plug threads. Sealant: Part No. -
Page 136
MT1–106 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Assembly of Transmission 34. AFTER INSTALLING EXTENSION HOUSING OR TRANSFER ADAPTOR CHECK FOLLOWING ITEMS (a) Check to see that the input and output shafts rotate smoothly. (b) Check to the that shifting can be made smoothly to all positions. -
Page 137
MT1–107 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – Assembly of Transmission 37.–1 (2WD) INSTALL SHIFT LEVER RETAINER Torque: 16 N–m (160 kgf –cm, 12 ft–lbf ) 37.–2(4WD) INSTALL SHIFT LEVER RETAINERS WITH NEW GASKETS (a) Apply liquid sealer to the bolt threads. Sealant: Part No, 08833–00080, THREE BOND 1344, LOCTITE 242 or equivalent (b) Install the torque the four bolts. -
Page 138
MT2–1 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – W55 AND W56 MANUAL TRANSMISSION… -
Page 139
MT2–2 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – DESCRIPTION DESCRIPTION PRECAUTIONS When working with FIPG material, you must be observe the following. • Using a razor blade and gasket scraper, remove all the old packing (FlPG) material from the gasket surfaces. • Thoroughly clean all components to remove all the loose material. •… -
Page 140
MT2–3 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – OPERATION OPERATION • The illustrations below show the engagements of transmission gears. -
Page 141
MT2–4 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – PREPARATION PREPARATION SST (SPECIAL SERVICE TOOLS) 09213–36020 Timing Gear Remover 09308–00010 Oil Seal Puller 09308–10010 Oil Seal Puller 09312–20011 Transmission Gear Remover & Replacer (09313–00010) Reverse Gear Remover (09313–00030) Rear Bearing Replacer (09313–00040) Plate wAw (09313–00050) Plate wBw 09316–60010 Transmission &… -
Page 142
MT2–5 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – PREPARATION (09608–00020) Remover & Replacer Handle (09608–00050) Drive Pinion Front Bearing Cup Replacer 09608–20012 Front Hub & Drive Pinion Bearing Tool Set (09608–00080) Replacer (09608–03020) Handle 09608–35014 Axle Hub & Drive Pinion Bearing Tool Set (09608–06020) Handle (09608–06090) Front Hub Outer &… -
Page 143: Recommended Tools
MT2–6 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – PREPARATION RECOMMENDED TOOLS 09031–00030 Pin Punch 09905–00012 Snap Ring No. 1 Expander 09042–00020 Torx Socket t40 EQUIPMENT Dial indicator or dial indicator with magnetic base Torque wrench LUBRICANT Classification Capacity Item API GL–4 2.6 liters (2.7 US qts, 2.3 Imp.qts) Manual transmission SAE 75W–90 or 80W–90 SSM (SPECIAL SERVICE MATERIALS)
-
Page 144
MT2–7 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – TROUBLESHOOTING TROUBLESHOOTING MT009–O1 You will find the troubles using the table well shown in this table, each number shows the priority of causes in troubles. Check each part in order. If necessary, replace these parts. See page Parts Name Trouble… -
Page 145
MT2–8 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – ASSEMBLY REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION ASSEMBLY REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION TRANSMISSION REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION… -
Page 146
MT2–9 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – ASSEMBLY REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION TRANSMISSION WITH TRANSFER REMOVAL AND INSTALLTION… -
Page 147
MT2–10 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COMPONENT PARTS REMOVAL COMPONENT PARTS REMOVAL COMPONENTS… -
Page 148
MT2–11 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COMPONENT PARTS REMOVAL… -
Page 149
MT2–12 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COMPONENT PARTS REMOVAL BASIC SUBASSEMBLY SEPARATION 1. REMOVE BACK – UP LIGHT SWITCH, VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR (2WD) AND ENGINE REAR MOU– NTING 2. REMOVE CLUTCH HOUSING FROM TRANSMIS– SION CASE Remove the nine bolts and clutch housing from the transmission case. -
Page 150
MT2–13 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COMPONENT PARTS REMOVAL 4. (4WD) REMOVE TRANSFER ADAPTOR (a) Remove the six bolts, shift lever retainer and gasket. (b) Remove the select return spring from the shift lever retainer. (c) Remove the two restrict pins and gaskets. (d) Remove the shift lever housing set bolt. -
Page 151
MT2–14 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COMPONENT PARTS REMOVAL (b) Using a snap ring pliers, remove the two bearing snap rings. 6. SEPARATE INTERMEDIATE PLATE FROM TRANS– MISSION CASE (a) Using a plastic hammer, carefully tap the transmission case. (b) Pull the transmission case from the intermediate plate. -
Page 152
MT2–15 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COMPONENT PARTS REMOVAL 10. REMOVE LOCKING BALL AND SPRING (a) Using a hexagon wrench, remove the four plugs. (b) Using a magnetic finger, remove the three springs and balls. 11. REMOVE SHIFT FORKS, SHIFT FORK SHAFTS AND REVERSE IDLER GEAR (a) Remove the No. -
Page 153
MT2–16 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COMPONENT PARTS REMOVAL (d) Remove the reverse idler gear and shaft. (e) Remove the No.1 shift fork and shaft. (f) Using a magnetic finger, remove the No–1 and No.2 interlock pins. (g) Using two screwdrivers and a hammer, tap out the snap ring from the No.2 fork shaft. -
Page 154
MT2–17 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COMPONENT PARTS REMOVAL (i) Using a magnetic finger, remove the No.3 interlock pin. (j) Using two screwdrivers and a hammer, tap out the snap ring from the No.3 fork shaft. (k) Using a pin punch and hammer, drive out the slotted spring pin from the No.3 shift fork. -
Page 155
MT2–18 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COMPONENT PARTS REMOVAL (n) Pull out the No.4 shift fork shaft. (o) Remove the interlock pin. (p) Remove the No.3 shift fork, fork shaft and reverse shift arm with the pin. 12. (2WD) REMOVE SPEED SENSOR DRIVE GEAR Pry out both ends of the clip and remove the drive gear. -
Page 156
MT2–19 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COMPONENT PARTS REMOVAL (b) Using SST, remove the rear bearing, spacer, 5th gear and bearing. SST 09213–36020 NOTICE: Be careful not to catch the output shaft rear bearing roller on the counter 5th gear. (c) Remove the spacer. 15. -
Page 157
MT2–20 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COMPONENT PARTS REMOVAL 17. REMOVE OUTPUT SHAFT REAR BEARING AND FIFTH GEAR (a) Using two screwdrivers and a hammer, tap out the snap ring. (b) Using SST, remove the rear bearing and 5th gear. SST 09312–20011 (09313–00030, 09313–00040, 09313–00050) 18. -
Page 158
MT2–21 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COMPONENT PARTS REMOVAL (b) Using a snap ring expander, remove the snap rings. 20. REMOVE OUTPUT SHAFT AND COUNTER GEAR AS A UNIT FROM INTERMEDIATE PLATE (a) Remove the output shaft, input shaft and counter gear as a unit from the intermediate plate by pulling on the counter gear and tapping on the intermediated plate with a plastic hammer. -
Page 159
MT2–22 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – INPUT SHAFT INPUT SHAFT COMPONENTS INPUT SHAFT INSPECTION INSPECT SYNCHRONIZER RING (a) Check for wear or damage. (b) Check the braking effect of the synchronizer ring. Turn the synchronizer ring in one direction while pushing it to the gear cone and check that the ring is locked. -
Page 160
MT2–23 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – INPUT SHAFT HINT: • When replacing either a synchronizer ring or gear, apply a small amount of fine compound between the synchronizer ring and gear cone. Lightly rub the synchronizer ring and gear cone together. • When replacing both the synchronizer ring and gear, there is no need to apply any compound or to rub them together. -
Page 161
MT2–24 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – INPUT SHAFT (d) Select a snap ring that will allow minimum axial play. Thickness m m (in.) Mark (e) Using a snap ring expander, install the snap ring. -
Page 162
MT2–25 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – OUTPUT SHAFT OUTPUT SHAFT COMPONENTS OUTPUT SHAFT DISASSEMBLY 1. INSPECT EACH GEAR THRUST CLEARANCE Using a feeler gauge, measure the thrust clearance of each gear. Standard clearance: 0.10–0.25 mm (0.0039–0.0098 in.) Maximum clearance: 0.30 mm (0.0118 in.) -
Page 163
MT2–26 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – OUTPUT SHAFT 2. INSPECT EACH GEAR OIL CLEARANCE Using a dial indicator, measure the oil clearance of each gear. Standard clearance: 1 st and 2nd gear 0.009–0.060 m m (0.0004–0.0024 in.) 3rd gear 0.015–0.066 mm (0.0006–0.0026 in.) Maximum clearance: 1st and 2nd gear 0.15 mm (0.0059 in.) -
Page 164
MT2–27 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – OUTPUT SHAFT 6. REMOVE NO.1 HUB SLEEVE, SHIFTING KEYS AND SPRINGS FROM CLUTCH HUB NO.1 (a) Remove the No. 1 clutch hub from the No. 1 hub sleeve. (b) Push the shifting key spring with screwdriver, remove the three shifting keys and key springs. -
Page 165
MT2–28 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – OUTPUT SHAFT (b) Push the shifting key spring with screwdriver, remove the three shifting keys and key springs. OUTPUT SHAFT COMPONENT PARTS INSPECTION 1. INSPECT SYNCHRONIZER RINGS (a) Check for wear or damage. (b) Check the braking effect of the synchronizer ring. Turn the synchronizer ring in one direction while pushing it to the gear cone and check that the ring is locked. -
Page 166
MT2–29 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – OUTPUT SHAFT 3. INSPECT OUTPUT SHAFT AND INNER RACE (a) Using vernier calipers, measure the output shaft flange thickness. Minimum thickness: 5.60 mm (0.2204 in.) If the thickness exceeds the minimum, replace the output shaft. (b) Using vernier calipers, measure the inner race flange thickness. -
Page 167
MT2–30 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – OUTPUT SHAFT OUTPUT SHAFT ASSEMBLY HINT: Coat all of the sliding and rotating surface with gear oil before assembly. 1. INSTALL NO.1 AND NO.2 CLUTCH HUB INTO HUB SLEEVE (a) Install the three shifting key springs to the clutch hub. (b) While pushing the shifting key spring with screw–… -
Page 168
MT2–31 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – OUTPUT SHAFT 3. INSTALL SNAP RING (a) Select a snap ring that will allow minimum axial play. Thickness mm (in.) Mark (b) Using a snap ring expander, install the snap ring. 4. INSPECT THIRD GEAR THRUST CLEARANCE Using a feeler gauge, measure the 3rd gear thrust clearance. -
Page 169
MT2–32 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – OUTPUT SHAFT 6. INSPECT SECOND GEAR THRUST CLEARANCE Using a feeler gauge, measure the 2nd gear thrust clearance. Standard clearance: 0.10–0.25 mm (0.0039–0.0098 in.) 7. INSTALL LOCKING BALL AND FIRST GEAR AS– SEMBLY (a) Install the locking ball in the shaft. (b) Apply gear oil to the bearing. -
Page 170
MT2–33 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COUNTER GEAR AND REVERSE IDLER GEAR COUNTER GEAR AND REVERSE IDLER GEAR COMPONENTS COUNTER GEAR COMPONENT PARTS DISASSEMBLY 1. REMOVE NO.3 HUB SLEEVE, SHIFTING KEYS AND SPRINGS FROM SYNCHRONIZER RING (a) Remove the synchronizer ring assembly from No.3 hub sleeve. -
Page 171
MT2–34 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COUNTER GEAR AND REVERSE IDLER GEAR (c) Remove the reverse synchronizer ring and 5th syn– chronizer ring. (d) Turn the reverse synchronizer pull ring, separate pull ring and corn ring. (e) While pushing the shifting key spring to out slide with two screwdrivers, remove the shifting keys and key springs, from remove synchronizer ring. -
Page 172
MT2–35 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COUNTER GEAR AND REVERSE IDLER GEAR 2. INSPECT COUNTER GEAR Using a micrometer, measure the outer diameter of the counter shaft journal. Minimum diameter: Part A 26.975 mm (1.0620 in.) Part B 29.95 mm (1.1791 in.) 3. -
Page 173
MT2–36 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COUNTER GEAR AND REVERSE IDLER GEAR 6. INSPECT CLEARANCE OF SHIFT FORKS AND HUB SLEEVES Using a feeler gauge, measure the clearance between the hub sleeve and shift fork. Maximum clearance: 1.0 mm (0.039 in.) If the clearance exceeds the maximum, replace the shift fork or hub sleeve. -
Page 174
MT2–37 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COUNTER GEAR AND REVERSE IDLER GEAR (f) Select a snap ring that will allow minimum axial play. Thickness mm (in.) Mark (g) Using a snap ring expander, install the snap ring. 2. IF NECESSARY, REPLACE COUNTER GEAR CENTER BEARING (a) Remove the bearing from the counter gear. -
Page 175
MT2–38 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COUNTER GEAR AND REVERSE IDLER GEAR (b) Using a screwdriver, push the three key springs into the synchronizer ring spring gear. (c) Install the synchronizer corn ring to reverse synchro– nizer pull ring. (d) Install the 5th synchronizer ring. (e) Install the reverse synchronizer ring. -
Page 176
MT2–39 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – FRONT BEARING RETAINER FRONT BEARING RETAINER COMPONENT OIL SEAL REPLACEMENT IF NECESSARY, REPLACE FRONT BEARING RE– TAINER OIL SEAL (a) Using a screwdriver, pry out the oil seal. (b) Using SST and a press, install a new oil seal. SST 09608–20012 (09608–03020, 09608–00080) Drive in depth: 11.4–12.0 mm (0.449–0.472 in.) from retainer. -
Page 177
MT2–40 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – EXTENSION HOUSING AND TRANSFER ADAPTOR EXTENSION HOUSING AND TRANSFER ADAPTOR COMPONENT… -
Page 178
MT2–41 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – EXTENSION HOUSING AND TRANSFER ADAPTOR MT0t1–01 REVERSE RESTRICT PIN REPLACEMENT 1. REMOVE REVERSE RESTRICT PIN (a) Using a hexagon wrench, remove the screw plug. (b) Using a pin punch and hammer, drive out the slotted spring pin. (c) Pull off the lever housing and slide out the shaft. -
Page 179
MT2–42 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – EXTENSION HOUSING AND TRANSFER ADAPTOR (c) Apply liquid sealer to the plug. Sealant: Part No. 08833–00080, THREE BOND 7344, LOC– TITE 242 or equivalent (d) install and torque the screw plug. Torque: 25 N–m (250 kgf–cm, 18 ft–lbf) BEARING REPLACEMENT IF NECESSARY, REPLACE REAR BEARING OUT REAR RACE… -
Page 180
MT2–43 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – EXTENSION HOUSING AND TRANSFER ADAPTOR (d) Using a screwdriver, install the snap ring. OIL SEAL REPLACEMENT (2WD) IF NECESSARY, REPLACE EXTENSION HOUSING OIL SEAL (a) Using SST, remove the oil seal. SST 09308–00010 or 09308–10010 (w/ output shaft installed) (b) Using SST, drive in a new oil seal. -
Page 181
MT2–44 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COMPONENT PARTS INSTALLATION COMPONENT PARTS INSTALLATION BASIC SUBASSEMBLY REASSEMBLY HINT: Coat all of the sliding and rotating surface with gear oil before assembly. 1. INSTALL OUTPUT SHAFT TO INTERMEDIATE PLATE (a) Before installing the output shaft, use SST to remove the counter gear center bearing outer race. -
Page 182
MT2–45 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COMPONENT PARTS INSTALLATION 3. INSTALL BEARING RETAINER (a) Using a snap ring expander, install the bearing snap ring. HINT: Be sure the snap ring is flush with the inter– mediate plate surface. (b) Using a torx socket wrench, install and torque the screws. -
Page 183
MT2–46 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COMPONENT PARTS INSTALLATION 6. INSTALL FIFTH GEAR AND OUTPUT SHAFT REAR BEARING Using SST, install the 5th gear and rear bearing. SST 09312–20011 (09313–00010, 09313–00030, 09313–00040, 09313–00050) 7. INSTALL SNAP RING (a) Select a snap ring that will allow minimum axial play. Thickness mm (in.) Mark (b) Using a screwdriver and hammer, tap in the snap ring. -
Page 184
MT2–47 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COMPONENT PARTS INSTALLATION 10. INSTALL SNAP RING (a) Select a snap ring that will allow minimum axial play. Thickness mm (in.) Mark (b) Using a screwdriver and hammer, tap in the snap ring. 11. INSTALL NO.3 HUB SLEEVE ASSEMBLY (a) Check for reverse synchronizer pull ring position. -
Page 185
MT2–48 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COMPONENT PARTS INSTALLATION 13. INSTALL SPACER AND BEARING (a) Install the spacer. (b) Using a socket wrench and hammer, drive in the bearing. HINT: When driving in the bearing, support the cou– nter shaft in front with a 3–5 Ib hammer or equiva– lent. -
Page 186
MT2–49 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COMPONENT PARTS INSTALLATION 17. INSTALL SHIFT FORKS, SHIFT FORK SHAFTS AND REVERSE IDLER GEAR (a) Install the reverse idler gear and shaft. (b) Install the No.3 shift fork, No.3 fork shaft and reverse shift arm. Coat the pin with MP grease and insert it into the •… -
Page 187
MT2–50 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COMPONENT PARTS INSTALLATION (d) Install the ball and spring. (e) Apply sealant to the plug. Sealant: Part No.08833–00080, THREE BOND 1344, LOC– TITE 242 or equivalent (f) Using a hexagon wrench, install and torque the plug. Torque: 25 N–m (250 kgf–cm, 18 ft–lbf) (g) Using a pin punch and hammer, drive in the slotted spring pin until it is flush with the No.3 shift fork. -
Page 188
MT2–51 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COMPONENT PARTS INSTALLATION (j) Install the No.2 shift fork and fork shaft. Apply MP grease to No.2 interlock pin and install • the pin into the shaft hole. Place the No.2 shift fork into the groove of No.2 •… -
Page 189
MT2–52 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COMPONENT PARTS INSTALLATION (n) Install and torque the No.1 and No.2 shift fork set bolts. Torque: 20 N–m (200 kgf.cm, 14 ft–lbf) 18. INSTALL LOCKING BALL AND SPRING (a) Install the balls and spring into each hole. (b) Apply liquid sealer to the plug threads. -
Page 190
MT2–53 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COMPONENT PARTS INSTALLATION 21. INSTALL OIL SEPARATOR Install the oil receiver and torque the two bolts. Torque: 18 N–m (185 kgf–cm, 13 ft–tbf) 22. DISMOUNT INTERMEDIATE PLATE FROM VISE (a) Dismount the intermediate plate from the vise. (b) Remove the bolts, nuts, plate washers and gasket. -
Page 191
MT2–54 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COMPONENT PARTS INSTALLATION 25. INSTALL FRONT BEARING RETAINER (a) Remove the any packing material and be careful not to drop oil on the contacting surface of the front bearing retainer or transmission case. (b) Apply seal packing to the retainer as shown, and install it to the transmission case. -
Page 192
MT2–55 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COMPONENT PARTS INSTALLATION (e) Install the shift lever housing to the shift and select lever shaft, push in the extension housing. (f) Install and torque the bolt. Torque: 39 N–m (400 kgf–cm, 29 ft–lbf) (g) Install the nine bolts to the extension housing. (h) Torque the bolts. -
Page 193
MT2–56 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COMPONENT PARTS INSTALLATION (e) Install the shift lever housing to the shift and select lever shaft, push in the transfer adaptor. (f) Install and torque the bolt. Torque: 39 N–m (400 kgf–cm, 29 ft–lbf) (g) Install the nine bolts to the transfer adaptor. (h) Torque the bolts. -
Page 194
MT2–57 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – COMPONENT PARTS INSTALLATION 31. INSTALL CLUTCH HOUSING (a) Install the clutch housing. (b) Install and torque the nine bolts. Torque: 37 N–m (375 kgf¿em, 27 ft–lbf) 32. INSTALL VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR (a) Install the speed sensor. (b) Install and torque the set bolt. -
Page 195
MT2–58 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS SERVICE DATA Output shaft 2nd gear journal diameter Limit Output shaft 3rd gear journal diameter Limit Output shaft flange thickness Limit Output shaft runout Limit 1 st gear inner race flange thickness Limit 1 st gear inner race outer diameter Limit… -
Page 196
MT2–59 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS Output shaft snap ring thickness No.2 clutch hub No.2 clutch hub No.2 clutch hub No.2 clutch hub No.2 clutch hub No.2 clutch hub Rear bearing Rear bearing Rear bearing Rear bearing Rear bearing Rear bearing Rear bearing Rear bearing Reverse gear… -
Page 197
MT2–60 MANUAL TRANSMISSION – SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS Oil seal drive in depth Front bearing retainer (from retainer end) TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS Part tightened Transfer x Transfer adaptor Engine rear mounting x Transmission Transmission x Engine Transmission x Stiffener plate Transmission x Starter Clutch tube bracket x Transmission Frame auxiliary crossmember Engine rear mounting bracket x Support member… -
Page 198: Automatic Transmission
AT–1 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION…
-
Page 199
AT–2 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – MEMO… -
Page 200
AT–3 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – A43D Automatic Transmission… -
Page 201
AT–4 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Description DESCRIPTION General The A43D is a 4–speed automatic transmission. The A43D transmission is mainly composed of the torque converter clutch, the overdrive (hereafter called 0/D) planetary gear unit, 3–speed planetary gear unit, the hydraulic control system and the electronic con– trol system. -
Page 202
AT–5 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Description General Specifications Type of Transmission Type of Engine Stall Torque Ratio Torque Converter Clutch Lock–Up Mechanism 1 st Gear 2nd Gear Gear Ratio 3rd Gear O/D Gear Reverse Gear O/D Direct Clutch Front Clutch Rear Clutch Plates (Disc/Plate) No.2 Brake No.3 Brake… -
Page 203
AT–6 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Operation OPERATION Mechanical Operation OPERATING CONDITIONS Shift lever position Gear position Parking Reverse Neutral 1 st 1 st… -
Page 204
AT–7 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Operation FUNCTION OF COMPONENTS NOMENCLATURE OPERATION O/D Direct Clutch (C Connects overdrive sun gear and overdrive carrier Prevents overdrive sun gear from turning either clockwise or counterclockwise O/D Brake (Bo) When transmission is being driven by engine, connects overdrive sun gear and O/D One–Way Clutch (Fo) overdrive carrier Front Clutch (C… -
Page 205
AT–8 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Operation FUNCTION OF COMPONENTS (Cont’d) The conditions of operation for each gear position are shown in the following illustrations:… -
Page 206
AT–9 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Operation FUNCTION OF COMPONENTS (Cont’d) -
Page 207
AT–10 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Operation Hydraulic Control System The hydraulic control system is composed of the oil pump, the valve body, the governor body, the accumu– lators, the clutches and brakes as well as the fluid passages which connect all of these components. Based in the hydraulic pressure created by the oil pump, the hydraulic control system governs the hydraulic pressure acting on the torque converter clutch, clutches and brakes in accordance with the vehicle driving conditions. -
Page 208
AT–11 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Basic Troubleshooting) TROUBLESHOOTING Basic Troubleshooting 1. Troubleshooting occuring with the automatic transmission can be caused by either the engine, electri– cal control or the transmission itself. These three areas should be distinctly isolated before proceeding with troubleshooting. -
Page 209
AT–12 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (General Troubleshooting General Troubleshooting Possible cause Problem Page Remedy Fluid discolored or AT–14 Fluid contaminated Replace fluid smells burnt AT–40 Torque converter clutch faulty Replace torque converter clutch Transmission faulty Disassemble and inspect transmission Vehicle does not AT–15 Manual linkage out of adjustment Adjust linkage… -
Page 210
AT–13 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (General Troubleshooting) General Troubleshooting (Cont’d) Page Remedy Problem Possible cause AT–15 Adjust linkage Drag, binding or Manual linkage out of adjustment Valve body faulty Inspect valve body tie–up on 1–2, 2–3 Disassemble and inspect or 3–O/D up–shift Transmission faulty transmission AT–15… -
Page 211
AT–14 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Preliminary Check) Preliminary Check 1. CHECK FLUID LEVEL HINT: • The vehicle must have been driven so that the engine and transmission are at normal operating temperature. (Fluid temperature: 70–80 C or 158–176 • Only use the COOL range on the dipstick as a rough reference when the fluid is replaced or the engine does not run. -
Page 212
AT–15 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Preliminary Check) 3. INSPECT THROTTLE CABLE (a) Depress the accelerator pedal all the way and check that the throttle valve opens fully. HINT: If the valve does not open fully, adjust the accel– erator cable. (b) Fully depress the accelerator pedal. -
Page 213
AT–16 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Overdrive Control System) Overdrive Control System ELECTRIC CONTROL CIRCUIT… -
Page 214
AT–17 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Overdrive Control System) TROUBLESHOOTING FLOW–CHART Trouble: No overdrive engagement with the main switch ON. (After warm–up) Check the following: • Main switch connector • O/D relay connector • O/D solenoid connector • Fuse • Severance or short in wire With ignition switch ON, is there battery positive voltage to harness terminal 2 of the O/D relay connector? -
Page 215
AT–18 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Overdrive Control System) INSPECTION OF OVERDRIVE CONTROL COMPONENTS 1. INSPECT OVERDRIVE RELAY (a) Remove the overdrive relay from the pedal bracket. (b) Using an ohmmeter, check that there is continuity between terminals 1 and 2. (c) Apply battery positive voltage to the relay terminals 2 and 3. -
Page 216
AT–19 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Overdrive Control System) 4. INSPECT–O/D OFF” INDICATOR (a) Turn on the ignition switch. (b) Check that the–O/D OFF” indicator does not light, when the O/D main switch is turned ON. (c) Check that the–O/D OFF” indicator lights, when the O/D main switch is turned OFF. -
Page 217
AT–20 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests) Mechanical System Tests STALL TEST The objective of this test is to check the overall performance of the transmission and engine by measuring the maximum engine speeds in the D and R positions. NOTICE: Perform the test at normal operating fluid temperature (50–80E C or 122–176E F). -
Page 218
AT–21 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests) TIME LAG TEST When the shift lever is shifted while the engine is idling, there will be a certain time lapse or lag before the shock can be felt. This is used for checking the condition of the O/D direct clutch, front clutch, rear clutch and No.3 brake. -
Page 219
AT–22 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests) HYDRAULIC TEST 1. PREPARATION (a) Warm up the transmission fluid. (b) Remove the transmission case test plug and connect the hydraulic pressure gauge. SST 09992–00094 (Oil pressure gauge) NOTICE: Perform the test at normal operating fluid temperature (50–80E C or 122–176E F). 2. -
Page 220
AT–23 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests) 3. MEASURE GOVERNOR PRESSURE (a) Check the parking brake to see that it is not applied. (b) Start the engine. (c) Shift into the D position and measure the governor pressure at the speeds specified in the table. EVALUATION If governor pressure is defective: Line pressure defective… -
Page 221
AT–24 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests ROAD TEST NOTICE: Perform this test at normal fluid temperature (50–80E C or 122–176E F). D POSITION TEST Shift into the D position and while driving with the accel– erator pedal held constant at the throttle valve full open and the O/D switch ON, check on the following points: (a) Check to see that the 1–2, 2–3 and 3–O/D up–shifts take place and also that the shift points conform to… -
Page 222
AT–25 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests) (d) While running in the D position, 2nd, 3rd and O/D gears, check to see that the possible kick–down ve– hicle speed limits for 2–1, 3–2 and O/D–3 kick–downs conform–to those indicated on the auto– matic shift schedule. -
Page 223
AT–26 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests (b) While running in the L position, release the accelera– tor pedal and check the engine braking effect. EVALUATION If there is no engine braking effect: No–3 brake is defective • (c) Check for abnormal noise during acceleration and deceleration. -
Page 224
AT–27 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Park Neutral Position Switch) Automatic Shift Schedule Throttle valve fully open ³ Fully closed km/h (mph) D position (2 position) L position * O/D–¿ 3 down–shift is possible up to maximum speed. Park Neutral Position Switch INSPECTION OF PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH Inspect that there is continuity between each terminals. -
Page 225
AT–28 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair ON–VEHICLE REPAIR Valve Body REMOVAL OF VALVE BODY 1. CLEAN TRANSMISSION EXTERIOR To prevent contamination, clean the exterior of the trans– mission. 2. DRAIN TRANSMISSION FLUID Remove the drain plug and the fluid into a suitable con– tainer. -
Page 226
AT–29 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair (b) Disconnect the throttle cable from the cam and re– move the valve body. INSTALLATION OF VALVE BODY 1. CONNECT THROTTLE CABLE TO CAM Push the cable fitting into the cam. INSTALL VALVE BODY (a) Align the manual valve lever with the manual valve. -
Page 227
AT–30 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair INSTALL PAN WITH NEW GASKET Be sure the pan is clean and the two magnets are in place. NOTICE: Do not use gasket sealer. Tighten the bolts evenly. Torque: 5.4 N–m (55 kgf–cm, 48 in.¿lbf) INSTALL DRAIN PLUG Torque the drain plug. -
Page 228
AT–31 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair Parking Lock Pawl REMOVAL OF PARKING LOCK PAWL 1. REMOVE VALVE BODY (See page AT–28) 2. REMOVE PARKING LOCK PAWL BRACKET Remove the two bolts and the bracket. 3. REMOVE SPRING FROM PARKING LOCK PAWL PIVOT 4. -
Page 229
AT–32 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair 2. REMOVE VALVE BODY (See page AT–28) 3. PUSH THROTTLE CABLE OUT OF TRANSMISSION CASE Using a 10–mm socket, push the throttle cable out. INSTALLATION OF THROTTLE CABLE 1. INSTALL CABLE IN TRANSMISSION CASE Be sure to push it in all the way. -
Page 230
AT–33 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair Extension Housing REPLACEMENT OF OIL SEAL 1. RAISE VEHICLE, AND POSITION PAN TO CATCH ANY FLUID THAT MAY DRIP 2. REMOVE PROPELLER SHAFT REMOVE REAR OIL SEAL NOTICE: Clean the rear extension housing before re– moving the seal. -
Page 231
AT–34 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair JACK UP TRANSMISSION SLIGHTLY Securely support the transmission on a transmission jack. Lift the transmission slightly to remove weight from the rear support member. 4. DISCONNECT CONNECTOR 5. REMOVE NO. 1 VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR (a) Remove the bolt and the vehicle speed sensor. -
Page 232
AT–35 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair INSTALLATION OF EXTENSION HOUSING 1. INSTALL NEW GASKET AND EXTENSION HOUSING ON TRANSMISSION (a) Clean the threads of the¿¿bolt and bolt hole. (b) Coat the threads of the¿¿bolt with sealant. Sealant: Part No. 08833–00080, THREE BOND 1344, LOCTITE 242 or equivalent (c) Install the extension housing over a new gasket with bolts, and then torque them. -
Page 233
AT–36 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair Governor Body REMOVAL OF GOVERNOR BODY 1. REMOVE EXTENSION HOUSING (See page AT–33) 2. REMOVE SPEEDOMETER DRIVE GEAR (a) Using snap ring pliers, remove the snap ring. (b) Slide off the speedometer gear. (e) Remove the lock ball and the outer snap ring. 3. -
Page 234
AT–37 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair 2. INSTALL SPEEDOMETER DRIVE GEAR (a) Install the snap ring and lock ball. (b) Slide the speedometer drive gear on the shaft. (c) Using snap ring pliers, install the outer snap ring. 3. INSTALL EXTENSION HOUSING (See page AT–34) -
Page 235
AT–38 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Removal and Installation of Transmission REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION OF TRANSMISSION Remove and install the parts as shown. -
Page 236
AT–39 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Removal and Installation of Transmission (MAIN POINT OF INSTALLATION) 1. CHECK TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH INSTALLATION Using calipers and a straight edge, measure from the in– stalled surface of the torque converter clutch to the front surface of the transmission housing. Correct distance: 20.0 mm (0.787 in.) If the distance is less than the standard, check for an im–… -
Page 237
AT–40 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Torque Converter Clutch and Drive Plate TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH AND DRIVE PLATE INSPECTION OF TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH AND DRIVE PLATE INSPECT ONE–WAY CLUTCH (a) Install SST into the inner race of the one–way clutch. SST 09350–20015 (09397–22020) (b) Install SST so that it fits in the notch of the con–… -
Page 238
AT–41 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – A340E Automatic Transmission… -
Page 239
AT–42 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Description DESCRIPTION General The A340E is a 4–speed, Electronic Controlled Transmission developed for use with high–performance en– gine such as the 3VZ–E. A lock–up mechanism is built into the torque converter clutch. The A340E automatic transmission is mainly composed of the torque converter clutch, the overdrive (here– after called O/D) planetary gear unit, 3–speed planetary gear unit, the hydraulic control system and the elec–… -
Page 240
AT–43 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Description General Specifications A340E Type of Transmission Type of Engine Stall Torque Ratio Torque Converter Clutch Lock–Up Mechanism 1 st Gear 2nd Gear Gear Ratio 3rd Gear O/D Gear Reverse Gear O/D Direct Clutch Forward Clutch Direct Clutch Plates (Disc/Plate) 2nd Brake… -
Page 241
AT–44 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Operation OPERATION Mechanical Operation OPERATING CONDITIONS Shift lever position Gear position Parking Reverse Neutral 1 st 1 st 1 st * 2nd * Down–shift only in the L position and 2nd gear–no up–shift. -
Page 242
AT–45 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Operation FUNCTION OF COMPONENTS OPERATION NOMENCLATURE Connects overdrive sun gear and overdrive carrier O/D Direct Clutch (C Prevents overdrive sun gear from turning either clockwise or counterclockwise O/D Brake (BO) O/D One–Way Clutch (Fo) When transmission is being driven by engine, connects overdrive sun gear and overdrive carrier Connects input shaft and front planetary ring gear Forward Clutch (Cl) -
Page 243
AT–46 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Operation FUNCTION OF COMPONENTS (Cont’d) The conditions of operation for each gear position are shown in the following illustrations:… -
Page 244
AT–47 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Operation FUNCTION OF COMPONENTS (Cont’d) -
Page 245
AT–48 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Operation HYDRAULIC CONTROL SYSTEM The hydraulic control system is composed of the oil pump, the valve body, the solenoid valves, and the clutches and brakes, as well as the fluid passages which connect all of these components. Based on the hydraulic pressure created by the oil pump, the hydraulic control system governs the hydraulic pressure acting on the torque converter clutch, clutches and brakes in accordance with the vehicle driving condi–… -
Page 246
AT–49 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Operation ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM The electronic control system, which controls the shift points and the operation of the lock–up clutch, is composed of the following three parts: 1. Sensors These sensors sense the vehicle speed, throttle opening and other conditions and send these data to the ECM in the form of electrical signals. -
Page 247
AT–50 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Operation FUNCTION OF ECM • Control of Shift Timing The ECM has programmed into its memory the optimum shift pattern for each shift lever position (D, 2, L position) and driving mode (Normal or Power). Based on the appropriate shift pattern, the ECM turns No. 1 and No.2 solenoid valves on or off in accor– dance with the vehicle speed signal from the vehicle speed sensor and the throttle opening signal from the throttle position sensor. -
Page 248
AT–51 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Basic Troubleshooting) TROUBLESHOOTING Basic Troubleshooting Before troubleshooting an electronic controlled transmission, first determine whether the problem is elec– trical or mechanical. To do this, just refer to the basic troubleshooting flow–chart provided below. If the cause is already known, using the basic troubleshooting chart below along with the general trouble– shooting chart on the following pages should speed the procedure. -
Page 249
AT–52 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (General Troubleshooting) General Troubleshooting Problem Possible cause Remedy Page Fluid discolored or Fluid contaminated Replace fluid AT–59 smells burnt Torque converter clutch faulty Replace torque converter clutch AT–96 Transmission faulty Disassemble and inspect transmission Vehicle does not Manual linkage out of adjustment Adjust linkage AT–60… -
Page 250
AT–53 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (General Troubleshooting) General Troubleshooting (Cont’d) Problem Possible cause Remedy Page No lock–up in 2nd, Electronic control faulty Inspect electronic control AT–63 3rd or 01D Valve body faulty Inspect valve body Solenoid valve faulty Inspect solenoid valve AT–72 Transmission faulty Disassemble and inspect… -
Page 251
AT–54 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Diagnosis System) Diagnosis System DESCRIPTION 1. A self–diagnosis function is built into the electrical control system. Warning is indicated by the overdrive OFF indica– tor light. HINT: Warning and diagnostic trouble codes can be read only when the overdrive switch is ON. If OFF, the overdrive OFF light is lit continuously and will not blink. -
Page 252
AT–55 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Diagnosis System) READ DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE 1. TURN IGNITION SWITCH AND O/D SWITCH TO ON Do not start the engine. HINT: Warning and diagnostic trouble codes can be read only when the overdrive switch is ON. If OFF, the overdrive OFF light will light continuously and will not blink. -
Page 253
AT–56 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Diagnosis System) DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES Code No. Light Pattern Diagnosis System Normal Defective No. 1 vehicle speed sensor (in ATM)– severed wire harness or short circuit Defective No. 2 vehicle speed sensor (in ATM)– severed wire harness or short circuit Severed No. -
Page 254
AT–57 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Diagnosis System) TROUBLESHOOTING FLOW–CHART HINT: • If diagnostic trouble code Nos. 42, 61, 62 or 63 are output, the overdrive OFF indicator light will begin to blink immediately to warn the driver. However, an impact or shock may cause the blinking to stop;… -
Page 255
AT–58 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Diagnosis System) Diagnostic trouble code 62 (No. 1 solenoid valve circuitry) Check resistance of No. 1 solenoid valve at ECM connector. (See page AT–72) Substitute another ECM. Replace No. 1 solenoid valve. Remove the oil pan and check resistance of No. 1 solenoid valve connector and body ground. -
Page 256
AT–59 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Preliminary Check) Preliminary Check 1. CHECK FLUID LEVEL HINT: The vehicle must have been driven so that the engine and transmission are at normal operating temperature. (Fluid temperature: 70–80 C or 158–176 Only use the COOL range on the dipstick as a rough reference when the fluid is replaced or the engine does not run. -
Page 257
AT–60 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Preliminary Check) INSPECT THROTTLE CABLE (a) Depress the accelerator pedal all the way and check that the throttle valve opens fully. HINT: If the valve does not open fully, adjust the accel– erator cable. (b) Fully depress the accelerator pedal. (c) Measure the distance between the end of the boot and stopper on the cable. -
Page 258
AT–61 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Preliminary Check) 6. INSPECT IDLE SPEED (IN POSITION) Connect a tachometer test probe to the data link connec– tor 1 terminal IG R, inspect the idle speed. Idle speed: 800 RPM Manual Shifting Test HINT: With this test, it can be determined whether the trouble lies within the electrical circuit or is a mechanical problem in the transmission. -
Page 259
AT–62 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Manual Shifting Test) REFERENCE: Possible gear position in accordance with solenoid operating conditions. BOTH SOLENOIDS NO. 1 SOLENOID NO.2 SOLENOID NORMAL MALFUNCTIONING MALFUNCTIONING MALFUNCTIONING Solenoid Valve Solenoid Valve Solenoid Valve Solenoid Valve Gear Gear Gear Gear Position Position… -
Page 260
AT–63 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) Electronic Control System PRECAUTION Do not open the cover or the case of the ECM and various computer unless absolutely necessary. (If the IC terminals are touched, the IC may be destroyed by static electricity.) ELECTRONIC CONTROL CIRCUIT… -
Page 261
AT–64 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) ELECTRONIC CONTROL COMPONENTS… -
Page 262
AT–65 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) TROUBLESHOOTING FLOW–CHART Trouble No. 1 No Shifting Warm up engine Engine coolant temp.: 80E C (176E F) ATF temp.: 50–80E C (122–176E F Connect a voltmeter to data link connector 1 terminals TT and El. Does TT terminal voltage vary with changes in throttle opening? Brake signal Is voltage between ECM terminals STP and E,… -
Page 263
AT–66 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) Continued from page AT–65 0³ 7V Connect solenoid wire connector and road test. • Transmission faulty Does data link connector 1 TT terminal voltage • Solenoid faulty rise from 0 V to 7 V in sequence? 0³… -
Page 264
AT–67 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) Shift point too high or too low Trouble No.2 Warm up engine Engine coolant temp.: 800C (1760F) ATF temp.: 50–80E C (122–176E F) Connect a voltmeter to data link connector 1 terminals TT and El. Does TT terminal voltage vary with changes in throttle opening? Brake signal Is voltage between ECM terminals STP and E,… -
Page 265
AT–68 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) Trouble No.3 No up–shift to overdrive (After warm–up) Road test while shifting manually with solenoid Faulty transmission wire connector disconnected. Is there over– drive up–shift in the D position when shifting from L to 2 to D? 0³7 V Connect solenoid wire connector, and while •… -
Page 266
AT–69 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) Trouble No.4 No lock–up (After warm–up) Warm up engine Engine coolant temp.: 80E C (176E F) ATF temp.: 50–80E C (122–176E F) • Lock–up solenoid stuck Road test • Faulty transmission Connect a voltmeter to data link connector 1 ter– •… -
Page 267
AT–70 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) INSPECTION OF TT TERMINAL VOLTAGE 1. INSPECT THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR SIGNAL (a) Turn the ignition switch to ON. Do not start the en– gine. (b) Connect a voltmeter to data link connector 1 ter– minals TT and El. -
Page 268
AT–71 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) INSPECTION OF ELECTRONIC CONTROL COMPONENTS 1. INSPECT VOLTAGE OF ECM CONNECTOR (a) Remove the cowl side trim of passenger side. (b) Turn on the ignition switch. (c) Measure the voltage at each terminal. Voltage ( V ) Measuring condition Terminal… -
Page 269
AT–72 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) Terminal Measuring condition Voltage (V) N position Except N position 2 position Except 2 position L position Except L position INSPECT SOLENOID (a) Disconnect the connector from ECM. (b) Measure the resistance between S, S2, SL and ground. -
Page 270
AT–73 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) If a malfunction is found during voltage inspection (step 1.), inspect the components listed below. 4. INSPECT PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH (See page AT–83) 5. INSPECT THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR Using an ohmmeter, check the resistance between each terminal. -
Page 271
AT–74 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests) Mechanical System Tests STALL TEST The object of this test is to check the overall performance of the transmission and engine by measuring the stall speeds in the D and R positions. NOTICE: Perform the test at normal operating fluid temperature (50–80E C or 122–176E F). -
Page 272
AT–75 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests) TIME LAG TEST When the shift lever is shifted while the engine is idling, there will be a certain time lapse or lag before the shock can be felt. This is used for checking the condition of the O/D direct clutch, forward clutch, direct clutch and first and reverse brake. -
Page 273
AT–76 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests) HYDRAULIC TEST PREPARATION (a) Warm up the transmission fluid. (b) Remove the transmission case test plug and connect the hydraulic pressure gauge. SST 09992–00094 (Oil pressure gauge) NOTICE: Perform the test at normal operating fluid temperature (50–80 C or 122–176 The line pressure test should always be carried out in pairs. -
Page 274
AT–77 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests) EVALUATION (a) If the measured values at all positions are higher than specified: Throttle cable out of adjustment Throttle valve defective Regulator valve defective (b) If the measured values at all positions are lower than specified: Throttle cable out of adjustment Throttle valve defective Regulator valve defective… -
Page 275
AT–78 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests) ROAD TEST NOTICE: Perform the test at normal operating fluid tem– perature (50–80E C or 122–176E F). 1. D POSITION TEST IN NORM AND PWR PATTERN RANGES Shift into the D position and hold the accelerator pedal constant at the full throttle valve opening posiiton. -
Page 276
AT–79 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests) (d) While running in the D position, 2nd, 3rd and O/D gears, check to see the possible kickdown vehicle speed limits for 2 R 1, 3 R 2 and O/D R 3 kickdowns conform to those indicated on the automatic shift schedule. -
Page 277
AT–80 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests) 3. L POSITION TEST (a) While running in the L position , check to see that there is no up–shift to 2nd gear. (b) While running in the L position, release the ac– celerator pedal and check the engine braking effect. -
Page 278
AT–81 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Automatic Shift Schedule) Automatic Shift Schedule CBU: Tire size P205175R14, P215/65R15 (Differential gear ratio: 3.417) km/h (mph) Throttle valve fully open [ ] Fully closed NORM D position PW R NORM 2 position NORM L position PW R Throttle valve opening 5% km/h (mph) -
Page 279
AT–82 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Automatic Shift Schedule) C & C: Tire size 185R14–8, 185R14–6 (Double tire) (Differential gear ratio: 4.100) km/h (mph) Throttle valve fully open [ ] Fully closed NORM D position NORM 2 position PW R NORM L position PW R Throttle valve opening 5%… -
Page 280
AT–83 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Park Neutral Position Switch) Park Neutral Position Switch INSPECTION OF PARK/NEUTRAL POSIITON SWITCH Inspect that there is continuity between each terminals. Terminal Shift Position… -
Page 281
AT–84 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair ON–VEHICLE REPAIR Valve Body REMOVAL OF VALVE BODY 1. CLEAN TRANSMISSION EXTERIOR To prevent contamination, clean the exterior of the trans– mission. 2. DRAIN TRANSMISSION FLUID Remove the drain plug and the fluid into a suitable con– tainer. -
Page 282
AT–85 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair WHEN REPLACING SOLENOIDS (a) Disconnect the connectors from the solenoids. (b) Remove the solenoid mounting bolts. (c) Remove the solenoids. DISCONNECT SOLENOID CONNECTORS Disconnect the three connectors from No.1, No.2 and lock–up solenoids. REMOVE VALVE BODY (a) Remove the seventeen bolts. -
Page 283
AT–86 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair (b) Finger tighten the all bolts first. Then tighten the bolts evenly. HINT: Each bolt length (mm, in.) is indicated in the fig– ure. Torque: 10 N–m (100 kgf–cm, 7 ft–lbf) CONNECT SOLENOID WIRING INSTALL OIL TUBES Tap the tubes with a plastic hammer to install them into the positions in the figure. -
Page 284
AT–87 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair (c) Install and torque the nineteen bolts. Torque:. 7.4 N–m (70 kgf–cm, 65 in.– Ibf) INSTALL DRAIN PLUG Torque the drain plug. Torque: 20 N–m (205 kgf–cm,15 ft–lbf) FILL TRANSMISSION WITH ATF Add only about two liters of ATF. Start the engine and shift through all the positions. -
Page 285
AT–88 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair 3. INSTALL PARKING LOCK PAWL BRACKET (a) Push lock rod fully toward. (b) Install the three bolts finger tight. (c) Check that the pawl operates smoothly. (d) Torque the bolts. Torque: 7.4 N–m (70 kgf–cm,65 in.¿Ibf) 4. -
Page 286
AT–89 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair Extension Housing REPLACEMENT OF OIL SEAL 1. RAISE VEHICLE, AND POSITION PAN TO CATCH ANY FLUID THAT MAY DRIP 2. REMOVE PROPELLER SHAFT (See page PR–3) 3. REMOVE REAR OIL SEAL NOTICE: Clean the rear extension housing before re– moving the seal. -
Page 287
AT–90 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair REMOVAL OF EXTENSION HOUSING 1. RAISE VEHICLE AND POSITION PAN TO CATCH ANY FLUID THAT MAY DRIP 2. REMOVE PROPELLER SHAFT (See page PR–3) 3. JACK UP TRANSMISSION SLIGHTLY Securely support the transmission on a transmission jack. Lift the transmission slightly to remove weight from the rear support member. -
Page 288
AT–91 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair 7. REMOVE ENGINE REAR MOUNTING FROM EXTENSION HOUSING Remove four bolts and the engine rear mounting from the extension housing. 8. REMOVE EXTENSION HOUSING AND GASKET Remove the six bolts. If necessary, tap the extension housing with a plastic hammer or wooden block to loosen INSTALLATION OF EXTENSION HOUSING 1. -
Page 289
AT–92 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair 3. INSTALL NO.2 VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR 4. INSTALL PROPELLER SHAFT (See page PR–3) 5. INSTALL NO. 1 VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR (a) Install a new O–ring on the sensor. (b) Install the No. 1 vehicle speed sensor. 6. -
Page 290
AT–93 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair INSTALLATION OF SENSOR ROTOR 1. INSTALL SENSOR ROTOR ON OUTPUT SHAFT (a) Make sure that the key is installed in the groove. (b) Install the sensor rotor on the shaft. 2. INSTALL SPEEDOMETER DRIVE GEAR (a) Slide the lock ball and the speedometer drive gear on the output shaft. -
Page 291
AT–94 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Removal and Installation of Transmission REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION OF TRANSMISSION Remove and install the parts as shown. -
Page 292
AT–95 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Removal and Installation of Transmission (MAIN POINT OF INSTALLATION) 1. CHECK TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH INSTALLATION Using calipers and a straight edge, measure from the in– stalled surface of the torque converter clutch to the front surface of the transmission housing. Correct distance: 18.0 mm (0.709 in.) If the distance is less than the standard, check for an im–… -
Page 293
AT–96 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Torque Converter Clutch and Drive Plate TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH AND DRIVE PLATE INSPECTION OF TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH AND DRIVE PLATE 1. INSPECT ONE–WAY CLUTCH (a) Install SST into the inner race of the one–way clutch. SST 09350–30020 (09351–32010) (b) Install SST so that it fits in the notch of the con–… -
Page 294
AT–97 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – A340H Automatic Transmission… -
Page 295
AT–98 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Description DESCRIPTION General The A340H automatic transmission is a four–speed, Electronic Controlled Transmission with electronically controlled 4WD transfer, developed with the aim of producing an easy–driving 4WD vehicle. The transfer section consists of planetary gears, hydraulic clutches and hydraulic brake. The operation of these is fully controlled by the ECM. -
Page 296
AT–99 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Description General Specifications Type of Transmission Type of Engine Stall Torque Ratio Torque Converter Clutch Lock–Up Mechanism 1 st Gear 2nd Gear Transmission 3rd Gear Gear Ratio O/D Gear Reverse Gear High (H2, H4) Transfer Low (L4) Forward Clutch Direct Clutch O/D Direct Clutch… -
Page 297
AT–100 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Operation OPERATION Mechanical Operation OPERATING CONDITIONS 1. Transmission No. 1 No. 2 Shift Lever Gear Solenoid Solenoid Position Valve Valve Parking Reverse Neutral * 2nd * Down–shift only in the L position and 2nd gear–no up–shift. I.P. -
Page 298
AT–101 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Operation FUNCTION OF COMPONENTS 1. Transmission Function Component Forward Clutch Connects input shaft and front planetary ring gear. Direct Clutch Connects input shaft and front & rear planetary sun gear. O/D Direct Clutch Connects overdrive sun gear and overdrive planetary carrier. Prevents front &… -
Page 299
AT–102 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Operation FUNCTION OF COMPONENTS (Cont’d) The conditions of operation for each gear position are shown in the following illustrations:… -
Page 300
AT–103 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Operation FUNCTION OF COMPONENTS (Cont’d) 2. Transfer Function Component Forward Clutch Connects transmission output shaft and transfer pinion gear. Connects transfer rear output shaft and front drive gear. Direct Clutch Prevents transfer ring gear from turning either clockwise or counterclockwise. O/D Direct Clutch The conditions of operation for each gear position are shown in the following illustrations:… -
Page 301
AT–104 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Operation Hydraulic Control System 1. Transmission The hydraulic control system is composed of the oil pump, the valve body, the solenoid valves, and the clut– ches and brakes, as well as the fluid passages which connect all of these components. Based on the hydraulic pressure created by the oil pump, the hydraulic control system governs the hydraulic pressure ac–… -
Page 302
AT–105 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Operation Electronic Control System The electronic control system, which controls the transmission and transfer shift timing and the operation of the lock–up clutch, is composed of the following three parts: 1. Sensors These sensors sense the vehicle speed, throttle opening and other conditions and send these data to the ECM in the form of electrical signals. -
Page 303
AT–106 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Basic Troubleshooting) TROUBLESHOOTING Basic Troubleshooting Before troubleshooting an electronic controlled transmission first determine whether the problem is electri– cal or mechanical. To do this, just refer to the basic troubleshooting flow–chart provide below. If the cause is already known, using the basic troubleshooting chart below along with the general trouble– shooting chart on the following pages should speed the procedure. -
Page 304
AT–107 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (General Troubleshooting) General Troubleshooting Problem Possible cause Remedy Page Fluid discolored or Fluid contaminated Replace fluid AT–115 smells burnt Torque converter clutch faulty Replace torque converter clutch AT–162 Transmission faulty Disassemble and inspect transmission Vehicle does not Manual linkage out of adjustment Adjust linkage AT–116… -
Page 305
AT–108 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (General Troubleshooting) General Troubleshooting (Cont’d) Problem Possible cause Remedy Page No lock–up in 2nd, Electronic control faulty Inspect electronic control AT–120 3rd or O/D Valve body faulty Inspect valve body Solenoid valve faulty Inspect solenoid valve Transmission faulty Disassemble and inspect transmission… -
Page 306
AT–109 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Diagnosis System) Diagnosis System DESCRIPTION A self–diagnosis function is built into the electrical control system. Warning is indicated by the overdrive OFF indica– tor light. HINT: Warning and diagnostic trouble codes can be read only when the overdrive switch is ON. If OFF, the overdrive OFF light is lit continuously and will not blink. -
Page 307
AT–110 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Diagnosis System) READ DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE 1. TURN IGNITION SWITCH AND O/D SWITCH TO ON Do not strat the engine. HINT: Warning and diagnostic trouble codes can be read only when the overdrive switch is ON. If OFF, the overdrive OFF light will light continuously and will not blink. -
Page 308
AT–111 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Diagnosis System) DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES Diagnosis System Light Pattern Code No. Normal Defective No. 1 vehicle speed sensor (in ATM)– severed wire harness or short circuit Defective No.2 vehicle speed sensor (in ATM)– severed wire harness or short circuit Severed No. -
Page 309
AT–112 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Diagnosis System) TROUBLESHOOTING FLOW–CHART HINT: • If diagnostic trouble code Nos. 42, 61, 62, 63 or 65 are output, the overdrive OFF indicator light will begin to blink immediately to warn the driver. However, an impact or shock may cause the blinking to stop;… -
Page 310
AT–113 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Diagnosis System) Diagnostic trouble code 62 (No. 1 solenoid valve circuitry) Check resistance of No. 1 solenoid valve at ECM connector. (See page AT–130) Substitute another ECM. Replace No. 1 solenoid valve. Remove the transmission oil pan and check resistance of No. -
Page 311
AT–114 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Diagnosis System) Diagnostic trouble code 65 (No.4 solenoid valve circuitry) Check resistance of No.4 solenoid valve at ECM connector. (See page AT–130) Substitute another ECM. Remove the transfer oil pan and check Replace No.4 solenoid valve. resistance of No.4 solenoid valve connector and body ground. -
Page 312
AT–115 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Preliminary Check) Preliminary Check 1. CHECK FLUID LEVEL (Transmission and transfer case) HINT: • The vehicle must have been driven so that the engine and transmission are at normal operating temperature. (Fluid temperature: 70–80 C or 158–176 •… -
Page 313
AT–116 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Preliminary Check) (f) Check the fluid level with the normal operating tem– perature (70–80°C or 158–176°F) and add as necessary. NOTICE: Do not overfill. (Transfer chain case) (a) Remove the transfer under cover. (b) Remove the drain plug with SST and drain the fluid. SST 09043–38 100 (c) Reinstall the drain plug securely with SST. -
Page 314
AT–117 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Preliminary Check) 4. INSPECT TRANSMISSION SHIFT LEVER POSITION When shifting the shift lever from the IV position to other positions, check that the lever can be shifted smoothly and accurately to each position and that the position in– dicator correctly indicates the position. -
Page 315
AT–118 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Preliminary Check, Manual Shifting Test) 7. INSPECT TRANSFER POSITION SWITCH If necessary, carry out the following adjustment proce– dures. (a) Loosen the transfer position switch bolt and set the transfer shift lever to the H4 position. (b) Align the groove and H4 basic line. -
Page 316
AT–119 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Manual Shifting Test) REFERENCE: Possible gear positions in accordance with solenoid operating conditions. BOTH SOLENOIDS NO.2 SOLENOID NO. 1 SOLENOID NORMAL MALFUNCTIONING MALFUNCTIONING MALFUNCTIONING Solenoid Valve Solenoid Valve Solenoid Valve Solenoid Valve Gear Gear Gear Gear Position Position… -
Page 317
AT–120 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) Electronic Control System PRECAUTION Do not open the cover or the case of the ECM and various computer unless absolutely necessary. (If the IC terminals are touched, the IC may be destroyed by static electricity.) ELECTRONIC CONTROL CIRCUIT… -
Page 318
AT–121 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) ELECTRONIC CONTROL COMPONENTS… -
Page 319
AT–122 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) TROUBLESHOOTING FLOW–CHART Trouble No. 1 No Shifting Warm up engine Engine Coolant temp.: 80 C (176 ATF temp.: 50–80 C (122–176 Connect a voltmeter to data link connector 1 terminals TT and E, . Does Tt terminal voltage vary with changes in throttle opening? Is voltage between ECM terminals STP and… -
Page 320
AT–123 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) Continued from page AT–122 0³ 7V • Transmission faulty Connect solenoid wire connector and road • Solenoid faulty test. Does data link connector 1 TT terminal voltage rise from 0 V to 7 V in sequence? 0³… -
Page 321
AT–124 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) Trouble No.2 Shift point too high or too low Warm up engine Engine coolant temp.: 80 C (176 ATF temp.: 50–80 (122–176 Connect a voltmeter to data link connector 1 terminals TT and E, . Does TT terminal voltage vary with changes in throttle opening? Is voltage between ECM terminals STP and… -
Page 322
AT–125 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – No up–shift to overdrive (After warm–up) Trouble No.3 Road test while shifting manually with sole– Faulty transmission noid wire connector disconnected. Is there overdrive up–shift in the D position when shifting from L to 2 to D? 0³7V Connect solenoid wire connector, and while Faulty transmission… -
Page 323
AT–126 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting( Electronic Control System) Trouble No. 4 No lock–up (After warm–up) Warm up engine Engine coolant temp.: 80E C(176E F) ATF temp.: 50–80E C (1 22–176E F) Road test • Lock–up solenoid stuck Connect a voltmeter to data link connector 1 •… -
Page 324
AT–127 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) Trouble No.5 Transfer gear no change L4 from H4 Check transfer position switch Faulty transfer position switch (See page AT–132) Connect a voltmeter to data link connector 1 ter– Faulty throttle position sensor minals TT and E, . -
Page 325
AT–128 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) INSPECTION OF TT TERMINAL VOLTAGE 1. INSPECT THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR SIGNAL (a) Turn the ignition switch to ON. Do not start the en– gine. (b) Connect a voltmeter to data link connector 1 termi– nals Tt and E,. -
Page 326
AT–129 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) INSPECTION OF ELECTRONIC CONTROL COMPONENTS 1. INSPECT VOLTAGE OF ECM CONNECTOR (a) Remove the cowl side trim of passenger side. (b) Turn on the ignition switch. (c) Measure the voltage at each terminal. Measuring condition Voltage i V j Terminal… -
Page 327
AT–130 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) Terminal Measuring condition Voltage (V) N position Except N position 2 position Except 2 position L position Except L position Transfer shift position H2 or H4 Transfer shift position L4 Fluid temp. 20E C (68E F) 2. -
Page 328
AT–131 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) If a malfunction is found during voltage inspection (step 1.), inspect the components listed below. 4. INSPECT PARK/ NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH (See page AT–144) 5. INSPECT THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR Using an ohmmeter, check the resistance between each terminal. -
Page 329
AT–132 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) 11. INSPECT TRANSFER POSITION SWITCH Check that there is continuity between each terminal. Terminal Shift position 12. INSPECT TRANSMISSION AND TRANSFER FLUID TEMPERATURE SENSOR Measure the resistance between terminals. Oil Temperature Resistance (/ ) -
Page 330
AT–133 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests) Mechanical System Tests STALL TEST The object of this test is to check the overall performance of the transmission and engine by measuring the stall speeds in the D and R positions. NOTICE: Perform the test at normal operating fluid temperature (50–80E C or 122–176E F). -
Page 331
AT–134 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests) TIME LAG TEST When the shift lever is shifted while the engine is idling, there will be a certain time lapse or lag before the shock can be felt. This is used for checking the condition of the O/D direct clutch, forward clutch, direct clutch and first and reverse brake. -
Page 332
AT–135 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests) HYDRAULIC TEST PREPARATION (a) Warm up the transmission fluid. (b) Remove the transmission case test plug and connect the hydraulic pressure gauge. SST 09992–00094 (Oil pressure gauge) NOTICE: Perform the test at normal operating fluid temperature (50–80 C or 122–176 The line pressure test should always be carried out in pairs. -
Page 333
AT–136 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests) EVALUATION (a) If the measured values at all positions are higher than specified: Throttle cable out of adjustment Throttle valve defective Regulator valve defective (b) If the measured values at all positions are lower than specified: Throttle cable out of adjustment Throttle valve defective Regulator valve defective… -
Page 334
AT–137 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests) ROAD TEST NOTICE: Perform the test at normal operating fluid tem– perature (50–80E C or 122–176E F). HINT: The transmission shift points for the H2, H4 and L4 transfer positions are different. Also, the O/D gear and lock–up are cancelled when L4 is engaged. -
Page 335
AT–138 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests) (c) Run at the D position lock–up or O/D gear and check for abnormal noise and vibration. HINT: The check for the cause of abnormal noise and vibration must be made with extreme care as it could also be due to loss of balance in the propeller shaft, differ- en–… -
Page 336
AT–139 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests (c) Check for abnormal noise at acceleration and decel– eration, and for shock at up–shift and down–shift. 3. L POSITION TEST (a) While running in the L position, check to see that there is no up–shift to 2nd gear. -
Page 337
AT–140 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests) P POSITION TEST Stop the vehicle on a gradient (more than 5E ) and after shifting into the P position, release the parking brake. Then check to see that the parking lock pawl holds the vehicle in place. -
Page 338
AT–141 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Automatic Shift Schedule) Automatic Shift Schedule km/h (mph) Throttle valve fully open ( ] Fully closed Transfer shift position “H2” or..”H4” NORM D position PW R NORM 2 position NORM L position km/h (mph) Throttle valve opening 5% Transfer shift position Lock–up OFF Lock–up ON… -
Page 339
AT–142 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Automatic Shift Schedule) TRANSFER HIGH–LOW SHIFT RANGE The A340H transfer differs from previous manual trans– fer in that high–low shifting is possible while the vehicle is in motion, though it is not possible at all vehicle speeds or throttle opening angles. -
Page 340
AT–143 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Automatic Shift Schedule) 2 Position: High–Low Shift Possibility Range D Position: High–Low Shift Possibility Range… -
Page 341
AT–144 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Park Neutral Position Switch) Low–High Shift Possibility Range (L, 2, D Position) Park Neutral Position Switch INSPECTION OF PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH Inspect that there is continuity between each terminals. Terminal Shift Position… -
Page 342
AT–145 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair ON–VEHICLE REPAIR Transmission Valve Body REMOVAL OF VALVE BODY AND/OR SOLENOID VALVE 1. CLEAN TRANSMISSION EXTERIOR To prevent contamination, clean the exterior of the trans– mission. 2. DRAIN TRANSMISSION FLUID Remove the drain plug and drain the fluid into a suitable container. -
Page 343
AT–146 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair (c) Remove the five bolts and oil strainer case. (d) Remove the two gaskets from the case. 7. WHEN REPLACING SOLENOIDS (a) Disconnect the connectors from the solenoids. (b) Remove the solenoid mounting bolts. (c) Remove the solenoids. -
Page 344
AT–147 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair (b) Remove the sixteen bolts. (c) Remove the two Co accumulator piston springs. (d) Remove the valve body. HINT: Be careful not to drop the check ball body and spring. INSTALLATION OF VALVE BODY AND/OR SOLENOID VALVE 1. -
Page 345
AT–148 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair (d) Install the sixteen bolts. HINT: Each bolt length (mm) is indicated in the figure. Torque: 10 N–m 0 00 kgf–cm, 7 ft–lbf) (e) Connect the throttle cable to the cam. 2. CONNECT CONNECTORS TO EACH SOLENOID 3. -
Page 346
AT–149 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair 5. INSTALL OIL STRAINER AND GASKETS (a) Install two new gaskets to the oil strainer case. (b) Install the oil strainer case and torque the five bolts. Torque: 10 N–m (100 kgf–cm, 7 ft–lbf) HINT: Each bolt length (mm) is indicated in the figure. -
Page 347
AT–150 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair (d) Apply seal packing to the oil pan as shown in the fig– ure. Seal packing: Part No. 08826–00090, THREE BOND 1281 or equivalent (e) Install and torque the nineteen bolts. Torque: 7.4 N–m (75 kgf–cm, 61 in.¿lbf) 7. -
Page 348
AT–151 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair Transfer Valve Body REMOVAL OF VALVE BODY AND/OR SOLENOID VALVE 1. CLEAN TRANSFER EXTERIOR To prevent contamination, clean the exterior of the trans– fer. 2. DRAIN TRANSFER CASE FLUID Remove the drain plug and drain fluid into a suitable con– tainer. -
Page 349
AT–152 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair (b) Install the blade of SST between the transfer case and oil pan, cut off applied sealer. SST 09032–00100 NOTICE: Be careful not to damage the oil pan flange. (c) Remove the transfer oil pan. 7. -
Page 350
AT–153 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair (b) Install the bolts as shown. Torque the bolts evenly. Torque: 10 N–m (100 kgf–cm, 7 ft–Ibf ) 2. WHEN REPLACING SOLENOID Install the solenoid and torque the bolt. Torque: 10 N–m (100 kgf–cm, 7 ft–lbf) 3. -
Page 351
AT–154 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair (d) Apply seal packing to the oil pan as shown in the fig– ure. Seal packing: Part No. 08826–00090, THREE BOND 1281 or equivalent (e) Apply sealant to the threads of the three bolts. Sealant: Part No. -
Page 352
AT–155 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair Throttle Cable REMOVAL OF THROTTLE CABLE 1. DISCONNECT THROTTLE CABLE FROM THROTTLE LINKAGE 2. DRAIN TRANSMISSION FLUID Remove the drain plug and drain the fluid into a suitable container. 3. REMOVE FRONT STABILIZER BAR (See page SA–123) 4. -
Page 353
AT–156 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair 8. REMOVE THROTTLE CABLE Remove the bolt and pull out the cable from the transmis– sion case. INSTALLATION OF THROTTLE CABLE 1. INSTALL CABLE INTO TRANSMISSION CASE (a) Be sure to push it in all the way. (b) Install the bolt. -
Page 354
AT–157 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair 5. IF THROTTLE CABLE IS NEW, STAKE STOPPER ON IN– NER CABLE HINT: New cable do not have a cable stopper staked. (a) Bend the cable so there is a radius of about 200 mm (7.87 in.). -
Page 355
AT–158 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair Parking Lock Pawl REMOVAL OF PARKING LOCK PAWL 1. REMOVE TRANSFER VALVE BODY (See page AT–151) 2. REMOVE PARKING LOCK PAWL BRACKET Remove the two bolts and bracket. 3. REMOVE SPRING, SHAFT AND PARKING LOCK PAWL Remove the spring, shaft and parking lock pawl. -
Page 356
AT–159 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Removal and Installation of Transmission REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION OF TRANSMISSION Remove and install the parts as shown. -
Page 357
AT–160 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Removal and Installation of Transmission (Cont’d) (MAIN POINT OF INSTALLATION) 1. CHECK TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH INSTALLATION Using calipers and a straight edge, measure from the in– stalled surface of the torque converter clutch to the front surface of the transmission housing. -
Page 358
AT–161 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Torque Converter Clutch and Drive Plate TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH AND DRIVE PLATE INSPECTION OF TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH AND DRIVE PLATE 1. INSPECT ONE–WAY CLUTCH (a) Install SST into the inner race of the one–way clutch. SST 09350–30020 (09351–32010) (b) Install SST so that it fits in the notch of the con–… -
Page 359
AT–162 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – MEMO… -
Page 360
AT–163 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – A340F Automatic Transmission… -
Page 361
AT–164 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Description DESCRIPTION GENERAL The A340F automatic transmission is a four–speed automatic transmission with mechanically controlled 4WD transfer, developed with the aim of producing an easy–driving 4WD vehicle. The transmission section has fundamentally the same construction as the A340E automatic transmission mounted in the TRUCK 2WD. -
Page 362
AT–165 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Description General Specifications Type of Transmission Type of Engine Stall Torque Ratio Torque Converter Clutch Lock–Up Mechanism 1 st Gear 2nd Gear Gear Ratio 3rd Gear O/D Gear Reverse Gear O/D Direct Clutch Forward Clutch Direct Clutch Plates (Disc/Plate) 2nd Brake 1 st &… -
Page 363
AT–166 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Operation OPERATION Mechanical Operation OPERATING CONDITIONS Shift lever position Gear position Parking Reverse Neutral * 2nd * Down–shift only in the L position and 2nd gear–no up–shift. -
Page 364
AT–167 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Operation FUNCTION OF COMPONENTS NOMENCLATURE OPERATION O/D Direct Clutch (Co) Connects overdrive sun gear and overdrive carrier O/D Brake (Bo) Prevents overdrive sun gear from turning either clockwise or counterclockwise O/D One–Way Clutch (Fo) When transmission is being driven by engine, connects overdrive sun gear and overdrive carrier Forward Clutch (Cl) Connects input shaft and front planetary ring gear… -
Page 365
AT–168 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Operation FUNCTION OF COMPONENTS (Cont’d) The conditions of operation for each gear position are shown in the following illustrations:… -
Page 366
AT–169 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Operation FUNCTION OF COMPONENTS (Cont’d) -
Page 367
AT–170 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Operation HYDRAULIC CONTROL SYSTEM The hydraulic control system is composed of the oil pump, the valve body, the solenoid valves, and the clutches and brakes, as well as the fluid passages which connect all of these components. Based on the hydraulic pressure created by the oil pump, the hydraulic control system governs the hydraulic pressure acting on the torque converter clutch, clutches and brakes in accordance with the vehicle driving condi–… -
Page 368
AT–171 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Operation ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM The electronic control system, which controls the shift points and the operation of the lock–up clutch, is composed of the following three parts: 1. Sensors These sensors sense the vehicle speed, throttle opening and other conditions and send these data to the ECM in the form of electrical signals. -
Page 369
AT–172 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Operation FUNCTION OF ECM • Control of Shift Timing The ECM has programmed into its memory the optimum shift pattern for each shift lever position (D, 2, L position) and driving mode (Normal or Power). Based on the appropriate shift pattern, the ECM turns No. 1 and No.2 solenoid valves on or off in accor– dance with the vehicle speed signal from the vehicle speed sensor and the throttle opening signal from the throttle position sensor. -
Page 370
AT–173 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Basic Troubleshooting) TROUBLESHOOTING Basic Troubleshooting Before troubleshooting an electronic controlled transmission, first determine whether the problem is elec– trical or mechanical. To do this, just refer to the basic troubleshooting flow–chart provided below. If the cause is already known, using the basic troubleshooting chart below along with the general trouble– shooting chart on the following pages should speed the procedure. -
Page 371
AT–174 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (General Troubleshooting) General Troubleshooting Page Possible cause Remedy Problem AT–181 Fluid discolored or Fluid contaminated Replace fluid AT–212 smells burnt Torque converter clutch faulty Replace torque converter clutch Transmission faulty Disassemble and inspect transmission AT–182 Manual linkage out of adjustment Adjust linkage Vehicle does not… -
Page 372
AT–175 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (General Troubleshooting) General Troubleshooting (Cont’d) Page Remedy Possible cause Problem AT–184 Inspect electronic control Electronic control faulty No lock–up in 2nd, Inspect valve body Valve body faulty 3rd or O/D AT–193 Inspect solenoid valve Solenoid valve faulty Disassemble and inspect Transmission faulty transmission… -
Page 373
AT–176 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Diagnosis System) Diagnosis System DESCRIPTION 1. A self–diagnosis function is built into the electrical control system. Warning is indicated by the overdrive OFF indica– tor light. HINT: Warning and diagnostic trouble codes can be read only when the overdrive switch is ON. If OFF, the overdrive OFF light is lit continuously and will not blink. -
Page 374
AT–177 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Diagnosis System) READ DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE 1. TURN IGNITION SWITCH AND O/D SWITCH TO ON Do not start the engine. HINT: Warning and diagnostic trouble codes can be read only when the overdrive switch is ON. If OFF, the overdrive OFF light will light continuously and will not blink. -
Page 375
AT–178 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Diagnosis System) DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES Light Pattern Diagnosis System Code No. Normal Defective No. 1 vehicle speed sensor (in combination meter)– severed wire harness or short circuit Defective No.2 vehicle speed sensor (in ATM)– severed wire harness or short circuit Severed No. -
Page 376
AT–179 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Diagnosis System) TROUBLESHOOTING FLOW–CHART HINT: • If diagnostic trouble code Nos. 42, 61, 62 or 63 are output, the overdrive OFF indicator light will begin to blink immediately to warn the driver. However, an impact or shock may cause the blinking to stop;… -
Page 377
AT–180 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Diagnosis System) Diagnostic trouble code 62 (No. 1 solenoid valve circuitry) Check resistance of No. 1 solenoid valve at EC M connector. (See page AT–193) Substitute another ECM. Remove the oil pan and check resistance of No. 1 Replace No. -
Page 378
AT–181 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Preliminary Check) Preliminary Check 1. CHECK FLUID LEVEL HINT: • The vehicle must have been driven so that the engine and transmission are at normal operating temperature. (Fluid temperature: 70–80 C or 158–176 • Only use the COOL range on the dipstick as a rough reference when the fluid is replaced or the engine does not run. -
Page 379
AT–182 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Preliminary Check) 3. INSPECT THROTTLE CABLE (a) Depress the accelerator pedal all the way and check that the throttle valve opens fully. HINT: If the valve does not open fully, adjust the accel– erator cable. (b) Fully depress the accelerator pedal. -
Page 380
AT–183 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Manual Shifting Test) Manual Shifting Test HINT: With this test, it can be determined whether the trouble lies within the electrical circuit or is a mechanical problem in the transmission. 1. DISCONNECT SOLENOID WIRE 2. INSPECT MANUAL DRIVING OPERATION Check that the shift and gear positions correspond with the table below. -
Page 381
AT–184 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) Electronic Control System PRECAUTION Do not open the cover or the case of the ECM and various computer unless absolutely necessary. (If the IC terminals are touched, the IC may be destroyed by static electricity.) ELECTRONIC CONTROL CIRCUIT… -
Page 382
AT–185 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) ELECTRONIC CONTROL COMPONENTS… -
Page 383
AT–186 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) TROUBLESHOOTING FLOW–CHART Trouble No. 1 No Shifting Warm up engine Engine coolant temp.: 80E C (176E F) ATF temp.: 50–80E C (122–176E F) Connect a voltmeter to data link connector 1 terminals T and El. -
Page 384
AT–187 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) Continued from page AT–186 0R7V • Transmission faulty Connect solenoid wire connector and road test. • Solenoid faulty Does data link connector 1 T terminal voltage rise from 0 V to 7 V in sequence? Proceed to trouble 3 (AT–190) 0R3V Are there 10–14 V between ECM… -
Page 385
AT–188 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) Trouble No.2 Shift point too high or too low Warm up engine Engine coolant temp.: 80 C (176 ATF temp.: 50–80 C (122–176 Connect a voltmeter to data link connector 1 terminals T and El. -
Page 386
AT–189 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) No up–shift to overdrive (After warm–up) Trouble No–3 Faulty transmission Road test while shifting manually with solenoid wire connector disconnected. Is there over– drive up–shift in the D position when shifting from L to 2 to D? 0R5V •… -
Page 387
AT–190 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) Trouble No.4 No lock–up (After warm–up) Warm up engine Engine coolant temp.: 80 C (176 ATF temp.: 50–80 C (122–176 • Lock–up solenoid stuck Road test Connect a voltmeter to data link connector 1 •… -
Page 388
AT–191 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) INSPECTION OF T TERMINAL VOLTAGE 1. INSPECT THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR SIGNAL (a) Turn the ignition switch to ON. Do not start the en– gine. (b) Connect a voltmeter to data link connector 1 termi– nals T and El. -
Page 389
AT–192 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) INSPECTION OF ELECTRONIC CONTROL COMPONENTS 1. INSPECT VOLTAGE OF ECM CONNECTOR (a) Remove the cowl side trim of passenger side. (b) Turn on the ignition switch. (c) Measure the voltage at each terminal. Terminal Measuring condition Voltage (V) -
Page 390
AT–193 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) Voltage (V) Measuring condition Terminal N position Except N position 2 position Except 2 position L position Except L position Transfer shift position H2 or H4 Transfer shift position L4 2. INSPECT SOLENOID (a) Disconnect the connector from the ECM. -
Page 391
AT–194 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) If a malfunction is found during voltage inspection (step 1.), inspect the components listed below. 4. INSPECT PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH (See page AT–203) 5. INSPECT THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR Using an ohmmeter, check the resistance between each terminal. -
Page 392
AT–195 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Electronic Control System) 11. INSPECT TRANSFER POSITION SWITCH Check that there is continuity between each terminal as shown. Specified Switch Position Continuity Push No continuity Free If operation is not as specified, replace the switch. 12. -
Page 393
AT–196 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests) Mechanical System Tests STALL TEST The object of this test is to check the overall performance of the transmission and engine by measuring the stall speeds in the D and R positions. NOTICE: Perform the test at normal operating fluid temperature (50–80E C or 122–176E F). -
Page 394
AT–197 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests) TIME LAG TEST When the shift lever is shifted while the engine is idling, there will be a certain time lapse or lag before the shock can be felt. This is used for checking the condition of the 0!D direct clutch, forward clutch, direct clutch and first and reverse brake. -
Page 395
AT–198 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests) HYDRAULIC TEST PREPARATION (a) Warm up the transmission fluid. (b) Remove the transmission case test plug and connect the hydraulic pressure gauge. SST 09992–00094 (Oil pressure gauge) NOTICE: Perform the test at normal operating fluid temperature (50–80E C or 122–176E F). •… -
Page 396
AT–199 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests) EVALUATION (a) If the measured values at all positions are higher than specified: Throttle cable out of adjustment Throttle valve defective Regulator valve defective (b) If the measured values at all positions are lower than specified: Throttle cable out of adjustment Throttle valve defective Regulator valve defective… -
Page 397
AT–200 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests) ROAD TEST NOTICE: Perform the test at normal operating fluid tem– perature (50–800C or 122–1760F). 1. D POSITION TEST IN NORM AND PWR PATTERN POSI– TIONS Shift into the D position and hold the accelerator pedal constant at the full throttle valve opening position. -
Page 398
AT–201 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests) (d) While running in the D position, 2nd, 3rd and O/D gears, check to see that the possible kick–down vehicle speed limits for 2³1, 3³2 and O/D³ 3 kick–downs conform to those indicated on the automatic shift schedule. -
Page 399
AT–202 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Mechanical System Tests) 3. L POSITION TEST (a) While running in the L position, check to see that there is no up–shift to 2nd gear. (b) While running in the L position, release the accel- erator pedal and check the engine braking effect. -
Page 400
AT–203 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Troubleshooting (Automatic Shift Schedule) Automatic Shift Schedule km/h (mph) [ ] Fully closed Throttle valve fully open NORM D position PW R NORM 2 position PW R NORM L position PW R Throttle valve opening 5% km/h (mph) Lock–up OFF Lock–up ON… -
Page 401
AT–204 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair ON–VEHICLE REPAIR Valve Body REMOVAL OF VALVE BODY 1. CLEAN TRANSMISSION EXTERIOR To prevent contamination, clean the exterior of the trans– mission. 2. DRAIN TRANSMISSION FLUID Remove the drain plug and the fluid into a suitable con– tainer. -
Page 402
AT–205 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair 5. REMOVE OIL TUBE Pry up both tube ends with a large screwdriver and re– move the tube. 6. REMOVE SOLENOID WIRING (a) Disconnect the three connectors from No.1, No.2 and lock–up solenoids. (b) Remove the stopper plate from the case. (c) Pull out the solenoid wiring from the transmission case. -
Page 403
AT–206 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair 2. INSTALL VALVE BODY (a) Align the manual valve lever with the manual valve. (b) Finger tighten the all bolts first. Then tighten the bolts evenly. HINT: Each bolt length (mm, in.) is indicated in the fig– ure. -
Page 404
AT–207 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair (b) Install the oil strainer case and torque the five bolts. Torque: 10 N–m (100 kgf–cm, 7 ft–lbf ) (c) Install a new gasket to the oil strainer case. (d) Install the oil strainer and torque the eleven bolts. Torque: 6.9 IV –m (70 kgf –cm, 61 in. -
Page 405
AT–208 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair 8. FILL TRANSMISSION WITH ATF Add only about two liters of ATF. Start the engine and shift through all the positions. Check the fluid level and add as necessary. NOTICE: Do not overfill. Fluid type: ATF DEXRONE II Parking Lock Pawl REMOVAL OF PARKING LOCK PAWL 1. -
Page 406
AT–209 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – On–Vehicle Repair 2. REMOVE VALVE BODY (See page AT–204) 3. PUSH THROTTLE CABLE OUT OF TRANSMISSION CASE Remove the retaining bolt and pull out the throttle cable. INSTALLATION OF THROTTLE CABLE 1. INSTALL CABLE IN TRANSMISSION CASE Install the retaining bolt and push in the throttle cable. -
Page 407
AT–210 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Removal and Installation of Transmission REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION OF TRANSMISSION Remove and Install the parts as shown. -
Page 408
AT–211 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Removal and Installation of Transmission (Cont’d) (MAIN POINT OF INSTALLATION) 1. CHECK TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH INSTALLATION Using calipers and a straight edge, measure from the in– stalled surface of the torque converter clutch to the front surface of the transmission housing. -
Page 409
AT–212 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Torque Converter Clutch and Drive Plate TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH AND DRIVE PLATE INSPECTION OF TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH AND DRIVE PLATE 1. INSPECT ONE–WAY CLUTCH (a) Install SST into the inner race of the one–way clutch. SST 09350–30020 (09351–32010) (b) Install SST so that it fits in the notch of the con–… -
Page 410: Shift Lock System
AT–213 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Shift Lock System SHIFT LOCK SYSTEM (Electrically Controlled Shift Lock System) COMPONENTS AND CIRCUIT…
-
Page 411
AT–214 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Shift Lock System INSPECTION OF ELECTRIC CONTROL COMPONENTS 1. INSPECT SHIFT LOCK CONTROL COMPUTER Using a voltmeter, measure the voltage at each termi– nals. Voltage (V) Measuring condition Terminal Connector IG SW ACC position • G SW ON posi- tion Depress brake pedal IG SW ACC position and P position… -
Page 412
AT–215 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION – Shift Lock System 4. INSPECT SHIFT LOCK CONTROL SWITCH Inspect that there is continuity between each terminals. : Continuity Terminal Shift Position P position (Release button is not pushed) R, N, D, 2, L positions (Mechanically Controlled Shift Lock System) COMPONENTS HINT: Do the following steps, after replacing the shift–… -
Page 413
TF–1 TRANSFER – TRANSFER… -
Page 414
TF–2 TRANSFER – Description DESCRIPTION TRANSFER The Transfer transmits the drive force from the transmission to the front wheels, switching between 2WD, 4WD (High) and 4WD (Low). In the Truck the types of gear used during deceleration produce 2 types of transfer. The specifications and cross–section diagrams are as shown. -
Page 415
TF–3 TRANSFER – Troubleshooting PRECAUTIONS When working with FIPG material, you must be observe the following. • Using a razor blade and gasket scraper, remove all the old packing (FIPG) material from the gasket sur– faces. • Thoroughly clean all components to remove all the loose material. •… -
Page 416
TF–4 TRANSFER – Removal of Transfer REMOVAL OF TRANSFER 1. REMOVE TRANSFER WITH TRANSMISSION MT – See pages MT–14 to 25 AT – See pages AT–210 and 211 2. (22R–E1G58, A340F) REMOVE BREATHER HOSE Disconnect the breather hose from transfer upper cover and transmission control retainer. -
Page 417
TF–5 TRANSFER – Installation of Transfer INSTALLATION OF TRANSFER 1. INSTALL TRANSFER AND PROPELLER SHAFT UPPER DUST COVER TO TRANSMISSION WITH NEW GASKET (a) Shift the two shift fork shafts to the high–four posi– tion. (b) Apply MP grease to the adaptor oil seal. (c) Place a new gasket to the transfer adaptor. -
Page 418
TF–6 TRANSFER – Installation of Transfer 2. INSTALL ENGINE REAR MOUNTING Torque: 25 N–m (260 kgf–cm, 19 ft–lbf) 3. (Regular Cab wI VF 1 A Type Transfer) INSTALL DYNAMIC DAMPER Torque: 37 N–m (380 kgf–cm, 27 ft–lbf) 4. (22R–ElG58, A340F) INSTALL BREATHER HOSE Connect the breather hose for transfer upper cover and transmission control retainer as shown. -
Page 419
TF–7 Components TRANSFER – (RF1A TYPE TRANSFER) COMPONENTS… -
Page 420
TF–8 TRANSFER – Disassembly of Transfer DISASSEMBLY OF TRANSFER (See page TF–7) 1. REMOVE No. 1 SPEED SENSOR 2. REMOVE TRANSFER INDICATOR SWITCH 3. REMOVE FRONT COMPANION FLANGE (a) Using a hammer and chisel, loosen the staked part of the nut. (b) Using SST to hold the flange, remove the nut and washer. -
Page 421
TF–9 TRANSFER – Disassembly of Transfer 7. REMOVE REAR CASE (a) Remove the ten bolts. (b) Using a plastic hammer, remove the rear case with the idler gear. HINT: Hold the front case so the rear does not descend. If it descends, the clutch hub and steel ball may fall out. 8. -
Page 422
TF–10 TRANSFER – Disassembly of Transfer 12. REMOVE SHIFT NO. 1 FORK AND CLUTCH SLEEVE (a) Shift the fork shafts to the high–low position. (b) Using a pin punch and a hammer, drive out the slot– ted spring pin. (c) Remove the shift No. 1 fork together with the clutch sleeve. -
Page 423
TF–11 TRANSFER – Disassembly of Transfer 17. REMOVE FRONT DRIVE SHIFT FORK SHAFT 18. REMOVE INTERLOCK PIN Using a magnetic finger, remove the interlock pin. 19. REMOVE HIGH AND LOW SHIFT FORK SHAFT (a) Using a pin punch and a hammer, drive out the slot– ted spring pin. -
Page 424
TF–12 TRANSFER – Disassembly of Transfer 22. REMOVE INPUT GEAR AND COUNTER GEAR FROM REDUCTION GEAR CASE (a) Using a snap ring pliers, remove the two snap rings. (b) Using a plastic hammer, tap out the input gear and counter gear from the reduction gear case. HINT: Place the reduction gear case on something soft such as wooden blocks. -
Page 425
TF–13 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Input Gear) COMPONENT PARTS Input Gear COMPONENTS REPLACEMENT OF BEARING IF NECESSARY, REPLACE INPUT GEAR BEARING (a) Using snap ring pliers, remove the snap ring. (b) Using SST and a press, remove the bearing. SST 09950–00020 (c) Using SST, press in a new bearing. -
Page 426
TF–14 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Input Gear) (d) Select a snap ring that will allow minimum axial play and install it on the shaft. Maximum play: 0.15 mm (0.0059 in.) Thickness mm (in.) Mark INSPECTION OF HUB SLEEVE AND SHIFT FORK MEASURE CLEARANCE OF SHIFT FORK AND HUB SLEEVE Using a feeler gauge, measure the clearance between the… -
Page 427
TF–15 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Idler Gear) Idler Gear COMPONENTS REPLACEMENT OF BEARING 1. IF NECESSARY, REPLACE IDLER GEAR REAR BEARING (a) Using snap ring pliers, remove the snap ring. (b) Using a press and 19 mm socket wrench, remove the bearing. -
Page 428
TF–16 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Idler Gear) 2. IF NECESSARY, REPLACE IDLER GEAR FRONT BEAR- (a) Using SST and a press, press out the bearing. SST 09310–35010 (b) Using SST and a press, press in a new bearing up to the position of the snap ring. -
Page 429: Counter Gear
TF–17 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Counter Gear) Counter Gear COMPONENTS REPLACEMENT OF BEARINGS 1. IF NECESSARY, REPLACE COUNTER GEAR FRONT BEARING AND SUB GEAR (a) Using snap ring pliers, remove the snap ring. (b) Using SST and a press, remove the bearing. SST 09950–00020 (c) Remove the spacer, thrust spring and sub gear.
-
Page 430
TF–18 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Counter Gear) (f) Select a snap ring that will allow minimum axial play and install it on the shaft. Maximum play: 0.15 mm (0.0059 in. ) mm (in.) Mark Thickness 2. IF NECESSARY, REPLACE COUNTER GEAR REAR BEARING (a) Using SST, remove the bearing. -
Page 431
TF–19 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Output Shaft) Output Shaft COMPONENTS DISASSEMBLY OF OUTPUT SHAFT ASSEMBLY REMOVE OUTPUT SHAFT FRONT BEARING, LOW GEAR AND SUB GEAR (a) Using snap ring pliers, remove the snap ring. (b) Using SST and a press, remove the bearing, No. 1 spacer and low gear. -
Page 432
TF–20 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Output Shaft) (d) Using snap ring pliers, remove the snap ring from the low gear. (e) Remove the spacer, thrust spring and sub gear. INSPECTION OF OUTPUT SHAFT ASSEMBLY 1. CHECK OIL CLEARANCE AND THRUST CLEARANCE OF TRANSFER LOW GEAR (a) Using a dial indicator, measure the oil clearance be–… -
Page 433
TF–21 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Output Shaft) (c) Using a dial indicator, measure the thrust clearance with the clutch hub and spacer installed. Standard clearance: 0.09 – 0.27 mm (0.0035 – 0.0106 in.) Maximum clearance: 0.32 mm (0.0126 in.) If the clearance exceeds the limit, replace the spacer. (d) Using a press, remove the ball, spacer, two needle roller bearings and transfer drive gear. -
Page 434
TF–22 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Output Shaft) ASSEMBLY OF OUTPUT SHAFT INSTALL OUTPUT SHAFT FRONT BEARING LOW GEAR AND SUB GEAR (a) Install the sub gear, thrust spring and spacer. (b) Using snap ring pliers, install the snap ring. (c) Apply MP grease to the needle roller bearing. (d) Install the low gear with needle roller bearing to the output shaft. -
Page 435
TF–23 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Front Drive Gear) Front Drive Gear COMPONENTS REPLACEMENT OF BEARINGS 1. IF NECESSARY, REPLACE FRONT DRIVE GEAR FRONT BEARING (a) Press out the bearing. (b) Using SST and a press, press in a new bearing. SST 09316–60010 (09316–00020) 2. -
Page 436
TF–24 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Oil Seals) Oil Seals COMPONENTS REPLACEMENT OF OIL SEALS 1. IF NECESSARY, REPLACE EXTENSION HOUSING OIL SEAL (a) Using SST, remove the two oil seals. SST 09308–00010 (b) Using SST and a hammer, drive in a new oil seal. SST 09310–35010 HINT: When assembling a new oil seal for the oil pump screw, position the flat surface upward. -
Page 437
TF–25 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Oil Seals) 2. IF NECESSARY, REPLACE FRONT DRIVE GEAR OIL SEAL (a) Using SST and a hammer, drive out the oil seal and dust cover. SST 09325–20010 HINT: Place the bearing retainer on something soft such as wooden blocks. -
Page 438
TF–26 TRANSFER – Assembly of Transfer ASSEMBLY OF TRANSFER (See page TF–7) 1. INSTALL OUTPUT SHAFT TO FRONT CASE (a) Using a plastic hammer, install the output shaft to the front case. HINT: Place the front case on something soft such as wooden blocks. -
Page 439
TF–27 TRANSFER – Assembly of Transfer 6. INSTALL REDUCTION GEAR CASE WITH NEW GASKET TO FRONT CASE (a) Place a new gasket on the front case. (b) Install the reduction gear case together with the in– put gear and counter gear. (c) Install and torque the bolts as shown in the figure. -
Page 440
TF–28 TRANSFER – Assembly of Transfer (b) Align the slotted spring hole in the fork with the hole in the shaft. (c) Using a pin punch and hammer, drive in the slotted spring pin. 10. INSTALL INTERLOCK PIN AND FRONT DRIVE SHIFT FORK SHAFT (a) Install the interlock pin. -
Page 441
TF–29 TRANSFER – Assembly of Transfer 13. INSTALL NEEDLE ROLLER BEARINGS, TRANSFER LOWER GEAR AND CLUTCH HUB 14. INSTALL NO. 1 SHIFT FORK AND HUB SLEEVE (a) Install the No.1 shift fork together with the hub sleeve to the front drive shift fork shaft. (b) Align the slotted pin hole in the fork with the hole in the shaft. -
Page 442
TF–30 TRANSFER – Assembly of Transfer 17. INSTALL REAR CASE WITH NEW GASKET (a) Place a new gasket on the front case. (b) Install the rear case together with the idler gear. (c) Install and torque the bolts as shown in the figure. Torque: (A) Bolt length 47 mm (1.85 in.) 39 N–m (400 kgf–cm, 29 ft–lbf) -
Page 443
TF–31 TRANSFER – Assembly of Transfer (c) Using SST to hold the flange, install the washer and nut. Torque the nut. SST 09330–00021 Torque: 123 N–m (1,250 kgf–cm, 90 ft–lbf) (d) Stake the nut. 22. INSTALL FRONT COMPANION FLANGE (a) Install the companion flange to the front drive gear. (b) Using SST to hold the flange, install the washer and nut. -
Page 444
TF–32 TRANSFER – Components (VF1A TYPE TRANSFER) COMPONENTS… -
Page 445
TF–33 TRANSFER – Components COMPONENTS (Cont’d) -
Page 446
TF–34 TRANSFER – Disassembly of Transfer DISASSEMBLY OF TRANSFER (See pages TF–32 and 33) 1. REMOVE SPEEDOMETER DRIVEN GEAR 2. REMOVE TRANSFER INDICATOR SWITCH 3. (22R–E/A340F) REMOVE TRANSFER L4 POSITION SWITCH 4. (22R–E/G58, A340F) REMOVE SHIFT GEAR HEAD NO. 1 AND NO.2 (a) Using a pin punch and hammer, drive out the two slotted spring pins. -
Page 447
TF–35 TRANSFER – Disassembly of Transfer 6.–2 (22R–E/G58, A340F) REMOVE UPPER COVER AND OIL DEFLECTOR Remove the four bolts and the upper cover and oil deflec– tor. 7. REMOVE FRONT COMPANION FLANGE (a) Using a hammer and chisel, loosen the staked part of the nut. -
Page 448
TF–36 TRANSFER – Disassembly of Transfer 10. REMOVE SPEEDOMETER DRIVE GEAR (a) Remove the speedometer drive gear. (b) Using a magnetic finger, remove the ball from the rear output shaft. 11. SEPARATE FRONT CASE AND REAR CASE (a) Remove the twelve bolts. (b) Using a plastic hammer, tap the rear case and sepa–… -
Page 449
TF–37 TRANSFER – Disassembly of Transfer 13. REMOVE FRONT DRIVE FORK SHAFT, FORK AND SPRING (a) Using a pin punch and hammer, drive out the two slotted spring pins. HINT: When the pin is removed from the front drive fork shaft, the shaft will spring loose if the pin punch is re–… -
Page 450
TF–38 TRANSFER – Disassembly of Transfer (d) Using a magnetic finger, remove the straight pin. 14. REMOVE HIGH AND LOW FORK SHAFT, FORK AND STOPPER 15. REMOVE REAR OUTPUT SHAFT, DRIVEN SPROCKET AND CHAIN (a) Using snap ring pliers, remove the snap ring. (b) Mount the rear case in the vise. -
Page 451
TF–39 TRANSFER – Disassembly of Transfer 16. (13150F, G58) REMOVE SYNCHRONIZER RING FROM INPUT SHAFT 17. REMOVE SEPARATER WITH OIL STRAINER (a) Remove the three bolts and the separater with the oil strainer. (b) Remove the 0–ring from the oil strainer pipe. 18. -
Page 452
TF–40 TRANSFER – Disassembly of Transfer (b) Pull out the planetary gear assembly with the input shaft. 21. REMOVE LOW GEAR SPLINE PIECE (a) Using a screwdriver, remove the snap ring. (b) Remove the low gear spline piece. 22. REMOVE NEEDLE ROLLER BEARING FROM INPUT SHAFT 23. -
Page 453
TF–41 TRANSFER – Disassembly of Transfer (b) Remove the input shaft stopper, thrust bearing, race and the two pins. 24. REMOVE INPUT SHAFT, THRUST BEARING AND RACE 25. REMOVE PLANETARY RING GEAR (a) Using a screwdriver, remove the snap ring. (b) Remove the plug, spring and pin. -
Page 454
TF–42 TRANSFER – Disassembly of Transfer 26. INSPECT TRANSFER INDICATOR SWITCH Check that there is continuity between terminals as shown. Switch Position Specified Push Continuity Free No continuity If operation is not as specified, replace the switch. 27. (22R–E/A340F) INSPECT TRANSFER L4 AND NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH Check that there is continuity between terminals as shown. -
Page 455: Oil Pump Body
TF–43 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Oil Pump Body) COMPONENT PARTS Oil Pump Body COMPONENTS DISASSEMBLY OF OIL PUMP BODY 1. CHECK OPERATION OF OIL PUMP Install the oil pump drive gear to the drive rotor, check that the drive rotor turns smoothly. 2.
-
Page 456
TF–44 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Oil Pump Body) (b) Using a magnetic finger, remove the spring and ball. (c) Using SST, pull out the seat. SST 09921–00010 (d) Remove the O–ring from the seat. 3. REMOVE OIL PUMP PLATE (a) Using a torx socket wrench, unscrew the three torx screws. -
Page 457
TF–45 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Oil Pump Body 3. CHECK SIDE CLEARANCE OF BOTH ROTORS Using a steel straight edge and feeler gauge, measure the clearance between the rotors and straight edge. Standard clearance: 0.03 – 0.08 mm (0.0012 – 0.0031 in.) Maximum clearance: 0.08 mm (0.0031 in.) If the clearance exceeds the limit, replace the drive rotor, driven rotor or pump body. -
Page 458
TF–46 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Oil Pump Body) (c) Apply liquid sealer to the plug. Sealant: Part No. 08833–00080, THREE BOND 1344, LOCTITE 242 or equivalent (d) Using SST, torque the plug. SST 09043–38100 Torque: 29 N–m (300 kgf–cm, 22 ft–lbf) 4. -
Page 459: Driven Sprocket
TF–47 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Driven Sprocket) Driven Sprocket COMPONENTS DISASSEMBLY OF DRIVEN SPROCKET 1. REMOVE FRONT BEARING Using a press, remove the front bearing. 2. REMOVE REAR BEARING Using SST and a press, remove the rear bearing. SST 09950–00020…
-
Page 460
TF–48 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Driven Sprocket) ASSEMBLY OF DRIVEN SPROCKET 1. INSTALL REAR BEARING Using a press, install the rear bearing. 2. INSTALL FRONT BEARING Using a press, install the front bearing. HINT: Make sure to install the bearing in the correct di– rection. -
Page 461
TF–49 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Rear Output Shaft Assembly) Rear Output Shaft Assembly COMPONENTS… -
Page 462
TF–50 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Rear Output Shaft Assembly) DISASSEMBLY OF REAR OUTPUT SHAFT ASSEMBLY 1. MEASURE DRIVE SPROCKET THRUST CLEARANCE Using a feeler gauge, measure the drive sprocket thrust clearance. Standard clearance: 0.10 – 0.25 mm (0.0039 – 0.0098 in.) Maximum clearance: 0.25 mm (0.0098 in.) If the clearance exceeds the limit, replace the drive sprocket. -
Page 463
TF–51 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Rear Output Shaft Assembly) 3.–2 (w/o A.D.D.) REMOVE REAR BEARING, SPACER AND DRIVE SPROCKET WITH FRONT DRIVE HUB SLEEVE ASSEMBLY (a) Using SST and a press, remove the bearing. SST 09950–00020 (b) Remove the spacer and ball. (c) Remove the drive sprocket with front drive hub and hub sleeve. -
Page 464
TF–52 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Rear Output Shaft Assembly) INSPECTION OF REAR OUTPUT SHAFT ASSEMBLY 1. INSPECT REAR OUTPUT SHAFT Using a micrometer, measure the outer diameter of the rear output shaft journal surface. Minimum diameter: Part A 27.98 mm (1.1016 in.) B 36.98 mm (1.4559 in.) 2. -
Page 465
TF–53 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Rear Output Shaft Assembly) ASSEMBLY OF REAR OUTPUT SHAFT ASSEMBLY 1.–1 (wI A.D.D.) INSTALL FRONT DRIVE CLUTCH HUB AND HUB SLEEVE (a) Install the front drive hub sleeve onto the clutch hub. HINT: Make sure to install the hub sleeve in the correct direction. -
Page 466
TF–54 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Rear Output Shaft Assembly) 2.–2 (w/o A.D.D.) INSTALL DRIVE SPROCKET WITH FRONT DRIVE HUB SLEEVE ASSEMBLY, SPACER AND REAR BEARING (a) Apply gear oil to the shaft and needle roller bearing. (b) Install the needle roller bearing in the drive sprocket. (c) Install the drive sprocket with the front drive hub sleeve. -
Page 467
TF–55 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Rear Output Shaft Assembly) 5.–1 (MT) INSTALL HIGH AND LOW HUB SLEEVE ASSEMBLY (a) Using SST and a hammer, drive in a new key re– tainer. SST 09316–60010 (09316–00010) NOTICE: Be careful not to deform or damage the key re– tainer. -
Page 468
TF–56 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Input Shaft) Input Shaft COMPONENTS DISASSEMBLY OF INPUT SHAFT REMOVE SUN GEAR (a) Using snap ring pliers, remove the snap ring. (b) Remove the sun gear from the input shaft. INSPECTION OF INPUT SHAFT 1. INSPECT INPUT SHAFT (a) Using a micrometer, measure the outer diameter of the input shaft journal surface. -
Page 469
TF–57 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Input Shaft) (b) Using a dial indicator, measure the inside diameter of the input shaft bushing. Maximum inside diameter: 39.14 mm (1.5409 in.) If the inside diameter exceeds the limit, replace the input shaft. 2. INSPECT SYNCHRONIZER RING (a) Turn the ring and push it in to check the braking ac–… -
Page 470
TF–58 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Planetary Gear) Planetary Gear COMPONENTS INSPECTION OF PLANETARY GEAR 1. MEASURE PLANETARY PINION GEAR THRUST CLEARANCE Using a feeler gauge, measure the planetary pinion gear thrust clearance. Standard clearance: 0.11 – 0.86 mm (0.0043 – 0.0339 in.) Maximum clearance: 0.86 mm (0.0339 in.) If the clearance exceeds the limit, replace the planetary gear assembly. -
Page 471
TF–59 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Planetary Gear) 3. IF NECESSARY, REPLACE PLANETARY GEAR OUTER BEARING (a) Using snap ring pliers, remove the snap ring. (b) Using SST and a press, remove the bearing. SST 09554–30011 and 09555–55010 (c) Using SST and a press, install a new bearing with the outer race snap ring groove toward the front. -
Page 472
TF–60 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Planetary Gear) 4. IF NECESSARY, REPLACE PLANETARY GEAR INNER BEARING (a) Using SST and a press, remove the bearing. SST 09550–10012 (09252–10010, 09557–10010) (b) Using SST and a press, install a new bearing. SST 09550–10012 (09252–10010, 09557–10010) and 09515–30010 Bearing depth: 5.0 –… -
Page 473
TF–61 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Oil Seals) Oil Seals COMPONENTS REPLACEMENT OF OIL SEALS 1. IF NECESSARY, REPLACE FRONT RETAINER OIL SEAL (a) Using a screwdriver and hammer, drive out the oil seal. (b) Using SST and a hammer, drive in a new oil seal un– til its surface is flush with the retainer upper surface. -
Page 474
TF–62 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Oil Seals) 2. IF NECESSARY, REPLACE FRONT CASE OIL SEAL (a) Using a screwdriver and hammer, drive out the oil seal. (b) Using SST and a hammer, drive in a new oil seal un– til its surface is flush with the case upper surface. SST 09316–60010 (09316–00010) (c) Coat the lip of the oil seal with MP grease. -
Page 475
TF–63 TRANSFER – Component Parts (Oil Seals) (b) Using a socket wrench and hammer, drive in a new oil seal. (c) Coat the lip of the oil seal with MP grease. 5. (22R–E/G58, A340F) IF NECESSARY, REPLACE SHIFT FORK SHAFT OIL SEALS (a) Using a screwdriver, pry out the oil seal. -
Page 476
TF–64 TRANSFER – Assembly of Transfer ASSEMBLY OF TRANSFER (See pages TF–32, 33) 1. INSTALL PLANETARY RING GEAR (a) Install the planetary ring gear to the front case. HINT: Make sure to install the ring gear in the correct di– rection. -
Page 477
TF–65 TRANSFER – Assembly of Transfer 3. INSTALL THRUST BEARING AND INPUT SHAFT STOPPER (a) Apply gear oil to the thrust bearing and race. (b) Install the race and thrust bearing. (c) Install the two pins onto the input shaft. (d) Install the input shaft stopper. -
Page 478
TF–66 TRANSFER – Assembly of Transfer 6. INSTALL LOW GEAR SPLINE PIECE (a) Install the low gear spline piece to the planetary car– rier. (b) Install the snap ring. HINT: Be sure the end gap of the snap ring is not aligned with cutout portion of the planetary carrier. -
Page 479
TF–67 TRANSFER – Assembly of Transfer 9. INSTALL OIL PUMP BODY ASSEMBLY (a) Install the oil pump body assembly. (b) Install and torque the three bolts. Torque: 11 N–m (115 kgf–cm, 8 ft–lbf) 10. INSTALL SEPARATER WITH OIL STRAINER (a) Coat a new O–ring with gear oil and install it to the oil strainer pipe. -
Page 480
TF–68 TRANSFER – Assembly of Transfer 12. INSTALL HIGH AND LOW FORK SHAFT, FORK AND STOPPER (a) Place the high and low shift fork into the groove of the hub sleeve. HINT: Make sure to install the shift fork in the correct direction. -
Page 481
TF–69 TRANSFER – Assembly of Transfer (e) Using a pin punch and hammer, drive in the two slotted spring pins. HINT: When installing the pin in the front drive fork shaft, push the shaft towards the rear case and install the pin while the spring is compressed. -
Page 482
TF–70 TRANSFER – Assembly of Transfer (b) Shift the high and low hub sleeve to low side (rear side). (c) Assemble the front case and rear case. (d) Install and torque the twelve bolts. Torque: 37 N–m (380 kgf–cm, 27 ft–lbf) 16. -
Page 483
TF–71 TRANSFER – Assembly of Transfer 19. INSTALL REAR COMPANION FLANGE HINT: Rear companion flange bolts are black. Install the rear companion flange in the same way as the front companion flange. 20.–1 (3VZ–E/R 150F) INSTALL CONTROL RETAINER (a) Install the select return spring to the control re– tainer. -
Page 484
TF–72 TRANSFER – Assembly of Transfer 22. (22R–E1G58, A340F)) INSTALL SHIFT GEAR HEAD NO. 1 AND NO.2 (a) Install two shift gear heads. (b) Using a pin punch and hammer, drive in the two slotted spring pins. 23. CHECK FOLLOWING ITEMS: (a) Check to see that the input shaft and output shafts rotate smoothly. -
Page 485
PR–1 PROPELLER SHAFT – PROPELLER SHAFT… -
Page 486
PR–2 PROPELLER SHAFT – PRECAUTIONS PRECAUTIONS Be careful not to grip the propeller shaft tube too tightly in the vise as this will cause deformation. TROUBLESHOOTING You will find the cause of trouble more easily by properly using the table shown below. In this table, the numbers indicate the priority of the probable cause of trouble. -
Page 487
PR–3 PROPELLER SHAFT – PROPELLER SHAFT PROPELLER SHAFT COMPONENTS… -
Page 488
PR–4 PROPELLER SHAFT – PROPELLER SHAFT… -
Page 489
PR–5 PROPELLER SHAFT – PROPELLER SHAFT PROPELLER SHAFT REMOVAL (2WD) 1. DISCONNECT PROPELLER SHAFT FLANGE FROM COMPANION FLANGE ON DIFFERENTIAL (a) Put matchmarks on the flanges. (b) Remove the four and nuts. 2. REMOVE CENTER SUPPORT BEARING FROM FRAME CROSSMEMBER (3–JOINT TYPE) 3. -
Page 490
PR–6 PROPELLER SHAFT – PROPELLER SHAFT 2. REMOVE FRONT PROPELLER SHAFT NO.2 DUST COVER (W/RF1 A Type Transfer) Remove the two bolts and two nuts and cover. (w/VF1 A Type Transfer and A340H) Remove the four bolts and cover. 3. REMOVE FRONT PROPELLER SHAFT DUST COVER SUBASSEMBLY (w/VF1 a Type Transfer and A340H) Remove the three bolts and cover. -
Page 491
PR–7 PROPELLER SHAFT – PROPELLER SHAFT 7. REMOVE REAR PROPELLER SHAFT (a) Put matchmarks on the flanges. (b) Remove the four and nuts. (c) Remove the rear propeller shaft. PROPELLER SHAFT DISASSEMBLY 1. SEPARATE PROPELLER SHAFT AND INTERMEDI– ATE SHAFT (a) Put matchmarks on the flanges. -
Page 492
PR–8 PROPELLER SHAFT – PROPELLER SHAFT 3. REMOVE SLEEVE YOKE FROM PROPELLER SHAFT (4WD) (a) Place matchmarks on the sleeve yoke and shaft. (b) Pull out the sleeve yoke from the shaft. PROPELLER SHAFT INSPECTION COMPONENTS 1. INSPECT PROPELLER AND INTERMEDIATE SHAFTS FOR DAMAGE OR RUNOUT If shaft runout is greater than maximum, replace the shaft. -
Page 493
PROPELLER SHAFT SPIDER BEARING REPLACEMENT 1. PLACE MATCHMARKS ON SHAFT AND YOKE 2. REMOVE SNAP RINGS (TOYOTA type) (a) Slightly tap in the bearing outer races. (b) Using two screwdrivers, remove the four snap rings from the grooves. (DANA type) (a) Slightly tap in the bearing outer races. -
Page 494
PR–10 PROPELLER SHAFT – PROPELLER SHAFT (c) Install the two removed bearing outer races to the spider. (d) Using SST, push out the bearing from the yoke. SST 09332 – 25010 (e) Clamp the outer bearing race in a vise and tap off the yoke with a hammer. -
Page 495
6. INSTALL SNAP RINGS (a) Install two snap rings of equal thickness which will allow 0–0.05 mm (0–0.0020 in.) axial play. HINT: Do not reuse the snap rings. (TOYOTA type) Thickness mm (in.) Mark Color… -
Page 496
PR–12 PROPELLER SHAFT – PROPELLER SHAFT (DANA type) Color Thickness mm (in.) Blue Yellow Silver Copper Black Green (b) Using a hammer, tap the yoke until there is no clear– ance between the bearing outer race and snap ring. 7. CHECK SPIDER BEARING (a) Check that the spider bearing moves smoothly. -
Page 497
PR–13 PROPELLER SHAFT – PROPELLER SHAFT HINT: When replacing the rear propeller shaft spider on 4WD vehicles, be sure that the grease fitting as– sembly hole is facing in the direction shown in the figure. -
Page 498
PR–14 PROPELLER SHAFT – PROPELLER SHAFT PROPELLER SHAFT ASSEMBLY HINT: When replacing the propeller shaft, install the new parts facing as shown in the illustration. 1. INSTALL CENTER SUPPORT BEARING ON INTER– MEDIATE SHAFT HINT: Install the center support bearing with the cutout toward the rear. -
Page 499
PR–15 PROPELLER SHAFT – PROPELLER SHAFT 2. INSTALL FLANGE ON INTERMEDIATE SHAFT (a) Coat the splines of the intermediate shaft with MP grease. (b) Place the flange on the shaft and align the match– marks. HINT: If replacing either the center flange or inter– mediate shaft, reassemble them so that the front yoke of the intermediate shaft and the rear yoke of the propeller shaft are facing in the same direction. -
Page 500
PR–16 PROPELLER SHAFT – PROPELLER SHAFT (b) Push the yoke into the transmission. 2. CONNECT PROPELLER SHAFT FLANGE TO CON– PANION FLANGE ON DIFFERENTIAL (a) Align the matchmarks on the flanges with four bolts and nuts. (b) Torque the bolts and nuts. Torque: 4WD 3VZ–E [MT] 76 N–m (780 kgf–cm, 56 ft–lbf) -
Page 501
PR–17 PROPELLER SHAFT – PROPELLER SHAFT 2. INSTALL FRONT PROPELLER SHAFT DUST COVER SUBASSEMBLY (W/VF1 A Type Transfer and A340H) (a) Install the cover. (b) Install and torque the three bolts. Torque: A bolts 36 N–m (370 kgf–cm, 27 ft–lbf) B bolts 23 N–m (230 kgf–cm, 17 ft–lbf) 3. -
Page 502
PR–18 PROPELLER SHAFT – PROPELLER SHAFT 6. CONNECT REAR PROPELLER SHAFT FLANGE TO COMPANION FLANGE ON TRANSFER (a) Align the matchmarks on the flanges and connect the flanges with four bolts and nuts. (b) Torque the bolts and nuts. Torque: 3VZ–E [MT] 76 N–m (780 kgf–cm, 56 ft–lbf) Ex. -
Page 503
PR–19 PROPELLER SHAFT – SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS SERVICE DATA Propeller shaft runout Spider bearing axial play Spider bearing selection Bearing cup outer diameter Bearing hole inner diameter Snap ring thickness TMC – made DANA–made… -
Page 504
PR–20 PROPELLER SHAFT – SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS Part tightened Front differential x Front propeller shaft (4WD) Front propeller shaft x Transfer (4WD) Propeller shaft x Rear differential Propeller shaft x Transfer Intermediate shaft x Propeller shaft (4WD) Propeller shaft x Differential (2WD) Intermediate shaft x Propeller shaft (2WD) Center support bearing x Frame Intermediate shaft x Center bearing x Joint flange… -
Page 505
SA–1 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – SUSPENSION AND AXLE… -
Page 506
SA–2 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Troubleshooting TROUBLESHOOTING Page Remedy Problem Possible cause Inflate tires to proper pressure or Tires worn or improperly inflated Wanders/pulls Alignment incorrect replace tires SA–3 SA–6 Check front alignment Wheel bearing adjusted too tight SA–13 SA–39 Front or rear suspension parts loose Adjust wheel bearing SA–17,… -
Page 507
SA–6 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Wheel Alignment (4WD) WHEEL ALIGNMENT 1. MAKE FOLLOWING CHECKS AND CORRECT ANY PROBLEMS (a) Check the tires for wear and proper inflation. Cold tire inflation pressure: See page A–25 (b) Check the wheel runout. Lateral runout: 1.2 mm (0.047 in.) or less (c) Check the front wheel bearings for looseness. -
Page 508
SA–7 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Wheel Alignment (4WD) If camber and/or caster are not within specification, ad– just by front and/or rear adjusting cams. (See Adjustment Chart) How to Read the Chart (Alignment measured with vehicle height set to stan- dard height for wheel alignment inspection) (a) Mark on the adjustment chart the alignment values… -
Page 509
SA–8 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Wheel Alignment (4WD) (c) Mark on the adjustment chart the alignment values measured at the non–loaded vehicle height. Example: Camber 1E 00’ Caster 2E 30’ (d) As shown in the illustration, read the distance from the standard value to the measured value, and ad–… -
Page 510
SA–9 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Wheel Alignment (4WD) 5. ADJUST WHEEL ANGLE Remove the caps of the knuckle stopper bolts and check the steering angles. Wheel angle 32E 00’ +1 Inside wheel –2 Max. Outside wheel at 200 Inside wheel 10’… -
Page 511
SA–10 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Wheel Alignment (4WD) (d) Torque the tie rod. Torque: 22 N–m (225 kgf–cm, 16 ft–lbf) HINT: Face the clamp bolt toward the front of the vehicle. 8. INSPECT SIDE SLIP (REFERENCE ONLY) Side slip: 3.0 mm/m (0.118 in./3.3 ft) or less… -
Page 512
SA–3 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Wheel Alignment (2WD) WHEEL ALIGNMENT 1. MAKE FOLLOWING CHECKS AND CORRECT ANY PROBLEMS (a) Check the tires for wear and proper inflation. Cold tire inflation pressure: See page A–23 (b) Check the wheel runout. Lateral runout: 1.2 mm (0.047 in.) or less (c) Check the front wheel bearings for looseness. -
Page 513
SA–4 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Wheel Alignment (2WD) 3. INSTALL WHEEL ALIGNMENT EQUIPMENT Follow the specific instructions of the equipment manu– facturer. 4. ADJUST WHEEL ANGLE Remove the caps of the knuckle stopper bolts and check the steering angles. Steering angles: See page A–24 HINT: When the steering wheel is fully turned, make sure that the wheel is not touching the body or brake flexible hose. -
Page 514
SA–5 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Wheel Alignment (2W–D) If camber caster is not within specification, adjust by adding or removing shims on the upper arm. Shim thickness mm (in. ) Thickness (0.157) (0.063) (0.047) If the steering axis inclination is not as specified after camber and caster have been correctly adjusted, recheck the steering knuckle and front wheel for bending or loose–… -
Page 515
SA–11 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Axle Hub and Steering Knuckle FRONT AXLE HUB AND STEERING KNUCKLE COMPONENTS… -
Page 516
SA–12 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Axle Hub and Steering Knuckle (Front Axle Hub) Front Axle Hub (See page SA–11) DISASSEMBLY OF FRONT AXLE HUB 1. REMOVE DISC BRAKE CYLINDER AND TORQUE PLATE (a) Remove the brake cylinder and suspend it with wire. (b) Remove the torque plate. -
Page 517
SA–13 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Axle Hub and Steering Knuckle (Front Axle Hub) (b) Using SST, carefully drive in a new bearing outer race. SST 09608–30012 (Inside race 09608–04020, 09608–04100) (Outside race 09608–04020, 09608–04060) ASSEMBLY OF FRONT AXLE HUB 1. -
Page 518
SA–14 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Axle Hub and Steering Knuckle (Front Axle Hub) (b) Snug down the bearing by turning the hub several times. (c) Loosen the nut until it can be turned by hand. (d) Using a spring tension gauge, measure and make a note of the frictional force of the oil seal. -
Page 519
SA–15 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Axle Hub and Steering Knuckle (Steering Knuckle) Steering Knuckle (See page SA–11) REMOVAL OF STEERING KNUCKLE 1. REMOVE FRONT AXLE HUB AND BRAKE CALIPER (See page SA–12) 2. REMOVE DUST COVER (a) Remove the two bolts. (b) Remove the two cotter pins, nuts and bolts and re–… -
Page 520
SA–16 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Axle Hub and Steering Knuckle (Steering Knuckle) INSTALLATION OF STEERING KNUCKLE 1. INSTALL STEERING KNUCKLE (a) Support the lower arm with a jack. (b) Install the steering knuckle to the upper ball joint and install the nut. (c) Push the upper arm and steering knuckle down and install the steering knuckle to the lower ball joint and install the nut. -
Page 521
SA–17 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Suspension FRONT SUSPENSION COMPONENTS… -
Page 522
SA–18 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Suspension (Ball Joint) Ball Joint (See page SA–17) INSPECTION OF BALL JOINTS 1. INSPECT LOWER BALL JOINT FOR EXCESSIVE LOOSENESS (a) Jack up the front of the vehicle and support it with stands. (b) Make sure the front wheels are in a straight forward position, and depress the brake pedal. -
Page 523
SA–19 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Suspension (Ball Joint) INSTALLATION OF BALL JOINTS 1. INSTALL UPPER BALL JOINT TO UPPER ARM Torque: 31 N–m (320 kgf–cm, 23 ft–lbf) 2. INSTALL LOWER BALL JOINT TO LOWER ARM Torque: 127 N–m (1,300 kgf–cm, 94 ft–lbf) 3. -
Page 524
SA–20 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Suspension (Torsion Bar Spring) Torsion Bar Spring (See page SA–17) REMOVAL OF TORSION BAR SPRING 1. JACK UP AND SUPPORT FRAME ON STANDS 2. REMOVE LOCK NUT AND MEASURE PROTRUDING BOLT END ”A”, AS SHOWN HINT: Use this measurement for reference when adjust–… -
Page 525
SA–21 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Suspension (Torsion Bar Spring) (d) Install the torsion bar spring torque arm side and in– stall the anchor arm to the adjusting bolt. (e) Torque the torque arm nuts. Torque: 49 N–m (500 kgf–cm, 36 ft–lbf) (f) Tighten the adjusting nut so that the bolt protrusion is equal to that before removal. -
Page 526
SA–22 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Suspension (Lower Suspension Arm and Shock Absorber) Lower Suspension Arm and Shock Absorber (See page SA–17) REMOVAL OF LOWER SUSPENSION ARM AND SHOCK ABSORBER 1. REMOVE TORSION BAR SPRING (See page SA–20) 2. DISCONNECT TIE ROD END (a) Remove the cotter pin and nut. -
Page 527
SA–23 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Suspension (Lower Suspension Arm and Shock Absorber) 7. REMOVE LOWER SUSPENSION ARM Remove the nut and lower suspension arm. REPLACEMENT OF LOWER ARM BUSHING 1. REMOVE BUSHING (a) Cut off the bushing rubber as shown in the figure. (b) Using SST, remove the bushing. -
Page 528
SA–24 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Suspension (Lower Suspension Arm and Shock Absorber) 3. CONNECT STRUT BAR TO LOWER ARM Torque: 95 N–m (970 kgf–cm, 70 ft–lbf) 4. CONNECT STABILIZER BAR TO LOWER SUSPENSION Torque: 13 N–m (130 kgf–cm, 9 ft–lbf) 5. -
Page 529
SA–25 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Suspension (Upper Suspension Arm) Upper Suspension Arm (See page SA–17) REMOVAL OF UPPER SUSPENSION ARM 1. DISCONNECT UPPER BALL JOINT FROM UPPER ARM (a) Support the lower arm with a jack. (b) Remove the four bolts and nuts, and disconnect the upper arm. -
Page 530
SA–26 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Suspension (Upper Suspension Arm) INSTALLATION OF UPPER SUSPENSION 1. INSTALL UPPER ARM (a) Install the upper arm together with the camber ad– justing shims. (b) Torque the bolts. Torque: 96 N–m (980 kgf–cm, 71 ft–lbf) HINT: Install an equal number and thickness of shims in their original position. -
Page 531
SA–27 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Suspension (Strut Bar) Strut Bar (See page SA–17) REMOVAL OF STRUT BAR 1. PLACE MATCHMARKS ON STRUT BAR 2. REMOVE FRONT NUT FROM STRUT BAR 3. REMOVE STRUT BAR FROM LOWER ARM Remove the nuts holding the strut bar to the lower arm, and remove the strut bar. -
Page 532
SA–28 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Suspension (Stabilizer Bar) Stabilizer Bar (See page SA–17) REMOVAL OF STABILIZER BAR 1. REMOVE ONE TORSION BAR SPRING (See page SA–20) 2. REMOVE STABILIZER BAR FROM LOWER ARMS (a) Remove the nuts and cushions holding both sides of the stabilizer bar from the lower arms, and discon–… -
Page 533
SA–29 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Free Wheeling Hub FREE WHEELING HUB COMPONENTS… -
Page 534
SA–30 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Free Wheeling Hub REMOVAL OF FREE WHEELING HUB 1. REMOVE FREE WHEELING HUB COVER (a) Set the control handle to FREE. (b) Remove the cover mounting bolts and pull off the cover. 2. REMOVE BOLT WITH WASHER 3. -
Page 535
SA–31 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Free Wheeling Hub (d) Remove the steel ball, spring and seal from the con– trol handle. INSPECTION OF FREE WHEELING HUB 1. INSPECT COVER, HANDLE AND SEAL Temporarily install the handle in the cover and check that the handle moves smoothly and freely. -
Page 536
SA–32 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Free Wheeling Hub 3. INSTALL TENSION SPRING IN CLUTCH Install the tension spring in the clutch with the spring end aligned with the initial groove. 4. INSTALL FOLLOWER PAWL TO CLUTCH (a) Place the follower pawl on the tension spring with one of the large tabs against the bent spring end. -
Page 537
SA–33 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Free Wheeling Hub (b) Insert the cover in the body and verify that the inner hub turns smoothly. (c) Remove the cover from the body. INSTALLATION OF FREE WHEELING HUB 1. INSTALL FREE WHEELING HUB BODY (a) Place a new gasket in position on the front axle hub. -
Page 538
SA–34 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Free Wheeling Hub (c) Install the cover to the body with the follower pawl tabs aligned with the non–toothed portions of the body. (d) Tighten the cover mounting bolts. Torque: 10 N–m (100 kgf–cm, 7 ft–lbf) -
Page 539
SA–35 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Axle Hub and Steering Knuckle FRONT AXLE HUB AND STEERING KNUCKLE COMPONENTS… -
Page 540
SA–40 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Axle Hub and Steering Knuckle (Steering Knuckle) Steering Knuckle (See page SA–35) REMOVAL OF STEERING KNUCKLE 1. REMOVE DISC BRAKE CYLINDER AND FRONT AXLE (See page SA–36) 2. REMOVE DUST COVER AND OIL SEAL 3. -
Page 541
SA–41 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Axle Hub and Steering Knuckle (Steering Knuckle) 7. REMOVE SNAP RING AND SPACER Using snap pliers, remove the snap ring and spacer. 8. REMOVE STEERING KNUCKLE (a) Remove the cotter pin and nut from the upper ball joint. -
Page 542
SA–42 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Axle Hub and Steering Knuckle (Steering Knuckle) 2. REMOVE DUST DEFLECTOR Using a screwdriver, pry out the dust deflector from the steering knuckle. 3. REMOVE STEERING KNUCKLE BUSHING (a) Using SST, pull out the steering knuckle outside bushing. -
Page 543
SA–43 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Axle Hub and Steering Knuckle (Steering Knuckle) (c) Apply molybdenum disulphide lithium base grease to the steering knuckle bushings. 5. INSTALL DUST DEFLECTOR TO STEERING KNUCKLE Using SST and a hammer, tap in a new dust deflector. SST 09608–35014 (09608–06020, 09608–06180) INSTALLATION OF STEERING KNUCKLE (See page SA–35) -
Page 544
SA–44 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Axle Hub and Steering Knuckle (Steering Knuckle) (d) Connect the upper ball joint to the steering knuckle and install and torque the nut. Torque: 142 N–m (1,450 kgf–cm, 105 ft–lbf) (e) Install a new cotter pin. 2. -
Page 545
SA–45 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Axle Hub and Steering Knuckle (Steering Knuckle) 5. CONNECT KNUCKLE ARM TO STEERING KNUCKLE (a) Clean the threads of the bolts and steering knuckle with toluene or trichloroethylene. (b) Apply sealant to the bolt threads. Sealant: Part No. -
Page 546: Front Drive Shaft
SA–46 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Drive Shaft FRONT DRIVE SHAFT COMPONENTS REMOVAL OF FRONT DRIVE SHAFT 1. LOOSEN NUTS HOLDING FRONT DRIVE SHAFT Loosen the six nuts, while depressing the brake pedal. 2. REMOVE FREE WHEELING HUB OR FLANGE (Free wheeling hub See page SA–29) (Flange…
-
Page 547
SA–47 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Drive Shaft 4. REMOVE FRONT DRIVE SHAFT First pull the front drive shaft inboard joint tulip from the side gear shaft, and then pull it out from the steering knuckle. DISASSEMBLY OF FRONT DRIVE SHAFT 1. -
Page 548
SA–48 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Drive Shaft (c) Using a brass bar and hammer, remove the tripod joint from the drive shaft. 5. REMOVE INBOARD JOINT BOOT 6. REMOVE OUTBOARD JOINT BOOT CLAMPS AND BOOT NOTICE: Do not disassemble the outboard joint. 7. -
Page 549
SA–49 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Drive Shaft 2. TEMPORARILY INSTALL BOOT AND NEW BOOT CLAMPS TO OUTBOARD JOINT HINT: Before installing the boot, wrap vinyl tape around the spline of the shaft to prevent damaging the boot. 3. TEMPORARILY INSTALL BOOT AND NEW BOOT CLAMPS FOR INBOARD JOINT TO DRIVE SHAFT 4. -
Page 550
SA–50 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Drive Shaft (d) Using a snap ring expander, install a new snap ring. 5. ASSEMBLE BOOT TO OUTBOARD JOINT Before assembling the boot, pack in grease. HINT: Use the grease (black) supplied in the boot kit. Grease capacity: 195 –… -
Page 551
SA–51 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Drive Shaft (c) Insure that the boot is not stretched or contracted when the drive shaft is at standard length. Standard length: 393.9 – 403.9 mm (15.508 – 15.902 in.) INSTALLATION OF FRONT DRIVE SHAFT (See page SA–46) 1. -
Page 552
SA–52 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Drive Shaft 4. INSTALL FREE WHEELING HUB OR FLANGE (Free wheeling hub See page SA–33) (Flange See page SA–39) 5. TORQUE FRONT DRIVE SHAFT INSTALLATION NUTS Torque the six nuts, while depressing the brake pedal. Torque: 83 N–m (845 kgf–cm, 61 ft–Ibf ) -
Page 553
SA–53 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (On–Vehicle Replacement of Rear Oil Seal) FRONT DIFFERENTIAL On–Vehicle Replacement of Rear Oil Seal 1. DRAIN DIFFERENTIAL OIL 2. DISCONNECT PROPELLER SHAFT Before disconnecting the propeller shaft from the front differential, place matchmarks on them. 3. -
Page 554
SA–54 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (On–Vehicle Replacement of Rear Oil Seal) (c) Using SST, remove the companion flange. SST 09557–22022 (09557–22030) 4. REMOVE OIL SEAL AND OIL SLINGER (a) Using SST, remove the oil seal. SST 09308–10010 (b) Remove the oil slinger. 5. -
Page 555
SA–55 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (On–Vehicle Replacement of Rear Oil Seal) 8. INSTALL COMPANION FLANGE (a) Using SST, install the companion flange on the drive pinion. SST 09557–22022 (09557–22030) (b) Coat the threads of the new nut with MP grease. (c) Using SST to hold the flange, torque the nut. -
Page 556
12. INSTALL DRAIN PLUG AND FILL DIFFERENTIAL WITH GEAR OIL (w/ A.D.D.) Oil type: Toyota ”GEAR OIL SUPER” oil (Part No. 08885 – 02106) or hypoid gear oil API GL–5 Recommended oil viscosity: SAE 75W–90 Capacity: 1.86 liters (1.97 US qts, 1.64 Imp. qts) (w/o A.D.D.) -
Page 557
SA–57 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Removal of Front Differential) Removal of Front Differential 1. DRAIN DIFFERENTIAL OIL 2. DISCONNECT PROPELLER SHAFT Before disconnecting the propeller shaft, place match– marks. 3. DISCONNECT DRIVE SHAFTS FROM SIDE GEAR SHAFT Loosen the six nuts, while depressing the brake pedal, and disconnect the drive shafts from the side gear shaft. -
Page 558
SA–58 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Removal of Front Differential) 5. REMOVE FRONT DIFFERENTIAL FRONT MOUNTING BOLT AND NUT 6. REMOVE FRONT DIFFERENTIAL (a) Hold the front differential with a jack. (b) Remove the left and right rear mounting bolts, and remove the front differential. -
Page 559
SA–59 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Replacement of Side Oil Seal – without A.D.D.) Replacement of Side Oil Seal (without A.D.D.) 1. REMOVE SIDE GEAR SHAFT Using SST, pull off the side gear shaft from the front dif– ferential. SST 09910–00015 (09911–00011, 09912–00010, 09914–00011) 2. -
Page 560
SA–60 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Replacement of Side Oil Seal – w/o A D D ) 4. INSTALL NEW SIDE GEAR SHAFT OIL SEAL (a) Using SST, drive in the oil seal until it is flush with the carrier end surface. SST 09550–22011 (09550–00020, 09550–00031) (b) Coat the lip of oil seal with MP grease. -
Page 561
SA–61 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Replacement of Side Oil Seal w/ A D D) Replacement of Side Oil Seal (with A.D.D.) REPLACEMENT OF LH SIDE OIL SEAL 1. REMOVE ACTUATOR (a) Remove the four bolts. (b) Using a hammer, remove the actuator. 2. -
Page 562
SA–62 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front DifferentiaL (Replacement of Side Oil Seal – w/ A D D ) (b) Using a plastic–faced hammer, tap on the tube to re– move it. (c) Remove the sleeve. (d) Remove the O–ring from the tube. 3. -
Page 563
SA–63 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front DifferentiaL (Replacement of Side Oil Seal – w/ A D D ) (b) With the oil seal lip facing upward, use press and plate to press in a new side oil seal until its end is flush with the surface of the tube. -
Page 564
SA–64 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Replacement of Side Oil Seal – w/ A D D ) 8. INSTALL SIDE GEAR SHAFT WITH TUBE TO DIFFERENTIAL CARRIER (a) Install a new 4–ring to the tube. (b) Install the sleeve onto the clutch hub. (c) Install the side gear shaft with tube. -
Page 565
SA–65 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Replacement of Side Oil Seal – w/ A D D ) 2. REPLACE SIDE OIL SEAL (a) Using SST, remove the oil seal. SST 09308–00010 (b) Using SST, install the new oil seal. SST 09550–22011 (09550–00020, 09550–0003) (c) Coat the lip of oil seal with MP grease. -
Page 566
SA–66 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/o A D D ) Disassembly and Assembly of Differential (with out A.D.D.) -
Page 567
SA–67 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/o A D D ) DISASSEMBLY OF DIFFERENTIAL 1. REMOVE DIFFERENTIAL COVER Remove the eight bolts and tap off the cover with a plastic–faced hammer. 2. CHECK SIDE GEAR BACKLASH Measure the side gear backlash while holding one pinion gear toward the case. -
Page 568
SA–68 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/o A D D ) 6. CHECK RING GEAR RUNOUT Using a dial indicator, measure the ring gear runout. Maximum runout: 0.07 mm (0.0028 in.) If the runout is greater than maximum, replace the ring gear and drive pinion as a set. -
Page 569
SA–69 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/o A D D ) (b) Using SST to hold the flange, remove the nut. SST 09330–00021 (c) Using SST, remove the companion flange. SST 09557–22022 (09557–22030) 12. REMOVE OIL SEAL AND OIL SLINGER (a) Using SST, remove the oil seal from the housing. -
Page 570
SA–70 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/o A D D ) (c) Using SST and a hammer, remove the two side bearing preload adjusting plate washers. SST 09504–22011 HINT: Measure the adjusting plate washer and note the thickness. -
Page 571
SA–71 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/o A D D ) 3. REMOVE SIDE BEARING FROM DIFFERENTIAL CASE Using SST, remove the side bearing from the differential case. SST 09950–20017 HINT: Fix the claws of SST to the notches in the differ– ential case. -
Page 572
SA–72 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/o A D D ) (b) Check the side gear backlash. Temporarily install the side gear shaft. • Measure the side gear backlash while holding • one pinion gear toward the case. Side gear backlash: 0.05 –… -
Page 573
SA–73 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/o A D D ) 8. INSTALL SIDE BEARINGS Using a press and SST, drive in the side bearings into the differential case. SST 09226–10010, 09950–20017 9. CHECK RING GEAR RUNOUT (a) Install the differential case onto the carrier and in–… -
Page 574
SA–74 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/o A D D ) ASSEMBLY OF DIFFERENTIAL (See page SA–67) 1. TEMPORARILY ADJUST DRIVE PINION PRELOAD (a) Install the following parts. Drive pinion • Front bearing • HINT: Assemble the spacer and oil seal after adjusting the gear contact pattern. -
Page 575
SA–75 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/o A D D ) 3. ADJUST RING GEAR BACKLASH (a) Install only the plate washer on the ring gear back side. HINT: Insure that the ring gear has backlash. (b) Snug down the washer and bearing by tapping on the ring gear with a plastic–faced hammer. -
Page 576
SA–76 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/o A D D ) (f) Remove the plate washers and differential case. (g) Install the plate washer into the lower part of the carrier. (h) Place the other plate washer onto the differential case together with the outer race, and install the dif–… -
Page 577
SA–77 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/o A D D ) 4. ADJUST SIDE BEARING PRELOAD (a) Remove the ring gear teeth plate washer and mea– sure the thickness. (b) Using the backlash as a reference, install a new washer of 0.06 –… -
Page 578
SA–78 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/o A D D ) 6. MEASURE TOTAL PRELOAD Using a torque wrench, measure the total preload. Total preload (starting): Add drive pinion preload 0.4 – 0.6 N–m (4 –… -
Page 579
SA–79 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/o A D D ) 8. REMOVE COMPANION FLANGE (See step 11 on page SA–68) 9. REMOVE FRONT BEARING (See step 12 on page SA–69) 10. INSTALL NEW BEARING SPACER AND FRONT BEARING (a) Install a new bearing spacer on the drive pinion. -
Page 580
SA–80 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/o A D D ) (a) If the preload is greater than specification, replace the bearing spacer. (b) If the preload is less than specification, retighten the nut 13 N–m (130 kgf–cm, 9 ft–lbf) a little at a time until the specified preload is reached. -
Page 581
SA–81 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/o A D D ) 17. INSTALL DIFFERENTIAL TUBE Install the differential tube to the differential carrier with the four bolts. Torque: 88 N–m (900 kgf–cm, 65 ft–lbf) 18. -
Page 582
SA–82 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/ A D D ) Disassembly and Assembly of Differential (with A.D.D.) -
Page 583
SA–83 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/ A D D ) DISASSEMBLY OF DIFFERENTIAL 1. REMOVE ACTUATOR (a) Remove the four bolts. (b) Using a hammer, remove the actuator. 2. REMOVE DIFFERENTIAL CARRIER COVER Remove the eight bolts and tap off the cover with a plastic–faced hammer. -
Page 584
SA–84 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/ A D D ) (c) Remove the sleeve. (d) Remove the 0–ring from the tube. 5. REMOVE CLUTCH CASE (a) Remove the two torx bolts. Torx wrench: E14 (Part No. 09044–00010 or locally manufactured tool) (b) Using a plastic–faced hammer, tap on the clutch case to remove it. -
Page 585
SA–85 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/ A D D ) 8. REMOVE RH SIDE OIL SEAL Using SST, remove the oil seal. SST 09308–00010 9. CHECK RING GEAR RUNOUT Using a dial indicator, measure the ring gear runout. Maximum runout: 0.07 mm (0.0028 in.) If the runout is greater than maximum, replace the ring gear and drive pinion as a set. -
Page 586
SA–86 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/ A D D ) 14. REMOVE COMPANION FLANGE (a) Using a hammer and chisel, loosen the staked part of the nut. (b) Using SST to hold the flange, remove the nut. SST 09330–00021 (c) Using SST, remove the companion flange. -
Page 587
SA–87 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/ A D D ) 17. REMOVE DIFFERENTIAL CASE AND RING GEAR (a) Place matchmarks on the bearing cap and differen– tial carrier. (b) Remove the two bearing caps. (c) Using SST and a hammer, remove the two side bearing preload adjusting plate washers. -
Page 588
SA–88 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/ A D D ) 2. REPLACE DRIVE PINION FRONT AND REAR BEARING OUTER RACES (a) Using a brass bar and hammer, drive out the outer race. (b) Using SST, drive in a new outer race. SST 09608–35014 Front outer race (09608–06020, 09608–06120) Rear outer race (09608–06020, 09608–06110) -
Page 589
SA–89 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/ A D D ) 6. ASSEMBLE DIFFERENTIAL CASE (a) Using SST, press the new needle bearing into the differential case. NOTICE: Press in the bearings, with the engraved side of each bearing facing outward from the differential case. -
Page 590
SA–90 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/ A D D ) (g) Stake the case. 7. INSTALL RING GEAR ON DIFFERENTIAL CASE (a) Clean the contact surfaces of the differential case and ring gear. (b) Heat the ring gear in boiling water. -
Page 591
SA–91 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/ A D D ) 9. CHECK RING GEAR RUNOUT (a) Install the differential case onto the carrier and in– stall the plate washers to where there is no play in the bearing. -
Page 592
SA–92 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/ A D D ) (b) Using a press and SST, remove the bearing. SST 09950–00020 (c) Remove the bearing retainer. (d) Install the bearing retainer. (e) Using a press and SST, install the new bearing. SST 09316–60010 (09316–00040) NOTICE: Be careful not to damage the bearing retainer. -
Page 593
SA–93 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/ A D D ) (b) Using a snap ring expander, install the snap ring. INSPECTION AND REPLACEMENT OF ACTUATOR 1. MEASURE CLEARANCE OF SLEEVE FORK AND CLUTCH SLEEVE Using a feeler gauge, measure the clearance between the sleeve fork and clutch sleeve. -
Page 594
SA–94 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/ A D D ) 4. REMOVE SLEEVE FORK PIN (a) Using SST, remove the screw plug. SST 09313–30021 (b) Using a hammer and punch, drive out the pin through the hole of clutch case cover. -
Page 595
SA–95 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/ A D D ) (d) Tighten the two bolts. Torque: 21 N–m (210 kgf–cm, 15 ft–lbf) 7. INSTALL SLEEVE FORK PIN (a) Using a hammer and punch, drive in the pin through the hole of clutch case cover. -
Page 596
SA–96 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/ A D D ) ASSEMBLY OF DIFFERENTIAL (See page SA–83) 1. TEMPORARILY ADJUST DRIVE PINION PRELOAD (a) Install the following parts. Drive pinion • Front bearing • HINT: Assemble the spacer and oil seal after adjusting the gear contact pattern. -
Page 597
SA–97 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/ A D D ) 3. ADJUST RING GEAR BACKLASH (a) Install only the plate washer on the ring gear back side. HINT: Insure that the ring gear has backlash. (b) Snug down the washer and bearing by tapping on the ring gear with a plastic–faced hammer. -
Page 598
SA–98 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/ A D D ) (f) Remove the plate washers and differential case. (g) Install the plate washer into the lower part of the carrier. (h) Place the other plate washer onto the differential case together with the outer race, and install the dif–… -
Page 599
SA–99 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/ A D D ) 4. ADJUST SIDE BEARING PRELOAD (a) Remove the ring gear teeth plate washer and mea– sure the thickness. (b) Using the backlash as a reference, install a new washer of 0.06 –… -
Page 600
SA–100 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/ A D D ) 6. MEASURE TOTAL PRELOAD Using a torque wrench, measure the total preload. Total preload (starting): Add drive pinion preload 0.4 – 0.6 N–m (4 – 6 kgf–cm, 3.5 – 5.2 in.–lbf) 7. -
Page 601
SA–101 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/ A D D ) 8. REMOVE COMPANION FLANGE (See step 14 on page SA–86) 9. REMOVE FRONT BEARING (See step 16 on page SA–86) 10. INSTALL NEW BEARING SPACER AND FRONT BEARING (a) Install a new bearing spacer on the drive pinion. -
Page 602
SA–102 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/ A D D ) (a) If the preload is greater than specification, replace the bearing spacer. (b) If the preload is less than specification, retighten the nut 13 N–m (130 kgf–cm,9 ft–lbf) a little at a time un– til the specified preload is reached. -
Page 603
SA–103 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/ A D D ) 17. INSTALL RH SIDE GEAR SHAFT (a) Install a new snap ring to the side gear shaft. (b) Using a plastic–faced hammer, tap on the side gear shaft to install it. -
Page 604
SA–104 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/ A D D ) 23. INSTAL LH SIDE GEAR SHAFT TO DIFFERENTIAL CARRIER (a) Remove any packing material and be careful not to get oil on the contacting surfaces of the differential carrier and clutch case. -
Page 605
SA–105 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (Disassembly and Assembly of Differential w/ A D D ) (c) Tighten the four bolts. Torque: 21 N–m (210 kgf–cm, 15 ft–lbf) -
Page 606
6. INSTALL DRAIN PLUG AND FILL DIFFERENTIAL WITH GEAR OIL (wI A.D.D.) Oil type: Toyota ”GEAR OIL SUPER” oil (Part No. 08885 – 02106) or hypoid gear oil API GL–5 Recommended oil viscosity: SAE 75W–90 Capacity: 1.86 liters (1.97 US qts, 1.64 Imp. qts) (w/o A.D.D.) -
Page 607
SA–107 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (A.D.D. Control System) A.D.D. Control System COMPONENTS… -
Page 608: Electrical Circuit
SA–108 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (A.D.D. Control System) ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT…
-
Page 609
SA–109 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (A.D.D. Control System) INSPECTION OF COMPONENTS 1. INSPECT A.D. D. SOLENOIDS (a) Measure the resistance of the solenoids. Resistance: 37 – 44 (b) Apply the battery voltage to the solenoid. Check that air flows from port E to port F. Check that air does not flow from port E to the air fil–… -
Page 610
SA–110 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Differential (A.D.D. Control System) 4. (Ex. 3VZ–E w/ATM ) INSPECT TRANSFER INDICATOR SWITCH (a) Check that there is continuity between terminals when the switch is pushed (transfer 4WD position). (b) Check that there is no continuity between terminals when the switch is free position (transfer H 2 posi–… -
Page 611
SA–111 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Suspension FRONT SUSPENSION COMPONENTS… -
Page 612
SA–112 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Suspension (Ball Joint) Ball Joint (See page SA–111) INSPECTION OF BALL JOINTS 1. INSPECT LOWER BALL JOINT FOR EXCESSIVE LOOSE– NESS (a) Jack up the front of the vehicle and support it with stands. (b) Make sure the front wheels are in a straight forward position, and depress the brake pedal. -
Page 613
SA–113 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Suspension (Ball Joint) INSTALLATION OF BALL JOINTS 1. INSTALL UPPER BALL JOINT TO UPPER SUSPENSION Torque: 33 N–m (340 kgf–cm, 25 ft–lbf) 2. INSTALL LOWER BALL JOINT TO LOWER SUSPENSION (a) Install the lower ball joint to the lower suspension arm. -
Page 614
SA–114 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Suspension (Torsion Bar Spring) Torsion Bar Spring (See page SA–111) REMOVAL OF TORSION BAR SPRING 1. PLACE MATCHMARKS ON TORSION BAR SPRING, ANCHOR ARM AND TORQUE ARM Remove the boots and place matchmarks on the torsion bar spring, anchor arm and torque arm. -
Page 615
SA–115 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Suspension (Torsion Bar Spring) (d) Tighten the adjusting nut so that the bolt protrusion is equal to that before removal. If Using a New Torsion Bar Spring (a) Remove the wheel. (b) Install the two boots to the torsion bar spring. (c) Apply a light coat of the molybdenum disulphide lithium base grease to the spline of the torsion bar spring. -
Page 616
SA–116 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Suspension (Lower Suspension Arm and Shock Absorber) Lower Suspension Arm and Shock Absorber (See page SA–111) REMOVAL OF LOWER SUSPENSION ARM AND SHOCK ABSORBER 1. REMOVE SHOCK ABSORBER 2. DISCONNECT STABILIZER BAR FROM LOWER SUSPENSION ARM 3. -
Page 617
SA–117 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Suspension (Lower Suspension Arm and Shock Absorber) PLACEMENT OF LOWER SUSPENSION ARM BUSHING 1. REMOVE FRONT AND REAR BUSHINGS Using SST, press out the bushings from the lower sus– pension arm. SST 09726–27011 (09726–02050, 09726–02060) 2. -
Page 618
SA–118 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Suspension (Lower Suspension Arm and Shock Absorber) 3. CONNECT STABILIZER BAR TO LOWER SUSPENSION Jack up the stabilizer bar and install the cushions, retain– ers, collar and bolt, and install and torque the nut. Torque: 25 N–m (250 kgf–cm, 19 ft–lbf) 4. -
Page 619
SA–119 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Suspension (Upper Suspension Arm) Upper Suspension Arm (See page SA–111) REMOVAL OF UPPER SUSPENSION ARM 1. REMOVE TORSION BAR SPRING (See page SA–114) 2. DISCONNECT UPPER SUSPENSION ARM FROM UPPER BALL JOINT Remove the cotter pin and nut, and using SST disconnect the upper ball joint from the steering knuckle. -
Page 620
SA–120 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Suspension (Upper Suspension Arm) 2. REMOVE FRONT BUSHING (a) Using a chisel and hammer, loosen the staked part of the nut. (b) Remove the nut. (c) Using SST, push out the front bushing. SST 09710–26010 (09710–05040, 09710–05050) 3. -
Page 621
SA–121 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Suspension (Upper Suspension Arm) 7. TORQUE UPPER ARM SHAFT (a) Install the retainers and new nuts. HINT: Position the upper arm shaft so that the frame in– stallation surface is level with the arm. (b) Torque the shaft nuts. -
Page 622
SA–122 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Front Suspension (Upper Suspension Arm, Stabilizer Bar) 3. CONNECT UPPER SUSPENSION ARM TO UPPER BALL JOINT (a) Connect the upper ball joint to the steering knuckle and install and torque the nut. Torque: 142 N–m (1,450 kgf–cm, 105 ft–lbf) (b) Install a new cotter pin. -
Page 623
SA–123 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Rear Axle Shaft (Single Tire) REAR AXLE SHAFT (Single Tire) COMPONENTS… -
Page 624
SA–124 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Rear Axle Shaft (Single Tire) REMOVAL OF REAR AXLE SHAFT 1. REMOVE WHEEL AND BRAKE DRUM 2. DISCONNECT BRAKE TUBE AND PARKING BRAKE CABLE 3. REMOVE FOUR BACKING PLATE MOUNTING NUTS 4. REMOVE REAR AXLE SHAFT FROM REAR AXLE HOUSING 5. -
Page 625
SA–125 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Rear Axle Shaft (Single Tire) (b) Using SST, press in a new bearing. SST 09515–30010 and 09608–35014 (09608–06180) 6. INSTALL NEW OUTER OIL SEAL Using SST, tap in a new oil seal. SST 09608–30012 (09608–04020, 09608–04070) 7. -
Page 626
SA–126 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Rear Axle Shaft (Single Tire) INSTALLATION OF REAR AXLE SHAFT (See page SA–123) 1. INSTALL REAR AXLE SHAFT IN BACKING PLATE (a) Apply MP grease to the oil seal lip. (b) Install the backing plate and bearing retainer on the rear axle shaft. -
Page 627
SA–127 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Rear Axle Shaft and Axle Hub (Double Tire) REAR AXLE SHAFT AND AXLE HUB (Double Tire) REMOVAL OF REAR AXLE SHAFT 1. REMOVE CONE WASHERS (a) Remove the six nuts and washers. (b) Install two service bolts and one turn. (c) Tap on the shaft and remove the six cone washers. -
Page 628
SA–128 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Rear Axle Shaft and Axle Hub (Double Tire) INSPECTION OF REAR AXLE SHAFT COMPONENTS 1. INSPECT REAR AXLE SHAFT Check for wear, damage or runout. Maximum runout: 2.0 mm (0.079 in.) 2. INSPECT OIL SEAL FOR WEAR OR DAMAGE If the oil seal is damaged or worn, replace it. -
Page 629
SA–129 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Rear Axle Shaft and Axle Hub (Double Tire) DISASSEMBLY OF REAR AXLE HUB 1. REMOVE REAR WHEEL AND REAR AXLE SHAFT (See page SA–127 2. REMOVE BEARING LOCK NUT (a) Remove the two bolts from the bearing lock nut. (b) Using SST, remove the bearing lock nut. -
Page 630
SA–130 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Rear Axle Shaft and Axle Hub (Double Tire) (b) Using SST, carefully tap in a new bearing outer race. SST Inner side 09608–35014 (09608–06020, 09608–06210) Outer side 09608–35014 (09608–06020, 09608–06200) 3. REPLACE HUB BOLT (a) Remove the six bolts and deflector. (b) Using the two service bolts, separate the hub and brake drum. -
Page 631
SA–131 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Rear Axle Shaft and Axle Hub (Double Tire) (e) Using a press, press in a new hub bolt. (f) Install and tighten the nut and stake the bolt. Torque: 147 N–m (1,500 kgf–cm, 108 ft–lbf) (g) Install the deflector and torque the six bolts. -
Page 632
SA–132 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Rear Axle Shaft and Axle Hub (Double Tire) 3. INSTALL INNER BEARING AND OIL SEAL (a) Place inner bearing into the hub. (b) Using SST, press in a new oil seal to the hub. SST 09608–35014 (09608–06020 and 09608–06180) (c) Apply MP grease to the oil seal lip. -
Page 633
SA–133 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Rear Axle Shaft and Axle Hub (Double Tire) (f) Using a spring tension gauge, measure and note fric– tion force of the oil seal. (starting) (g) Using SST, tighten the bearing lock nut until the pre– load is within the specification below. -
Page 634
SA–134 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Differential DIFFERENTIAL COMPONENTS… -
Page 635
SA–135 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Differential ON–VEHICLE REPLACEMENT OF OIL SEAL 1. DISCONNECT PROPELLER SHAFT FROM DIFFERENTIAL (a) Place matchmarks on the flanges. (b) Remove the four bolts and nuts. 2. REMOVE COMPANION FLANGE (See step 7 on page SA–138) 3. -
Page 636
SA–136 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Differential 11. CHECK DIFFERENTIAL OIL LEVEL Fill with hypoid gear oil if necessary. Oil type: API GL–5 hypoid gear oil Viscosity: Above – 180C (0E F) SAE 90 Below – 180C (0E F ) SAE 80V1r or 80w–90 Capacity: liters (US qts, Imp. -
Page 637
SA–137 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Differential DISASSEMBLY OF DIFFERENTIAL (See page SA–134) HINT: If the differential is noisy, perform the following preinspection before disassembly to determine the cause. If the differential has severe problems, disassemble and repair it as necessary. 1. -
Page 638
SA–138 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Differential 6. CHECK TOTAL PRELOAD Using a torque meter, measure the total preload. Total preload (starting): Add drive pinion preload 0.4 – 0.6 N–m (4 – 6 kgf–cm, 3.5 – 5.2 in.–Ibf) 7. REMOVE COMPANION FLANGE (a) Using a hammer and chisel, loosen the staked part of the nut. -
Page 639
SA–139 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Differential 10. REMOVE DIFFERENTIAL CASE AND RING GEAR (a) Place matchmarks on the bearing cap and differen– tial carrier. (b) Remove the two adjusting nut locks. (c) Remove the two bearing caps and two adjusting nuts. -
Page 640
SA–140 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Differential 13. REPLACE DRIVE PINION FRONT AND REAR BEARING OUTER RACES (a) Using a hammer and brass bar, drive out the outer race. (b) Using a press and SST, drive in a new outer race. Front side 09608–35014 (09608–06020, 09608–06110) Rear side 8 in. -
Page 641
SA–141 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Differential REPLACEMENT OF DIFFERENTIAL CASE COMPONENT PARTS (2 Pinion Type) 1. DISASSEMBLE DIFFERENTIAL CASE Using a hammer and punch, drive out the straight pin. Remove the pinion shaft, two pinion gears, two side gears and two thrust washers. 2. -
Page 642
SA–142 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Differential (4 Pinion Type) 1. DISASSEMBLE DIFFERENTIAL CASE (a) Place the matchmarks on the LH and RH cases. (b) Remove the eight bolts. (c) Using a plastic hammer, separate the LH and RH cases. 2. REMOVE FOLLOWING PARTS FROM CASE: Two side gears •… -
Page 643
SA–143 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Differential (e) Hold the side gear, measure the side gear backlash. Backlash: 0.05 – 0.20 mm (0.0020 – 0.0079 in.) HINT: Measure the backlash at the RH case at the LH case. (f ) If the backlash is not within specification, install a thrust washer of a different thickness. -
Page 644
SA–144 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Differential ASSEMBLY OF DIFFERENTIAL 1. INSTALL RING GEAR ON DIFFERENTIAL CASE (a) Clean the contact surfaces of the differential case and ring gear. (b) Heat the ring gear in boiling water. (c) After the moisture on the ring gear has completely evaporated, quickly install the ring gear to the differ–… -
Page 645
SA–145 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Differential 4. TEMPORARILY ADJUST DRIVE PINION PRELOAD (a) Install the following parts. Drive pinion • Front bearing • HINT: Assemble the spacer, oil slinger and oil seal after adjusting the gear contact pattern. (b) Install the companion flange with SST. SST 09557–22022 (7.5 in. -
Page 646
SA–146 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Differential 5. INSTALL DIFFERENTIAL CASE IN CARRIER (a) Place the bearing outer races on their respective bearings. Make sure the left and right outer races are not interchanged. (b) Install the case in the carrier. HINT: Make sure that there is backlash between the ring gear and drive pinion. -
Page 647
SA–147 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Differential (d) While turning the ring gear, use SST to fully tighten the adjusting nut on the drive pinion side. After the bearings are settled, loosen the adjusting nut on the drive pinion side. SST 09504–00011 (e) Place a dial indicator on the top of the adjusting nut on the ring gear side. -
Page 648
SA–148 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Differential (k) Using a torque meter, measure the total preload. Total preload (starting): Add drive pinion preload 0.4 – 0.6 N–m (4 – 6 kgf –cm, 3.5 – 5.2 in.–Ibf) Backlash: 0.13 – 0.18 mm (0.0051 – 0.0071 in.) 9. -
Page 649
SA–149 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Differential If the teeth are not contacting properly, use the following chart to select a proper washer for correction. Washer thickness 10. REMOVE COMPANION FLANGE (See step 7 on page SA–138) 11 REMOVE FRONT BEARING (See step 9 on page SA–138) 12. -
Page 650
SA–150 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Differential (b) Coat the threads of a new nut with MP grease. (c) Using SST to hold the flange, tighten the nut. SST 09330–00021 Torque: 7.5 in. 108 N–m (1,100 kgf–cm, 80 ft–lbf ) 8 in. 196 N–m (2,000 kgf–cm, 145 ft–lbf) 15. -
Page 651
SA–151 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Differential Maximum lateral runout: 0.10 mm (0.0039 in.) 17. STAKE DRIVE PINION NUT 18. INSTALL ADJUSTING NUT LOCKS (a) (7.5 in.) Select either a lock No. 1 or No. 2, whichever will fit the adjusting nuts. (b) Install the lock on the bearing caps. -
Page 652
SA–152 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Differential 4. CONNECT PROPELLER SHAFT FLANGE TO COMPANION FLANGE (a) Align the matchmarks on the flanges and connect the flanges with four bolts and nuts. (b) Torque the bolts and nuts. Torque: 4WD 3VZ–E [MT] 76 N–m (780 kgf–cm, 56 ft–lbf) Ex. -
Page 653: Rear Suspension
SA–153 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Rear Suspension (Shock Absorber) REAR SUSPENSION Shock Absorber COMPONENTS REMOVAL OF SHOCK ABSORBER 1. JACK UP AND SUPPORT BODY (a) Jack up and support the body on stands. (b) Lower the axle housing until the leaf spring tension is free, and keep it at this position.
-
Page 654
SA–154 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Rear Suspension (Shock Absorber INSPECTION OF SHOCK ABSORBER 1. INSPECT SHOCK ABSORBER Compress and extend the shock absorber and check that there is no abnormal resistance or unusual operation sounds. If there is any abnormality, replace the shock absorber with new one. -
Page 655
SA–155 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Rear Suspension (Leaf Spring) Leaf Spring COMPONENTS… -
Page 656
SA–156 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Rear Suspension (Leaf Spring) COMPONENTS… -
Page 657
SA–157 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Rear Suspension (Leaf Spring) REMOVAL OF LEAF SPRING 1. JACK UP AND SUPPORT BODY (a) Jack up and support the body on the stands. (b) Lower the axle housing until the leaf spring tension is free, and keep it at this position. 2. -
Page 658
SA–158 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Rear Suspension (Leaf Spring) REPLACEMENT OF BUSHING REPLACE BUSHINGS WITH PRESS Using a press and socket wrench, replace the eye bush– ings. REPLACEMENT OF LEAF SPRING 1. BEND OPEN SPRING CLIP Using a chisel, pry up the spring clip. 2. -
Page 659
SA–159 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Rear Suspension (Leaf Spring) 6. INSTALL SPRING CENTER BOLT (a) Align the leaf holes and secure the leaves with a vise. (b) Install and tighten the spring center bolt. Torque: 44 N–m (450 kgf–cm, 33 ft–Ibf) 7. -
Page 660
SA–160 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Rear Suspension (Leaf Spring 2. INSTALL U–BOLTS (a) Install the pads and pad retainer on the leaf spring. (b) (4WD) Install the spring bumper. M Install the spring seat, U–bolts, washers and nuts. (d) Tighten the U–bolt mounting nuts. Torque: 2W D 0.5 ton 147 N–m… -
Page 661
SA–161 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Rear Suspension (Leaf Spring) 6. TIGHTEN HANGER PIN AND SHACKLE PIN Tighten the hanger pin nut. Torque: 0.5 ton 157 N–m (1,600 kgf–cm, 116 ft–Ibf ) 1 ton and C&C 91 N–m (930 kgf –cm, 67 ft–Ibf) Tighten the shackle nuts. -
Page 662
SA–162 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Rear Suspension (Stabilizer Bar) Stabilizer Bar (See page SA–153) REMOVAL OF STABILIZER BAR 1. JACK UP AND SUPPORT VEHICLE 2. DISCONNECT STABILIZER BAR LINK FROM BODY (a) Disconnect the stabilizer bar link from the body. (b) Remove the retainers and cushion from the link. -
Page 663
SA–163 SUSPENSION AND AXLE – Rear Suspension (Stabilizer Bar) 2. INSTALL STABILIZER BAR (a) Place the stabilizer bar to the rear axle housing. (b) Install the cushion and bracket. Torque: 13 N–m (130 kgf–cm, 9 ft–lbf) 3. CONNECT STABILIZER BAR LINK (a) Position the link to the body. -
Page 664
BR–1 BRAKE SYSTEM – BRAKE SYSTEM… -
Page 665
BR–2 BRAKE SYSTEM – Precautions PRECAUTIONS 1. Care must be taken to replace each part properly as it could affect the performance of the brake system and re– sult in a driving hazard. Replace the parts with parts of the same part number or equivalent. 2. -
Page 666
BR–3 BRAKE SYSTEM – Troubleshooting TROUBLESHOOTING (Cont’d) Page Remedy Possible cause Problem Check for cause. Replace Oil or grease on shoes or pads Hard pedal but shoes or pads brakes inefficient Replace brake shoes BR–40, 47 Brake shoes distorted, linings worn or Replace pads glazed, drums worn BR–18, 26… -
Page 667
BR–4 BRAKE SYSTEM – Troubleshooting TROUBLESHOOTING (Cont’d) Problem Possible cause Remedy Page Squeaking, squealing Brake drums and linings, rotors and pads Inspect, repair or replace BR–18, 26 groaning or worn or scored 33,40 chattering noise Dirty, greased, contaminated or glazed 47, 55 when brakes are linings or pads… -
Page 668
BR–5 BRAKE SYSTEM – Troubleshooting TROUBLESHOOTING (Cont’d) Page Possible cause Remedy Problem Groaning, clicking or Stones or foreign material trapped inside Remove foreign material rattling noise when wheel covers brakes are not Loose wheel nuts Tighten to correct torque applied Replace if stud holes are elongated Inspect and adjust… -
Page 669
BR–6 BRAKE SYSTEM – Checks and Adjustments CHECKS AND ADJUSTMENTS CHECK AND ADJUSTMENT OF BRAKE PEDAL 1. CHECK THAT PEDAL HEIGHT IS CORRECT, AS SHOWN PEDAL HEIGHT FROM ASPHALT SHEET: 2WD 148 MM (5.83 IN.) 4WD 145 MM (5.71 IN.) 2. -
Page 670
BR–7 BRAKE SYSTEM – Checks and Adjustments 4. CHECK THAT PEDAL RESERVE DISTANCE IS CORRECT, AS SHOWN Release the parking brake. With engine running, depress the pedal and measure the pedal reserve distance, as shown. Pedal reserve distance from asphalt sheet at 490 N (50 kgf, 110.2 lbf): (2WD) 22R–E Engine… -
Page 671
BR–8 BRAKE SYSTEM – Checks and Adjustments BLEEDING OF BRAKE SYSTEM HINT: If any work is done on the brake system or if air is suspected in the brake lines, bleed the system of air. NOTICE: Do not let brake fluid remain on a painted sur– face. -
Page 672
BR–9 BRAKE SYSTEM – Checks and Adjustments CHECK AND ADJUSTMENT OF PARKING BRAKE 1. CHECK THAT PARKING BRAKE LEVER TRAVEL IS CORRECT Pull the parking brake lever all the way up, and count the number of clicks. Parking brake lever travel at 196 N (20 kgf, 44.1 lbf) 2WD 1/2 ton 12 –… -
Page 673: Master Cylinder
BR–10 BRAKE SYSTEM – Master Cylinder MASTER CYLINDER REMOVAL OF MASTER CYLINDER 1. DISCONNECT LEVEL WARNING SWITCH CONNECTOR 2. DRAW OUT FLUID WITH SYRINGE NOTICE: Do not let brake fluid remain on a painted sur– face. Wash it off immediately. 3.
-
Page 674
BR–11 BRAKE SYSTEM – Master Cylinder COMPONENTS DISASSEMBLY OF MASTER CYLINDER 1. REMOVE MASTER CYLINDER BOOT Using a screwdriver, remove the master cylinder boot. 2. REMOVE RESERVOIR (a) Remove the set screw and pull out the reservoir. (b) Remove the cap and strainer from the reservoir. 3. -
Page 675
BR–12 BRAKE SYSTEM – Master Cylinder 5. REMOVE PISTON STOPPER BOLT Using a screwdriver, push the pistons in all the way and remove the piston stopper bolt and gasket. HINT: Tape the screwdriver tip before use. 6. REMOVE TWO PISTONS AND SPRINGS (a) Push in the piston with a screwdriver and remove the snap ring with snap ring pliers. -
Page 676
BR–13 BRAKE SYSTEM – Master Cylinder ASSEMBLY OF MASTER CYLINDER (See page BR–11) 1. APPLY LITHIUM SOAP BASE GLYCOL GREASE TO RUB– BER PARTS INDICATED BY ARROWS 2. INSTALL TWO SPRINGS AND PISTONS NOTICE: Be careful not to damage the rubber lips on the pistons. -
Page 677
BR–14 BRAKE SYSTEM – Master Cylinder 6. INSTALL MASTER CYLINDER BOOT Facing the up mark on the master cylinder boot upwards, install the cylinder boot to the master cylinder. -
Page 678
BR–15 BRAKE SYSTEM – Master Cylinder INSTALLATION OF MASTER CYLINDER (See page BR–10) 1. ADJUST LENGTH OF BRAKE BOOSTER PUSH ROD BEFORE INSTALLING MASTER CYLINDER (See page BR–17) 2. INSTALL MASTER CYLINDER Install the master cylinder and gasket on the brake booster with four nuts. -
Page 679: Brake Booster
BR–16 BRAKE SYSTEM – Brake Booster BRAKE BOOSTER REMOVAL OF BRAKE BOOSTER 1. REMOVE MASTER CYLINDER (See page BR–10) 2. DISCONNECT VACUUM HOSE FROM BRAKE BOOSTER 3. REMOVE PEDAL RETURN SPRING 4. REMOVE CLIP AND CLEVIS PIN 5. REMOVE BRAKE BOOSTER, GASKET AND CLEVIS…
-
Page 680
BR–17 BRAKE SYSTEM – Brake Booster INSTALLATION OF BRAKE BOOSTER (See page BR–16) 1. ADJUST LENGTH OF BOOSTER PUSH ROD (a) Install the gasket on the master cylinder. (b) Set the SST on the gasket, and lower the pin until its tip slightly touches the piston. -
Page 681: Front Brake
BR–33 BRAKE SYSTEM – Front Brake – 4WD (S12 + 12 Type Disc) FRONT BRAKE 4WD (S12 + 12 Type Disc) COMPONENTS REPLACEMENT OF BRAKE PADS HINT: If a squealing noise occurs from the brakes while driving, check the pad wear indicator plate. If the pad wear indicator plate contacts the rotor disc, the brake pads should be replaced.
-
Page 682
BR–34 BRAKE SYSTEM – Front Brake – 4WD (S12 + 12 Type Disc) 3. REMOVE FOLLOWING PARTS (a) Clip (b) Two pins (c) Anti–rattle spring (d) Two pads (e) Four anti–squeal shims 4. CHECK ROTOR DISC THICKNESS (See step 2 on page BR–37) 5. -
Page 683
BR–35 BRAKE SYSTEM – Front Brake – 4WD (S12 + 12 Type Disc) 8. INSTALL TWO PINS 9. INSTALL CLIP REMOVAL OF CYLINDER (See page BR–33) 1. REMOVE FRONT WHEEL 2. DISCONNECT BRAKE TUBE Using SST, disconnect the brake tube. Use a container to catch the brake fluid. -
Page 684
BR–36 BRAKE SYSTEM – Front Brake – 4WD (S12 + 12 Type Disc) DISASSEMBLY OF CYLINDER (See page BR–33) 1. REMOVE CYLINDER BOOT SET RINGS AND BOOTS Using a screwdriver, remove the four cylinder boot set rings and four boots. 2. -
Page 685
BR–37 BRAKE SYSTEM – Front Brake – 4WD (S12 + 12 Type Disc) INSPECTION AND REPAIR OF FRONT BRAKE COMPONENTS 1. MEASURE PAD LINING THICKNESS Standard thickness: 9.5 mm (0. 374 in.) Minimum thickness: 1.5 mm (0.059 in.) Replace the pads if the thickness is less than the mini– mum (the 1.5 mm slit is no longer visible) or if it shows sign of uneven wear. -
Page 686
BR–38 BRAKE SYSTEM – Front Brake – 4WD (S12 + 12 Type Disc) ASSEMBLY OF CYLINDER (See page BR–33) 1. APPLY LITHIUM SOAP BASE GLYCOL GREASE TO PARTS INDICATED BY ARROWS 2. INSTALL PISTON SEALS INTO CYLINDER 3. INSTALL PISTONS INTO CYLINDER 4. -
Page 687
BR–39 BRAKE SYSTEM – Front Brake – 4WD (S12 + 12 Type Disc) INSTALLATION OF CYLINDER (See page BR–33) 1. INSTALL CYLINDER Install the brake cylinder, and torque the two mounting bolts. Torque: 123 N–m (1,250 kgf–cm, 90 ft–lbf) 2. INSTALL PADS (See steps 6 to 9 on pages BR–34 and 35) -
Page 688
BR–55 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear Brake – 4WD REAR BRAKE COMPONENTS REMOVAL OF REAR DRUM BRAKE 1. INSPECT SHOE LINING THICKNESS Remove the inspection hole plug, and check the shoe lin– ing thickness through the hole. If less than minimum, replace the shoes. Minimum thickness: 1.0 mm (0.039 in.) 2. -
Page 689
BR–56 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear Brake – 4WD 4. REMOVE REAR SHOE (a) Using SST, disconnect the return spring. SST 09703–30010 (b) Using SST, remove the shoe hold–down spring, cups and pin. SST 09718–00010 (c) Disconnect the anchor spring from the rear shoe and remove the rear shoe. -
Page 690
BR–57 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear Brake – 4WD 7. REMOVE AUTOMATIC ADJUSTING LEVER AND PARKING BRAKE LEVER (a) Remove the E–ring. (b) Remove the automatic adjusting lever. (c) Remove the C–washer. (d) Remove the parking brake lever. 8. REMOVE AND DISASSEMBLE PARKING BRAKE BELLCRANK (a) Remove the clip and disconnect the parking brake cable. -
Page 691
BR–58 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear Brake – 4WD 10. DISASSEMBLE WHEEL CYLINDER Remove the following parts from the wheel cylinder: Two boots • Two pistons • Two piston cups • Spring • INSPECTION AND REPAIR OF REAR BRAKE COMPONENTS 1. INSPECT DISASSEMBLED PARTS Inspect the disassembled parts for wear, rust or damage. -
Page 692
BR–59 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear Brake – 4WD ASSEMBLY OF REAR BRAKES (See page BR–55) HINT: Assemble the parts in the correct direction as shown. 1. ASSEMBLE AND INSTALL PARKING BRAKE BELL- CRANK (a) Apply high temperature grease to the rotating parts of the bellcrank. -
Page 693
BR–60 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear Brake – 4WD (g) Install the parking brake cable No.2 to the parking brake bellcrank No. 1 or No. 2. (h) Hook the bellcrank No. 3 to the cable No. 2, and then install the bellcrank No.3 with a new C– washer. -
Page 694
BR–61 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear Brake – 4WD (b) Apply high temperature grease to the adjuster bolt threads and ends. 6. INSTALL PARKING BRAKE LEVER AND AUTOMATIC ADJUSTING LEVER (a) Install the parking brake lever with a new C– washer. (b) Install the automatic adjusting lever with the E–… -
Page 695
BR–62 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear Brake – 4WD 9. INSTALL REAR SHOE (a) Install the anchor spring between the front and rear shoes. (b) Set the rear shoe in place with the end of the shoe inserted in the wheel cylinder and the adjuster in place. -
Page 696
BR–63 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear Brake – 4WD 11. CHECK OPERATION OF AUTOMATIC ADJUSTING MECHANISM (a) Move the parking brake lever of the front shoe back and forth, as shown. Check that the adjuster turns. If the adjuster does not turn, check for incorrect instal– lation of the rear brakes. -
Page 697
BR–64 BRAKE SYSTEM – Load Sensing Proportioning and By–Pass Valve (LSP & BV) LOAD SENSING PROPORTIONING AND BY–PASS VALVE (LSP & BV) COMPONENTS CHECK AND ADJUSTMENT OF FLUID PRESSURE 1. SET REAR AXLE LOAD Rear axle load (includes vehicle weight): 2WD 1 ton, C &… -
Page 698
BR–65 BRAKE SYSTEM – Load Sensing Proportioning and By–Pass Valve (LSP & 13V) 3. RAISE FRONT BRAKE PRESSURE TO 7,845 kPa (80 kgf/cm , 1,138 psi) AND CHECK REAR BRAKE PRES– SURE Rear brake pressure: 2WD 1 ton, C & C (SRW) 4,413±490 kPa kgf/cm (45±5 , 640±71 psi) -
Page 699
BR–66 BRAKE SYSTEM – Load Sensing Proportioning and By–Pass Valve (LSP & BV) (b) In event the pressure cannot be adjusted by the No. 1 shackle, raise or lower the valve body. Low pressure – Lower High pressure – Raise (c) Torque the nuts. -
Page 700
BR–67 BRAKE SYSTEM – Load Sensing Proportioning and By–Pass Valve (LSP & BV) REMOVAL OF LSP & BV OR LSPV (See page BR–64) 1. DISCONNECT SHACKLE NO.2 FROM BRACKET 2. REMOVE LSP & BV (LSPV) ASSEMBLY (a) Using SST, disconnect the brake tube from the valve body. -
Page 701
BR–68 BRAKE SYSTEM – Load Sensing Proportioning and By–Pass Valve (LSP & BV) 4. DISASSEMBLE LOAD SENSING SPRING Disassemble the following parts. (a) Bushings (b) Collars (c) Rubber plates (d) Load sensing valve boot (e) Load sensing spring boot INSPECTION OF LSP & BV OR LSPV INSPECT VALVE PISTON PIN AND LOAD SENSING CONTACT SURFACE FOR WEAR Wear limit: 0.7 mm (0.028 in.) -
Page 702
BR–69 BRAKE SYSTEM – Load Sensing Proportioning and By–Pass Valve (LSP & BV) 3. CONNECT VALVE BODY AND NO. 1 SHACKLE TO LOAD SENSING SPRING CAUTION: When connecting the shackle to the load sensing spring with a bolt and nut, insert the bolt from the front side of vehicle. -
Page 703
BR–70 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System REAR–WHEEL ANTI–LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM General Description • The Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System is a brake system which controls the wheel cylinder hydraulic pressure of the rear wheels during sudden braking and braking on slippery road surfaces, preventing the rear wheels from locking. -
Page 704
BR–71 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System WIRING DIAGRAM… -
Page 705
BR–72 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System CONNECTORS… -
Page 706
BR–73 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System Diagnosis System DESCRIPTION If a functional malfunction occurs, diagnosis system will identify the problem and ECU stores the codes for the trouble items. At the same time, the system informs the driver of a mal– function via the ”REAR ANTILOCK”… -
Page 707
BR–74 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System (d) In event of a malfunction, 4 seconds later the warn– ing light will begin to blink. Read the number of blinks. (See DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE on page BR–75) HINT: The first number of blinks will equal the first digit of a two digit diagnostic trouble code. -
Page 708
Code No. Light Pattern Diagnosi Trouble Part Open circuit in solenoid relay circuit or solenoid circuit Solenoid • Solenoid relay • Short circuit in solenoid relay circuit Wire harness and connec– • tor of solenoid and/or sole– noid relay circuit Short circuit in solenoid circuit Speed sensor •… -
Page 709
BR–76 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System CLEARING OF DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES CLEAR DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (a) Turn the ignition switch to ON. (b) Disconnect the service connector. HINT: Keep the vehicle stopped (vehicle speed 0 km/h (0 mph)). (c) Using SST, connect the terminal Tc to E, of the data link connector 1. -
Page 710
BR–77 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System (h) Check that the warning light goes off. -
Page 711
BR–78 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System Troubleshooting Problem Always comes on after ignition switch is turned to ON. Does not come on for about 3 seconds after ignition switch on. ”REAR ANTILOCK” warning light Comes on and off. Comes on while running. -
Page 712
BR–79 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System Continued from page BR–78 Is connector of ECU properly connected ? Faulty connector. And are all terminals in the connector ? Faulty power circuit. Is there 10 – 14 V between terminal IG on ECU wire harness side connector and body ground ? (Ignition switch on) Short circuit in wire harness between ECU termi–… -
Page 713
BR–80 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System ”REAR ANTILOCK” warning light does not come on for about 2 seconds after ignition switch on. Disconnect service connector and ground the terminal W of the wire harness side connector. (Ignition switch on) Bulb burned out or open circuit in wire harness Does warning light come on ? between warning light and service connector ter–… -
Page 714
BR–81 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System ”’REAR ANTILOCK” warning light comes on and off . • Short circuit in wire harness between ECU terminal TS and data link connector 1 terminal Ts. • Short circuit in wire harness between ECU terminal TC and data link connector 1 terminal Tc. •… -
Page 715
BR–82 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System Continued from page BR–81 Is there foreign material or ferric chips Clean chips from speed sensor. on the speed sensor tip ? Disconnect connector from ECU and inspect continuity between speed sensor terminals on wire harness side. Does any abnormal change occur in Faulty wire harness. -
Page 716
BR–83 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System works inefficiently. Disconnect service connector and con– nect the terminal Tc to E , of the data link connector 1. (See page BR–73) Does warning light show the diagnostic See diagnostic trouble code. -
Page 717
BR–84 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System Deceleration Sensor and Speed Sensor Diagnosis System PRECAUTION • While checking the deceleration sensor and speed sen– sor diagnosis system, the Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System does not work and brake system works as nor– mal brake system. -
Page 718
BR–85 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System (e) Drive the vehicle straight ahead at about 20 km/h (12.4 mph) or more, depress the brake pedal strongly. (f) Check that the warning light turns on while braking. (g) Drive the vehicle straight ahead at about 50 km/h (31 mph) or more, and stop the vehicle. -
Page 719
BR–86 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System (I) If the system is operating normally (no malfunction), the warning light will blink once every 0.5 seconds. (m) Repair the system. (n) After the malfunctioning components have been re– paired, clear the diagnostic trouble codes stored in the ECU. -
Page 720
BR–87 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System Brake Actuator COMPONENTS INSPECTION OF BRAKE ACTUATOR 1. CHECK BRAKE FLUID PRESSURE (a) Remove the bleeder plug from the rear wheel cylin– der and connect SST. SST 09709–29017 (b) Bleed the air from SST. (c) With the engine off, hold the brake pedal depressed for about 10 seconds with the pressure at 1,961 kPa (20 kgf/crn… -
Page 721
BR–88 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System (d) With the engine running, hold the brake pedal de– pressed for about 1 0 seconds with the pressure at 5,844 kPa (60 kgf/cm , 853 psi), and check that there is no change in the pedal reserve distance. If there is a change in the brake pedal reserve distance, inspect the brake actuator. -
Page 722
BR–89 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System With the engine running, the brake and power steering fluid pressure should conform to the following table. Brake Fluid Pressure PS Fluid Pressure If not within specification, check the actuator. 4. CHECK ACTUATOR OPERATION (a) Disconnect the connector from the actuator. -
Page 723
BR–90 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System 5. REMOVE ACTUATOR CHECKER (SST) Remove SST, then connect the connectors of the actua– tor and solenoid relay. SST 09990–00150 and 09990–00205 6. REMOVE SST FROM WHEEL CYLINDER SST 09709–29017 7. REMOVE PRESSURE GAUGE FROM PS PUMP Remove the pressure gauge from the PS line, then bleed the power steering system. -
Page 724
BR–91 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System 4. DISCONNECT POWER STEERING LINES FROM ACTUA– HINT: Turn the steering wheel clockwise until it locks before disconnecting the PS lines. And if you cannot work from the upper side, work from the wheel house. (a) Remove the two union bolts and disconnect the two power steering pressure tubes. -
Page 725
BR–92 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System INSTALLATION OF BRAKE ACTUATOR 1. INSTALL BRACKET TO ACTUATOR Install the bracket to the actuator with the three bolts. Torque: 13 N–m (130 kgf–cm, 9 ft–lbf) 2. INSTALL ACTUATOR Install the actuator in place and tighten the three bolts. Torque: 28 N–m (290 kgf–cm, 21 ft–lbf) HINT: Install the bolts in following order. -
Page 726
BR–93 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System 6. CONNECT CONNECTOR Connect the connector to the actuator. 7. INSTALL BATTERY Install the tray and battery in place, then connect the wire harnesses to the terminals. 8. BLEED SYSTEM (a) Fill brake reservoir with brake fluid. (b) Fill PS reservoir with fluid. -
Page 727
BR–94 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System BLEEDING OF REAR–WHEEL ANTI–LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM HINT: Whenever PS hoses or PS pressure tube are dis– connected or actuator is removed from the vehicle, the Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System should be bled in the following procedure. -
Page 728
BR–95 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System Control Relay INSPECTION OF SOLENOID RELAY INSPECT SOLENOID RELAY OPERATION Inspect the relay continuity between terminals. Terminal Condition Constant Apply battery positive voltage between terminals 1 and ’6 If relay operation is not as specified, replace the solenoid relay. -
Page 729: Speed Sensor
BR–96 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System Speed Sensor INSPECTION OF SPEED SENSOR 1. INSPECT SENSOR INSTALLATION Check that the sensor installation bolt is tightened prop– erly. If not, tighten the bolt. Torque: 19 N–m (195 kgf–cm, 14 ft–lbf) 2.
-
Page 730
BR–97 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System 3. VISUALLY INSPECT SENSOR ROTOR SERRATIONS (a) Disconnect the speed sensor wire harness clamp bolt. (b) Remove the speed sensor installation bolt and pull out the speed sensor. (c) Remove the differential carrier assembly. (See page SA–136) NOTICE: To prevent damage to the ring gear serrations, do not strike the ring gear. -
Page 731
BR–98 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System INSPECTION OF SPEED SENSOR AND SENSOR ROTOR SERRATIONS (REFERENCE) INSPECT SPEED SENSOR AND SENSOR ROTOR SERRA– TIONS BY USING AN OSCILLOSCOPE (a) Remove the glove box assembly and disconnect the radio speaker connector. (b) Disconnect the connector from the rear–wheel anti–… -
Page 732
BR–99 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System Deceleration Sensor INSPECTION OF DECELERATION SENSOR INSPECT SENSOR INSTALLATION (a) Remove the two clips, then remove the instrument lower center cover. (b) Inspect that the sensor direction is correct. (c) Check that the sensor installation bolts are tight– ened properly. -
Page 733
BR–100 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System Circuit REMOVAL OF REAR–WHEEL ANTI–LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM ECU 1. REMOVE GLOVE BOX ASSEMBLY Remove the four screws and a bolt, then remove the glove box assembly and disconnect the radio speaker connector. -
Page 734
BR–101 BRAKE SYSTEM – Rear–Wheel Anti–Lock Brake System 2. INSPECT SYSTEM CIRCUIT WITH CONNECTOR DIS– CONNECTED (a) Disconnect the connector from the ECU and inspect at the wire harness side connector. Voltage or Trouble Part Condition Tester Connection Check Item Resistance Value PKB switch, Ignition SW on and PKB lever pulled… -
Page 735
SR–1 STEERING – STEERING… -
Page 736
SR–2 STEERING – Precaution PRECAUTION Care must be taken to replace parts properly because they may affect the performance of the steering system and result in a driving hazard. TROUBLESHOOTING Problem Possible cause Remedy Page Hard steering Tires improperly inflated Inflate tires to proper pressure SA–3, 6 Insufficient lubricant… -
Page 737: Oil Level
SR–3 STEERING – On–Vehicle Inspection ON–VEHICLE INSPECTION STEERING WHEEL FREEPLAY 1. CHECK THAT STEERING WHEEL FREEPLAY IS CORRECT With the vehicle stopped and pointed straight ahead, rock the steering wheel gently back and forth with light finger pressure. Freeplay should not exceed the maxi– mum limit.
-
Page 738
SR–4 STEERING – Steering Column STEERING COLUMN REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION OF STEERING COLUMN Remove and install the parts as shown. (MAIN POINTS OF REMOVAL) 1. REMOVE STEERING WHEEL Using SST, remove the steering wheel. SST 09609–20011 2. DISCONNECT MAIN SHAFT (a) Place matchmarks on the worm shaft and main shaft. -
Page 739
SR–5 STEERING – Steering Column (Non–Tilt Steering Column) Non–Tilt Steering Column COMPONENTS… -
Page 740
SR–6 STEERING – Steering Column (Non–Tilt Steering Column) DISASSEMBLY OF STEERING COLUMN 1. REMOVE COLUMN HOLE COVER (a) Disconnect the intermediate shaft from the main shaft. (b) Remove two bolts and the dust seal. (c) Remove the column hole cover. 2. -
Page 741
SR–7 STEERING – Steering Column (Non–Tilt Steering Column) INSPECTION AND REPLACEMENT OF NON–TILT STEERING COLUMN 1. INSPECT UPPER BRACKET Check that the steering lock mechanism operates prop– erly. 2. IF NECESSARY, REPLACE IGNITION KEY CYLINDER (a) Place the ignition key at the ACC position. (b) Push down the stop key with a thin rod, and pull out the key cylinder. -
Page 742
SR–8 STEERING – Steering Column (Non–Tilt Steering Column) ASSEMBLY OF NON–TILT STEERING COLUMN (See page SR–5) 1. INSTALL UPPER BRACKET TO COLUMN TUBE (a) Install the upper bracket with two new tapered–head bolts. (b) Tighten the tapered–head bolts until the bolt heads break off. -
Page 743
SR–9 STEERING – Steering Column (Tilt Steering Column) Tilt Steering Column COMPONENTS… -
Page 744
SR–10 STEERING – Steering Column (Tilt Steering Column) DISASSEMBLY OF STEERING COLUMN (See page SR–9) 1. REMOVE UPPER BRACKET (a) Using a centering punch, mark the center of the tapered–head bolt. (b) Using a 3 – 4 mm (0. 12 – 0.16 in.) drill, drill into the tapered–head bolt. -
Page 745
SR–11 STEERING – Steering Column (Tilt Steering Column) 6. REMOVE TWO TILT PAWLS (a) Remove the nut and bolt. (b) Remove the two pawls with the collars. 7. REMOVE TILT LEVER ASSEMBLY, TILT LEVER, TILT SUB LEVER AND LEVER LOCK BOLT Remove one screw and tilt lever assembly. -
Page 746
SR–12 STEERING – Steering Column (Tilt Steering Column) 10. REMOVE MAIN SHAFT (a) Using SST to hold the main shaft, remove the snap ring with snap ring pliers. SST 09950–20017 (b) Remove the main shaft from the column tube. (c) Remove the spring, thrust collar and bearing. 11. -
Page 747
SR–13 STEERING – Steering Column (Tilt Steering Column) INSPECTION AND REPLACEMENT OF STEERING COLUMN 1. INSPECT KEY CYLINDER Check that the steering lock mechanism operates prop– erly. 2. 1F NECESSARY, REPLACE KEY CYLINDER (a) Place the ignition key at the ACC position. (b) Push down the stop key with a thin rod, and pull out the key cylinder. -
Page 748
SR–14 STEERING – Steering Column (Tilt Steering Column) ASSEMBLY OF TILT STEERING COLUMN (See page SR–9) 1. COAT MOLYBDENUM DISULPHID LITHIUM BASE GREASE ON FOLLOWING PARTS:… -
Page 749
SR–15 STEERING – Steering Column (Tilt Steering Column) 2. INSTALL MAIN SHAFT (a) Install the main shaft with the bearing, collar and spring. (b) Using SST to hold the main shaft, install the snap ring with snap ring pliers. SST 09950–20017 3. -
Page 750
SR–16 STEERING – Steering Column (Tilt Steering Column) (c) Using a plastic hammer, drive in the steering bolts. INSTALL TILT LEVER LOCK BOLT, TILT LEVER ASSEMBLY, TILT LEVER AND TILT SUB LEVER (a) Install the tilt lever lock bolt to the upper column tube. -
Page 751
SR–17 STEERING – Steering Column (Tilt Steering Column) 10. SELECT STEERING PAWL STOPPERS FOR BOTH SIDES (a) With the steering lock pawl and the ratchet en– gaged, select and install two tilt steering pawl stop– pers. (b) Check that the alignment marks on the stopper and pawl align when the stopper is rotated to the pawl side. -
Page 752
SR–18 STEERING – Steering Column (Tilt Steering Column) 14. INSTALL UPPER COLUMN BRACKET (a) Install the upper column bracket with new two tapered–head bolts. (b) Tighten the tapered–head bolts until the bolt heads break off. 15. CHECK OPERATION OF TILT STEERING LEVER AND SUPPORT (a) Check that there is no axial play at the end of the main shaft. -
Page 753
SR–19 STEERING – Manual Gear Housing (2WD) MANUAL GEAR HOUSING (2WD) REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION OF MANUAL GEAR HOUSING Remove and install the parts as shown. (MAIN POINTS OF REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION) 1. DISCONNECT UNIVERSAL JOINT (a) Loosen the column side set bolt. (b) Remove the gear side set bolt. -
Page 754
SR–20 STEERING – Manual Gear Housing (2WD) 3. CONNECT PITMAN ARM TO GEAR HOUSING (a) Align the alignment marks on the sector shaft and pitman arm and install the spring washer and arm. (b) Tighten the pitman arm nut. Torque: 123 N–m (1,250 kgf–cm, 90 ft–lbf) 4. -
Page 755
SR–21 STEERING – Manual Gear Housing (2WD) DISASSEMBLY OF MANUAL GEAR HOUSING 1. REMOVE BLEEDER PLUG AND DRAIN GEAR OIL 2. REMOVE END COVER AND SECTOR SHAFT (a) Remove the adjusting screw lock nut and three bolts. (b) Remove the end cover by turning the adjusting screw clockwise with a screwdriver. -
Page 756
SR–22 STEERING – Manual Gear Housing (2WD) 2. INSPECT WORM BEARINGS AND OIL SEAL Check for wear or damage. If a problem is found, replace the bearings, bearing races and oil seal. 3. IF NECESSARY, REPLACE OIL SEAL (a) Remove the oil seal with a screwdriver. (b) Using SST, install a new oil seal. -
Page 757
SR–23 STEERING – Manual Gear Housing (2WD) 8. IF NECESSARY, REPLACE OIL SEAL (a) Remove the oil seal with a screwdriver from the gear housing. (b) Using SST and a hammer, install a new oil seal. SST 09630–00012 (09631–00020, 09631–00090) ASSEMBLY OF STEERING GEAR HOUSING (See page SR–19) 1. -
Page 758
SR–24 STEERING – Manual Gear Housing (2WD) 4. INSTALL SECTOR SHAFT (a) Install the adjusting screw and thrust washer onto the sector shaft. (b) Set the ball nut at the center of the worm shaft. In– stall the sector shaft into the gear housing so that the center teeth mesh together. -
Page 759
SR–25 STEERING – Manual Gear Housing (2WD) 9. MEASURE SECTOR SHAFT BACKLASH Install a dial indicator. Check that the sector shaft has no backlash within 100 degrees of the left and right sides from neutral position. 10. REPLENISH WITH GEAR OIL Oil type: API GL–4, SAE 90 Capacity:… -
Page 760
SR–26 STEERING – Manual Gear Housing (4WD) MANUAL GEAR HOUSING (4WD) REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION OF MANUAL GEAR HOUSING Remove and install the parts as shown. (MAIN POINTS OF REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION) 1. DISCONNECT UNIVERSAL JOINT (a) Loosen the column side set bolt. (b) Remove the gear side set bolt. -
Page 761
SR–27 STEERING – Manual Gear Housing (4WD) 3. CONNECT PITMAN ARM TO GEAR HOUSING Align alignment marks on the pitman arm and the sector shaft, and install the spring washer and nut. Torque: 177 N–m (1,800 kgf–cm, 130 ft–lbf ) 4. -
Page 762
SR–28 STEERING – Manual Gear Housing (4WD) DISASSEMBLY OF MANUAL GEAR HOUSING 1. REMOVE BLEEDER PLUG AND DRAIN GEAR OIL 2. REMOVE END COVER (a) Remove the adjusting screw lock nut and four bolts. (b) Remove the end cover by turning the adjusting screw clockwise. -
Page 763
SR–29 STEERING – Manual Gear Housing (4WD) 6. REMOVE WORM SHAFT Pull the worm shaft out of the gear housing. NOTICE: Do not disassemble the ball nut from the worm shaft. -
Page 764
SR–30 STEERING – Manual Gear Housing (4WD) INSPECTION AND REPLACEMENT OF MANUAL GEAR HOUSING 1. INSPECT WORM AND BALL NUT (a) Check the worm and ball nut for wear or damage. (b) Check that the nut rotates smoothly down the shaft by its own weight. -
Page 765
SR–31 STEERING – Manual Gear Housing (4WD) (c) Using SST, remove the outer race from the gear housing. SST 09612–65014 (09612–01030) (d) Using SST, press in a new outer race into the gear housing. SST 09550–10012 (09552–10010, 09559–10010) (e) Using SST, remove the outer race from the adjusting screw. -
Page 766
SR–32 STEERING – Manual Gear Housing (4WD) (b) Using a socket wrench, drive in a new oil seal. 4. MEASURE SECTOR SHAFT THRUST CLEARANCE Using a feeler gauge, measure the shaft thrust clearance. Maximum clearance: 0.05 mm (0.0020 in.) or less If necessary, install a new thrust washer to provide the minimum clearance between the sector shaft and adjust–… -
Page 767
SR–33 STEERING – Manual Gear Housing (4WD) ASSEMBLY OF MANUAL GEAR HOUSING (See page SR–27) 1. APPLY MP GREASE TO BUSHING, NEEDLE ROLLER BEARING AND OIL SEALS 2. INSTALL WORM SHAFT INTO GEAR HOUSING Place the worm bearing on the shaft and install the shaft into the housing. -
Page 768
SR–34 STEERING – Manual Gear Housing (4WD) 5. INSTALL END COVER (a) Apply sealant to new gasket and end cover. Sealant: Part No. 08833–00080, THREE BOND 1344, LOCTITE 242 or equivalent (b) Install the end cover over the gasket. (c) Loosen the adjusting screw as far as possible. (d) Torque the four cover bolts. -
Page 769
SR–35 STEERING – Manual Gear Housing (4WD) 10. REPLENISH WITH GEAR OIL Oil type: API GL–4, SAE 90 Capacity: 400 cc (24.4 cu in.) Oil level: (at installation) 14 – 17 mm (0.55 – 0.67 in.) from top 11. INSTALL BLEEDER PLUG Torque: 20 N–m (200 kgf–cm, 14 ft–lbf) -
Page 770: Power Steering
SR–36 STEERING – Power Steering (Description) NEUTRAL (STRAIGHT–AHEAD) POWER STEERING POSITION Description Fluid from the pump is sent to the control valve. If the control valve is in the neutral position, all Two types of power steering are the standard type the fluid will flow through the control valve into and the PPS (progressive power steering) type.
-
Page 771
SR–37 STEERING – Power Steering (Description) SERVICE HINT Troubles with the power steering system are usu– ally concerned with hard steering due to the fact that there is no assist. In such cases, before at– tempting to make repairs, it is necessary to deter– mine whether the trouble lies with the pump or with the gear housing. -
Page 772: Fluid Level Check
SR–40 STEERING – Power Steering (On–Vehicle Inspection) On–Vehicle Inspection CHECK DRIVE BELT TENSION Using a belt tension gauge, check the drive belt tension. Belt tension gauge: Nippondenso BTG–20 (95506–00020) or Borroughs No. BT–33–73F Drive belt tension: New belt 441 – 667 N–m (45 –…
-
Page 773
SR–41 STEERING – Power Steering (On–Vehicle Inspection) REPLACEMENT OF POWER STEERING FLUID 1. JACK UP FRONT OF VEHICLE AND SUPPORT IT WITH STANDS 2. REMOVE FLUID RETURN HOSE FROM RESERVOIR TANK AND DRAIN FLUID INTO CONTAINER 3. WITH ENGINE IDLING, TURN STEERING WHEEL FROM LOCK TO LOCK WHILE DRAINING FLUID 4. -
Page 774
SR–42 STEERING – Power Steering (On–Vehicle Inspection) BLEEDING OF POWER STEERING SYSTEM NOTICE: The air bleeding method for vehicles equipped with the rear–wheel anti–lock brake system is different to the former method. For details, see page BR–95. 1. CHECK FLUID LEVEL IN RESERVOIR TANK Check the fluid level and add fluid if necessary. -
Page 775
SR–43 STEERING – Power Steering (On–Vehicle Inspection) 4. CHECK FLUID PRESSURE READING WITH VALVE CLOSED Close the pressure gauge valve and observe the reading on the gauge. Minimum pressure: 3VZ Engine 7,845 kPa (80 kg f/cm , 1,138 psi) Ex. 3VZ Engine 7,355 kPa (75 kgf/cm , 1,067 psi) NOTICE: Do not keep the valve closed for more than 10 sec–… -
Page 776
SR–44 STEERING – Power Steering (On–Vehicle Inspection) (d) Apply battery positive voltage to the solenoid. NOTICE: Do not apply voltage more than 30 seconds to • avoid burning out the solenoid. If repeating this step, wait until the solenoid cools •… -
Page 777: Power Steering Pump
SR–45 STEERING – Power Steering (Power Steering Pump) Power Steering Pump REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION OF POWER STEERING PUMP Remove and install the parts as shown.
-
Page 778
SR–46 STEERING – Power Steering (Power Steering Pump) (MAIN POINTS OF REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION) 1. (RN Series/4WD) DISCONNECT AND CONNECT PRESSURE TUBE Using SST, disconnect and connect the pressure tube from/to the PS pump. SST 09631–22020 Torque: 36 N–m (370 kgf–cm, 27 ft–lbf) HINT: Use a torque wrench with a fulcrum length of 300 mm (11.81 in.). -
Page 779
SR–47 STEERING – Power Steering (Power Steering Pump) COMPONENTS (VZN series) DISASSEMBLY OF POWER STEERING PUMP 1. CLAMP PS PUMP IN VISE NOTICE: Do not tighten the vise too tight. 2. REMOVE AIR CONTROL VALVE (a) Remove the air control valve. (b) Remove the union seat. -
Page 780
SR–48 STEERING – Power Steering (Power Steering Pump) 4. REMOVE PRESSURE PORT UNION AND FLOW CONTROL VALVE (a) Remove the pressure port union. (b) Remove the O–ring from the pressure port union. (c) Remove the flow control valve and spring. 5. -
Page 781
SR–49 STEERING – Power Steering (Power Steering Pump) 8. REMOVE ROTOR AND FRONT PLATE (a) Using a screwdriver, remove the snap ring. (b) Remove the rotor and front plate from the pump shaft. (c) Remove the two 0–rings from the front plate. (d) Remove the straight pin from the front plate. -
Page 782
SR–50 STEERING – Power Steering (Power Steering Pump) INSPECTION OF POWER STEERING PUMP 1. CHECK OIL CLEARANCE OF SHAFT AND BUSHING Using a micrometer and calipers, check the oil clearance. Standard clearance: 0.01–0.03 mm (0.0004 – 0.0012 in.) Maximum clearance: 0.07 mm (0.0028 in.) If more than maximum, replace the entire PS pump. -
Page 783
SR–51 STEERING – Power Steering (Power Steering Pump) (b) Check the flow control valve for leakage. Close one of the holes and apply compressed air [392 – 490 kPa (4 – 5 kgf/cm , 57 – 71 psi)] into the opposite side, and confirm that air does not come out from the end hole. -
Page 784
SR–52 STEERING – Power Steering (Power Steering Pump) ASSEMBLY OF POWER STEERING PUMP (See page SR–47) 1. COAT ALL SLIDING SURFACES WITH POWER STEERING FLUID BEFORE ASSEMBLY 2. INSTALL ADJUSTING STAY Install the adjusting stay and torque the two bolts. Torque: 41 N–m (420 kgf–cm, 30 ft–lbf) 3. -
Page 785
SR–53 STEERING – Power Steering (Power Steering Pump) (c) Align the hole of the front plate and straight pin and tap in the pump shaft with a plastic hammer. NOTICE: Be careful not to damage the oil seal and 0–rings. 5. -
Page 786
SR–54 STEERING – Power Steering (Power Steering Pump) (d) Install the snap ring. 9. CHECK PUMP SHAFT PRELOAD (a) Check that the shaft rotates smoothly without ab– normal noise. (b) Temporarily install the pulley nut and check the ro– tating torque. Rotating torque: 0 .3 N–m (2.8 kgf–cm, 2.4 in.–lbf) or less 10. -
Page 787
SR–55 STEERING – Power Steering (Power Steering Pump) 12. INSTALL AIR CONTROL VALVE (a) Install a new union seat to the housing. (b) Install and torque the air control valve. Torque: 36 N–m (370 kgf–cm, 27 ft–lbf) -
Page 788
SR–56 STEERING – Power Steering (Power Steering Pump) COMPONENTS (RN series) DISASSEMBLY OF POWER STEERING PUMP 1. CLAMP PS PUMP IN VISE NOTICE: Do not tighten the vise too tight. 2. REMOVE AIR CONTROL VALVE (a) Remove the air control valve. (b) Remove the union seat. -
Page 789
SR–57 STEERING – Power Steering (Power Steering Pump) 3. REMOVE SUCTION PORT UNION (a) Remove the bolt and union. (b) Remove the 0–ring from the union. 4. REMOVE FOUR FRONT HOUSING BOLTS 5. REMOVE FRONT HOUSING (a) Place matchmarks on the front and rear housing. (b) Using a plastic hammer, tap off the front housing. -
Page 790
SR–58 STEERING – Power Steering (Power Steering Pump) (d) Using a plastic hammer, lightly tap the rotor shaft out of the front housing. 8. REMOVE REAR PLATE AND SPRING Using a plastic hammer, tap the bottom end of the rear housing, and remove the rear plate and spring. -
Page 791
SR–59 STEERING – Power Steering (Power Steering Pump) (c) Pull out the bolt and remove the spring seat. (d) Remove the O–ring from the spring seat. INSPECTION OF POWER STEERING PUMP 1. INSPECT BUSHING AND MEASURE BUSHING OIL CLEARANCE (a) Check the bushing for wear or damage. The bushing cannot be replaced separately. -
Page 792
SR–60 STEERING – Power Steering (Power Steering Pump) HINT: There are five vane lengths with the following ro– tor and cam ring numbers: Rotor and cam mm (in.) Vane length ring number 5. INSPECT FLOW CONTROL VALVE (a) Check the flow control valve for wear or damage. (b) Apply fluid to the valve and check that it falls smoothly into the valve hole by its own weight. -
Page 793
SR–61 STEERING – Power Steering (Power Steering Pump) ASSEMBLY OF POWER STEERING PUMP (See page SR–56) 1. INSTALL FLOW CONTROL SPRING SEAT (a) Install a new O–ring to the spring seat. (b) Install the spring seat to the housing. (e) Using snap ring pliers, install the snap ring. 2. -
Page 794
SR–62 STEERING – Power Steering (Power Steering Pump) 6. INSTALL OIL SEAL (a) Apply a light coat of MP grease to a new oil seal lip. (b) Using SST and a hammer, install the oil seal. SST 09608–30012 (09608–04030) 7. INSTALL NEW O–RING 8. -
Page 795
SR–63 STEERING – Power Steering (Power Steering Pump) (b) Place the spring on the rear plate. 12. INSTALL REAR HOUSING (a) Align the matchmarks on the front and rear housing and assemble them. (b) Tighten the front and rear housing mount bolts by hand. -
Page 796
SR–64 STEERING – Power Steering (Power Steering Pump) 16. CHECK ROTOR SHAFT ROTATION CONDITION (a) Check that the rotor shaft rotates smoothly without abnormal noise. (b) Provisionally install the pulley nut and check the ro– tation torque. Rotation torque: 0.3 N–m (2.8 kgf–cm, 2.4 in.–lbf ) or less… -
Page 797
SR–65 STEERING – Power Steering (Gear Housing) Gear Housing (2WD) REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION OF GEAR HOUSING Remove and install the parts as shown. -
Page 798
SR–66 STEERING – Power Steering (Gear Housing) (MAIN POINTS OF REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION) 1. DISCONNECT UNIVERSAL JOINT (a) Loosen the column side set bolt. (b) Remove the gear side set bolt. (c) Place matchmarks on the flexible coupling and worm shaft. (d) Slide the shaft rearward to disconnect the shaft from the worm shaft. -
Page 799
SR–67 STEERING – Power Steering (Gear Housing) COMPONENTS… -
Page 800
SR–68 STEERING – Power Steering (Gear Housing) DISASSEMBLY OF GEAR HOUSING (See page SR–67) 1. MOUNT HOUSING ON STAND Mount the gear housing on SST and clamp SST in a vise. SST 09630–00012 (09631–00140) 2. (w/PPS) REMOVE SOLENOID VALVE (a) Remove the two bolts and solenoid valve. (b) Remove the 0–rings. -
Page 801
SR–69 STEERING – Power Steering (Gear Housing) (c) Pull out the valve body and power piston assembly. NOTICE: Ensure that the power piston nut does not come off the worm shaft. (d) Remove the 0–ring. -
Page 802
SR–70 STEERING – Power Steering (Gear Housing) INSPECTION AND REPLACEMENT OF GEAR HOUSING 1. CHECK BALL CLEARANCE (a) Mount the valve body in a vise. (b) Using a dial indicator, check the ball clearance. Move the worm gear up and down. Maximum ball clearance: 0.15 mm (0.0059 in.) If clearance is excessive, the power control valve assem–… -
Page 803
SR–71 STEERING – Power Steering (Gear Housing) (d) Using SST, press out the bearings. SST 09630–00012 (09631–00020, 09631–00070) (e) Using SST, press in a new lower bearing. SST 09630–00012 (09631–00020, 09631–00100, 09631–00170) HINT: Install the lower bearing so that it is positioned 23.1 mm (0.909 in.) away from the housing inner end surface. -
Page 804
SR–72 STEERING – Power Steering (Gear Housing) (k) Using SST, drive a new oil seal into the gear hous– ing. SST 09630–00012 (09631–00020, 09631–00170) 5. IF NECESSARY, REPLACE CONTROL VALVE TEFLON RING AND O–RING (a) Using a screwdriver, remove the teflon ring and 0–ring. -
Page 805
SR–73 STEERING – Power Steering (Gear Housing) ASSEMBLY OF GEAR HOUSING (See page SR–67) 1. INSTALL WORM GEAR VALVE BODY ASSEMBLY (a) Install the three 0–rings to the gear housing and valve body. (b) Mount the gear housing on SST and clamp SST in vise. -
Page 806
SR–74 STEERING – Power Steering (Gear Housing) 4. DETERMINE CENTER POSITION OF GEAR HOUSING (a) Using SST, turn the worm shaft so full lock in both directions and determine the exact center. SST 09616–00010 (b) Place matchmarks on the worm shaft and housing to show neutral position. -
Page 807
SR–75 STEERING – Power Steering (Gear Housing) Gear Housing (4WD) REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION OF GEAR HOUSING Remove and install the parts as shown. -
Page 808
SR–76 STEERING – Power Steering (Gear Housing) (MAIN POINT OF REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION) 1. REMOVE RESERVOIR TANK 2. REMOVE AIR CLEANER ASSEMBLY 3. DISCONNECT UNIVERSAL JOINT (a) Loosen the column side set bolt. (b) Remove the gear side set bolt. (c) Place matchmarks on the universal joint and worm shaft. -
Page 809
SR–77 STEERING – Power Steering (Gear Housing) 6. DISCONNECT AND CONNECT RETURN HOSE (a) Using a screwdriver, loosen the clamp and discon– nect the return hose. (b) When connecting, check that hose and tube con– nections are as shown and tighten the screw. NOTICE: At installation, be sure that the clamp does not touch the other parts. -
Page 810
SR–78 STEERING – Power Steering (Gear Housing) COMPONENTS… -
Page 811
SR–79 STEERING – Power Steering (Gear Housing) DISASSEMBLY OF GEAR HOUSING (See page SR–76) 1. MOUNT HOUSING ON STAND Mount the gear housing on SST and clamp SST in a vise. SST 09630–00012 (09631–00140) 2. REMOVE END COVER (a) Remove the adjusting screw lock nut. (b) Remove the four bolts and No. -
Page 812
SR–80 STEERING – Power Steering (Gear Housing) 4. REMOVE PLUNGER GUIDE NUT (a) Using SST, remove the plunger guide nut. SST 09043–38100 (b) Remove the spring, plunger and plunger guide nut. (e) Remove the O–ring. 5. REMOVE WORM GEAR VALVE BODY ASSEMBLY (a) Remove the four cap bolts from the housing. -
Page 813
SR–81 STEERING – Power Steering (Gear Housing) INSPECTION AND REPLACEMENT OF GEAR HOUSING 1. CHECK BALL CLEARANCE (a) Mount the valve body in a vise. (b) Using a dial indicator, check the ball clearance. Move the worm gear up and down. Maximum ball clearance: 0.15 mm (0.0059 in.) If clearance is excessive, the power control valve assem–… -
Page 814
SR–82 STEERING – Power Steering (Gear Housing) (d) Using SST, remove the upper bearing. SST 09612–65014 (09612–01030) (e) Using SST, press out the lower bearing. SST 09630–00012 (09631–00020, 09631–00090) (f) Using SST, press in a new lower bearing. SST 09630–00012 (09631–00020, 09631–00090) HINT: Install the lower bearing so that it is positioned 23.1 mm (0.909 in.) away from the housing inner end surface. -
Page 815
SR–83 STEERING – Power Steering (Gear Housing) (j) Form a new teflon ring into a heart shape and install it with hand. (k) Using SST, form the teflon ring. NOTICE: The teflon ring must be squeezed before in– serting the cross shaft or damage will result. SST 09630–00012 (09631–00120) (l) Using SST, drive a new oil seal into the gear hous–… -
Page 816
SR–84 STEERING – Power Steering (Gear Housing) (b) Using a plastic hammer and extension bar, tap in a new union seat. ASSEMBLY OF GEAR HOUSING (See page SR–76) 1. INSTALL WORM GEAR VALVE BODY ASSEMBLY (a) Install the three 0–rings to the gear housing and valve body. -
Page 817
SR–85 STEERING – Power Steering (Gear Housing) 3. INSTALL CROSS SHAFT AND END COVER (a) Install a new 0–ring on the end cover. (b) Assemble the cross shaft to the end cover. HINT: Fully loosen the adjusting screw. (c) Set the worm gear at the center of the gear housing. (d) Install and push the cross shaft into the gear hous–… -
Page 818
SR–86 STEERING – Power Steering (Gear Housing) 8. CHECK TOTAL PRELOAD Using SST with a torque meter, check total preload. SST 09616–00010 Total preload (Starting): 0.5 – 0.9 N–m (5 – 9.5 kgf–cm, 4.3 – 8.3 in.–lbf) -
Page 819
SR–87 STEERING – Power Steering (Progressive Power Steering) Progressive Power Steering (PPS) DESCRIPTION AND ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT… -
Page 820
SR–88 STEERING – Power Steering (Progressive Power Steering) TROUBLESHOOTING Trouble • Hard steering at idle or low–speed driving. • Steering too sensitive during high–speed driving. Preliminary Check • Check tire pressure. • Check lubrication of suspension and steering linkage. • Check front wheel alignment. •… -
Page 821
SR–89 STEERING – Power Steering (Progressive Power Steering) CONTINUED FROM PREVIOUS PAGE Check 2. Check that there is continuity between the ECU terminal G ND and body ground. Open circuit in wire harness between the ECU terminal • GND and body ground. Body ground faulty. -
Page 822
SR–90 STEERING – Power Steering (Progressive Power Steering) CONTINUED FROM PREVIOUS PAGE Check 5. Measure the resistance between terminals SOL + and SOL –. Standard resistance: 6 – 11 Ω Open circuit in wire harness between the terminals SOL • + and SOL –. -
Page 823
SR–91 STEERING – Power Steering (Progressive Power Steering) ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM Solenoid Valve ON–VEHICLE INSPECTION 1. DISCONNECT WIRING CONNECTOR 2. MEASURE RESISTANCE Measure the resistance between SOL – and SOL +. Resistance: 6 – 11 3. CONNECT WIRING CONNECTOR CHECK SOLENOID OPERATION 1. -
Page 824
SR–92 STEERING – Power Steering (Progressive Power Steering) Power Steering ECU INSPECTION OF ECU 1. JACK UP VEHICLE AND SUPPORT IT ON STANDS 2. REMOVE CENTER CONSOLE HINT: Do not disconnect the ECU connector. 3. START ENGINE 4. MEASURE VOLTAGE OF ECU (a) Using a voltmeter, measure the voltage between ECU terminals GND and SOL E) while the engine is idling. -
Page 825
SR–93 STEERING – Steering Linkage (2WD) STEERING LINKAGE (2WD) REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION OF STEERING LINKAGE Remove and install the parts as shown. HINT: When connecting the ball stud to the arm or rod, re– • move the grease on the joint surfaces. After torquing the ball stud nut to specified torque, ad–… -
Page 826
SR–94 STEERING – Steering Linkage (2WD) (MAIN POINTS OF REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION) 1. DISCONNECT AND CONNECT PITMAN ARM FROM/TO SECTOR SHAFT (a) Loosen the pitman arm nut. (b) Using SST, disconnect the pitman arm from the sec– tor shaft. SST 09610–55012 (c) When connecting, align alignment marks on the pit–… -
Page 827
SR–95 STEERING – Steering Linkage (2WD) 5. CONNECT TIE ROD (a) Screw the tie rod ends into the tie rod. HINT: The tie rod length should be approximately 314.5 mm (12.382 in.), and the remaining length of threads on both tie rod ends should be equal. (b) Turn the tie rods so that they cross at about 90 de–… -
Page 828
SR–96 STEERING – Steering Linkage (2WD) 2. REMOVE IDLER ARM WITH SHAFT Remove the nut and pull the idler arm with the shaft off the idler arm bracket. 3. REMOVE OIL SEAL Using a screwdriver, remove the oil seal. ASSEMBLY OF IDLER ARM BRACKET 1. -
Page 829
SR–97 STEERING – Steering Linkage (4WD) STEERING LINKAGE (4WD) REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION OF STEERING LINKAGE Remove and install the parts as shown. HINT: (See page SR–93) -
Page 830
SR–98 STEERING – Steering Linkage (4WD) (MAIN POINTS OF REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION) 1. DISCONNECT AND CONNECT PITMAN ARM FROM/TO SECTOR SHAFT (a) Loosen the pitman arm nut. (b) Using SST, disconnect the pitman arm from the sec– tor shaft. SST 09628–62011 (c) When connecting, align alignment marks on the pit–… -
Page 831
SR–99 STEERING – Steering Linkage (4WD) 5. CONNECT TIE ROD (a) Screw the tie rod ends into the tie rod. HINT: The tie rod length should be approximately 328.5 mm (12.933 in.), and the remaining length of threads on both tie rod ends should be equal. (b) Turn the tie rods so that they cross at about 90 de–… -
Page 832
SR–100 STEERING – Steering Linkage (4WD) 2. REMOVE IDLER ARM WITH SHAFT Remove the nut and pull the idler arm with the shaft off the idler arm bracket. 3. REMOVE OIL SEAL Using a screwdriver, remove the oil seal. ASSEMBLY OF IDLER ARM BRACKET 1. -
Page 833
SR–101 STEERING – Steering Linkage (4WD) 5. IF NECESSARY, REPLACE BUSHINGS (a) Using a screwdriver, remove the bushings. (b) Using SST, install each bushing to the idler arm bracket. SST 09620–30010 (09627–30010, 09631–00020) 6. INSTALL IDLER ARM BRACKET CAP (a) Apply sealant to the cap end. Sealant: Part No. -
Page 834: Body Electrical System
BE–1 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM…
-
Page 835
BE–2 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – General Information GENERAL INFORMATION Wiring color code Wire colors are indicated by an alphabetical code. B = Black L = Blue R = Red BR = Brown LG = Light Green V = Violet G = Green O = Orange W = White GR = Gray P = Pink * =Yellow The first letter indicates the basic wire color and the sec–… -
Page 836
BE–3 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – General Information Replacement of High Current Fuse, Medium Current Fuse and Fuse HINT: If replacing the fuse be sure to replace it with a fuse of fusible link with and equal amperege rating. NOTICE: 1. Turn off all electrical components and the ignition switch before replacing a fuse or fusible link. -
Page 837
BE–4 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – General Information Check for Voltage (a) Establish conditions in which voltage is present at the check point. Example: (A) Ignition switch on (B) Ignition switch and switch 1 (SW 1) on. (C) Ignition switch, switch 1 (SW 1) and relay on (switch 2 (SW2) off). -
Page 838
BE–5 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – General Information (c) Use a volt/ohmmeter with high impedance (10 k/V minimum) for troubleshooting of the electrical cir– cuit. Check the Bulb (a) Remove the bulb. (b) There should be continuity between the respective terminals of the bulb together with a certain amount of resistance. -
Page 839: Power Source
BE–6 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Power Source POWER SOURCE Parts Location…
-
Page 840
BE–7 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Power Source Wiring Diagram… -
Page 841: Ignition Switch
BE–8 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Ignition Switch IGNITION SWITCH Parts Location Wiring and Connector Diagrams Parts Inspection Ignition System INSPECT SWITCH (ignition Switch /Continuity) Terminal Switch position LOCK START If continuity is not as specified, replace the switch.
-
Page 842
BE–9 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Ignition Switch Key Confine Prevention System 1. INSPECT SWITCH (Key Unlock Warning Switch/Continuity) Terminal Switch position OFF (Key removed) ON (Key set) (Door Courtesy Switch/Continuity) See step 2 on page BE–42. If continuity is not as specified, replace the switch. 2. -
Page 843: Lighting System
BE–10 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Lighting System LIGHTING SYSTEM Parts Location…
-
Page 844
BE–11 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Lighting System Wiring and Connector Diagrams… -
Page 845
BE–12 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Lighting System… -
Page 846
BE–13 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Lighting System… -
Page 847
BE–14 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Lighting System Troubleshooting Page Possible cause Remedy Problem Replace sealed beam headlight Only one light does Light bulb burned out Repair as necessary Socket, wire or ground faulty not light up Replace fusible link Fusible link blown Headlights do not Check relay light up… -
Page 848
BE–15 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Lighting System Troubleshooting (Cont’d) Problem Possible cause Remedy Page Turn signal do not Replace fuse and check for HAZ–HORN fuse blown BE–3 operate short Check flasher Turn signal flasher faulty BE–23 Check switch Turn signal/hazard switch faulty BE–23 Repair as necessary Wiring or ground faulty… -
Page 849
BE–16 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Lighting System Parts Adjustment Adjustment of Light Aiming Parts Replacement Components… -
Page 850
BE–17 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Lighting System Disassembly of Combination Switch NOTICE: w/ Cruise Control System To prevent damage to the slip ring when removing the steering wheel, be careful of the following points. • Keep the steering wheel in the ”straight–ahead” steer– ing position. -
Page 851
BE–18 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Lighting System 5. REMOVE HEADLIGHT DIMMER AND TURN SIGNAL SWITCH Remove four screws and the switch from the switch body. 6. REMOVE WIPER AND WASHER SWITCH Remove two screws and the switch from the switch body. -
Page 852
BE–19 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Lighting System Parts Inspection Headlight, Taillight and Daytime Running Light System 1. INSPECT COMBINATION SWITCH (Light Control Switch /Continuity) Terminal (Color) Switch position TAIL HEAD (Headlight Dimmer and Turn Signal Switch/Continuity) Headlight Dimmer Switch Terminal (Color) Switch position Flash Low beam… -
Page 853
BE–20 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Lighting System (Headlight Dimmer Relay/Continuity) Terminal Condition Constant Apply battery positive voltage to terminals 2 and 4. If continuity is not as specified, replace the relay. 1. INSPECT DAYTIME RUNNING LIGHT RELAY (Relay Circuit) Disconnect the connector from the relay and inspect the connector on the wire harness side as shown in the chart. -
Page 854
BE–21 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Lighting System (Relay Circuit/Connector connected) Connect the wire harness side connector to the relay and inspect wire harness side connector from the back side as shown. Check for Tester connection Condition Specified value Voltage No voltage Light control switch position TAIL or HEAD… -
Page 855: Illuminated Entry System
BE–22 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Lighting System Lights–On Warning System 1. INSPECT DOOR COURTESY SWITCH See combination meter on page BE–39. 2. INSPECT LIGHT REMAINDER RELAY (Relay Circuit/Operation) (a) Connect the positive (+) lead from the battery to terminal 3 and the negative (–) lead to terminal 4. (b) Check that the buzzer does not sound when con–…
-
Page 856
BE–23 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Lighting System Turn Signal and Hazard Warning System 1. INSPECT SWITCHES (Turn Signal Switch /Continuity) See Headlight Dimmer and Turn Signal Switch on page BE–1 (Hazard Warning Switch/Continu- ity) Terminal Switch position If continuity is not as specified, replace the switch. 2. -
Page 857
BE–24 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Wiper and Washer System WIPER AND WASHER SYSTEM Parts Location Wiring and Connector Diagrams (w/ MIST Wiper) -
Page 858
BE–25 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Wiper and Washer System (w/ Intermittent Wiper) Troubleshooting Problem Possible cause Remedy Page Wipers do not WIPER fuse blown Replace fuse and check for BE–3 operate or return short to off position Check motor Wiper motor faulty BE–27 Check switch Wiper switch faulty… -
Page 859: Wiper System
BE–26 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Wiper and Washer System Parts Inspection Wiper System 1. INSPECT SWITCHES (Wiper and Washer Switch/Continuity) w/ Mist Wiper Terminal (Color) Switch position MIST Wiper Washer wI Intermittent Wiper Terminal (Color) Switch position MIST Wiper Washer If continuity is not as specified, replace the switch.
-
Page 860
BE–27 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Wiper and Washer System 2. INSPECT MOTOR (Operation at Low Speed) Connect the positive (+) lead from the battery to termi– nal 2 and the negative (–) lead to the motor body, check that the motor operates at low speed. If operation is not as specified, replace the motor. -
Page 861: Washer System
BE–28 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Wiper and Washer System Washer System 1. INSPECT WASHER SWITCH (Front Windshield Washer Switch) See Wiper and Washer Switch on page BE–27. 2. INSPECT WASHER MOTOR Connect the positive (+) lead from the battery to termi– nal 2 and the negative (–) lead to terminal 1, check that the motor operates.
-
Page 862: Combination Meter
BE–29 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Combination Meter COMBINATION METER Parts Location…
-
Page 863
BE–30 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Combination Meter Meter Circuit (w/o Tachometer) Wiring connector side Speed Sensor SIG–VAL ETC Pattern select switch A/T Oil Temperature switch Cruise Control Main Switch Fuel Sender Gauge–Terminal 2 GAUGE Fuse Ground Park/Neutral Position Switch Park/Neutral Position Switch Park/Neutral Position Switch Park/Neutral Position Switch Park/Neutral Position Switch… -
Page 864
BE–31 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Combination Meter (w/ Tachometer) Wiring connector side Speed Meter SIG–VAL ECM Pattern Select Switch Fuel Sender Gauge–terminal 3 A/T Oil Temperature Switch Cruise Control Main Switch Fuel Sender Gauge–terminal 4 GAUGE Fuse Ground Ground Park/Neutral Position Switch Park/Neutral Position Switch Park/Neutral Position Switch Park/Neutral Position Switch… -
Page 865
BE–32 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Combination Meter Troubleshooting Problem Possible cause Remedy Page Gauges and indicator GAUGE fuse faulty Replace fuse and check for BE–3 lights do not operate Wiring or ground faulty short Repair as necessary Voltmeter does not Voltmeter faulty Check voltmeter BE–33… -
Page 866
BE–33 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Combination Meter Parts Inspection Allowable range Standard indication Speedometer System 1. INSPECT SPEEDOMETER (ON–VEHICLE) (a) Using a speedometer tester, inspect the speedome– ter for allowable indication error and check the oper– ation of the odometer. (km/h) HINT: The wear and tire over or under inflation will in–… -
Page 867
BE–34 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Combination Meter Fuel Gauge System 1. INSPECT RECEIVER GAUGE (a) Disconnect the connector from the sender gauge. (b) Turn the ignition switch ON, check that the receiver gauge needle indicates EMPTY. (c) Connect terminals 1 and 2 on the wire harness side connector through a 3.4 W test bulb. -
Page 868
BE–35 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Combination Meter 2. INSPECT SENDER GAUGE (Operation) (a) Connect a series of three 1.5 v dry cell batteries. (b) Connect the positive (+) lead from the dry cell bat– teries to terminal 2 through a 3.4 W test bulb and the negative (–) lead to terminal 1. -
Page 869
BE–36 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Combination Meter 2. INSPECT WARNING SWITCH (a) Apply battery positive voltage between terminals 1 and 4 through a 3.4 W test bulb, check the bulb lights up. HINT: It will take a short time for the bulb to light up. (b) Submerge the switch in fuel, check that the bulb goes out. -
Page 870
BE–37 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Combination Meter (Resistance) Measure the resistance between terminals. HINT: Connect the test leads so that the current form the ohmmeter can flow according to the above order. If resistance value is not as specified, replace the receiver gauge. -
Page 871: Brake Warning System
BE–38 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Combination Meter (e) Ground terminal on the wire harness side connector through a 3.4 W test bulb. (d) Turn the ignition switch ON, check that the bulb lights up and the receiver gauge needle moves to high side.
-
Page 872
BE–39 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Combination Meter (Parking Brake Switch) (a) Check that there is continuity between terminals with the switch ON (switch pin released). (b) Check that there is no continuity between terminals with the switch OFF (switch pin pushed). If operation is not as specified, replace the switch. -
Page 873: Seat Belt Warning System
BE–40 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Combination Meter Seat Belt Warning System 1. INSPECT WARNING SWITCH (a) Disconnect the wire harness side connector from the integration relay. (b) Ground terminal 8 on the wire harness side connec– tor. (c) Turn the ignition switch ON, check that the warninc light lights up.
-
Page 874
BE–41 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Combination Meter 3. INSPECT INTEGRATION RELAY Remove the integration relay and inspect the connectors on the wire harness side and the junction block side as shown in the chart. Wire Harness Side Tester Specified value Check for Condition connection… -
Page 875
BE–42 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Combination Meter Illumination Control System INSPECT LIGHT CONTROL RHEOSTAT 1. STEP TYPE (w/ o Tachometer) Gradually turn the rheostat knob from the bright side to dark side, check that the resistance between terminals increases from approximately 0 to 5.1 If operation is not as specified, replace the rheostat. -
Page 876
BE–43 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Power Window Control System POWER WINDOW CONTROL SYSTEM Parts Location Wiring and Connector Diagrams… -
Page 877
BE–44 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Power Window Control System Troubleshooting Problem Possible cause Remedy Page Power window does GAUGE fuse blown Replace fuse and check for BE–3 not operate at all short Check relay Door lock control relay faulty BE–51 Repair as necessary Wiring or ground faulty One touch power… -
Page 878
BE–45 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Power Window Control System (Master Switch: Illumination) (a) Set the window lock switch to the unlock position. (b) Connect the positive (+) lead from the battery to terminal 9 and negative (–) lead to terminal6, check that all the illuminations light up. -
Page 879
BE–46 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Power Window Control System (e) Check that the current increases approximately 14.5 A or more when the window stops going down. HINT: The circuit breaker opens some 4–40 seconds after the window stops going down, so that check must be made before the circuit breaker operates. -
Page 880
BE–47 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Power Window Control System (Right Side Door Motor/ Motor Operation) (a) Connect the positive (+) lead from the battery to terminal 1 and the negative (–) lead to terminal 2, check that the motor turns clockwise. (b) Reverse the polarity, check that the motor turns counterclockwise. -
Page 881
BE–48 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Power Door Lock Control System POWER DOOR LOCK CONTROL SYSTEM Parts Location Wiring and Connector Diagrams… -
Page 882
BE–49 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Power Door Lock Control System Troubleshooting Page Possible cause Remedy Problem Replace fuse and check for BE–3 GAUGE fuse blown Door lock system short does not operate at Check solenoid BE–50 Door lock solenoid faulty Check relay BE–51 Door lock control relay faulty… -
Page 883
BE–50 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Power Door Lock Control System (Key Unlock Warning Switch/ Continuity) See Step l of Key Confine Prevention System on page BE–9. (Door Courtesy Switch/ Continuity) See Step of Open Door Warning System on page BE–41. HINT: Door key lock and unlock switch is built into the front door lock assembly. -
Page 884
BE–51 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Power Door Lock Control System 3. INSPECT DOOR LOCK CONTROL RELAY (Relay Circuit) Disconnect the connector from the relay and inspect the connector on the wire harness side as shown in the chart. Tester Specified value Condition Check for connection… -
Page 885
BE–52 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Power Door Lock Control System (Key–Off Power Window Signal) HINT: When the relay circuit is as specified, inspect the key–off power window signal. (a) Connect the connector to the relay. (b) Connect the positive (+) lead from the voltmeter to terminal 5 and negative (–) lead to terminal 10. -
Page 886
BE–53 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Power Mirror Control System POWER MIRROR CONTROL SYSTEM Parts Location Wiring and Connector Diagrams… -
Page 887
BE–54 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Power Mirror Control System Troubleshooting Page Possible cause Remedy Problem Replace fuse and check for BE–3 RADIO fuse blown Remote control mir– short ror system does not Check switch operate BE–54 Mirror switch faulty Check motor BE–55 Mirror motor faulty Repair as necessary… -
Page 888
BE–55 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Power Mirror Control System 2. INSPECT MIRROR MOTOR (a) Connect the positive (+) lead from the battery to terminal 3 and negative (–) lead to terminal 1, check that the mirror turns to left side. (b) Reverse the polarity, check that the mirror turns to right side. -
Page 889: Cruise Control System
BE–56 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM Parts Location…
-
Page 890
BE–57 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System… -
Page 891
BE–58 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System Wiring Diagram… -
Page 892
BE–59 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System Connector Diagrams… -
Page 893
BE–60 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System System Description Standby Operation • When the ignition switch is turned ON (IG), current flows from the battery to terminal 6 of the Cruise Control ECU (hereafter called ECU). • When the ignition switch is turned ON (IG), current flows from the battery to terminal 2 of the Main Relay. -
Page 894
BE–61 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System Diagnosis System Output of Diagnostic Trouble Code READ DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (Type A) (a) Turn the ignition switch on. (b) Push the SET/COAST switch on, and keep it on. (c) Push the main switch on. (d) Check that the indicator light ”CRUISE”… -
Page 895
BE–62 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System (Type6) (a) If while driving with the cruise control on, the sys– tem is canceled by a malfunction in either the actuator, speed sensor or cruise control switch circuit, the cruise control indicator light ”CRUISE” will blink 5 times. -
Page 896
BE–63 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System Troubleshooting You will find the troubles easier using the table well shown below. In this table, each number shows the priority of causes in troubles. Check each part in order. G, H Chart No. -
Page 897
BE–64 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System Inspection Chart INSPECTION OF POWER SOURCE CIRCUIT Turn ignition switch on • Short circuit in wire harness between EN– Is ENGINE fuse Replace fuse. GINE fuse and terminal 2 of main relay. normal? Is operation nor–… -
Page 898
BE–65 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System CONTINUED FROM PREVIOUS PAGE Disconnect combination switch connector. Is there continuity between terminal 4 of main Short circuit in wire harness between termi– nals 4 of main relay and 4I6 of slip ring. relay connector on wire harness side and ground? Connect connector to main relay. -
Page 899
BE–66 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System CONTINUED FROM PREVIOUS PAGE Is there continuity between terminals 2I2 and Open circuit in cruise control switch be– 4I5 of speed control switch? tween terminals 2I2 and 4I5. Connect connectors to slip ring. Short circuit in wire harness between ter–… -
Page 900
BE–67 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System CONTINUED ON PREVIOUS PAGE INSPECT INDICATOR LIGHT CIRCUIT Is GAUGE fuse normal? Replace fuse. • Short circuit in wire harness between Is operation nor– GAUGE fuse and terminal 4 of CC ECU. mal? Fuse faulty. -
Page 901
BE–68 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System INSPECTION OF CRUISE CONTROL SWITCH CIRCUIT Turn ignition switch off. CRUISE CONTROL SWITCH Disconnect connector from control switch. INSPECT CONTROL SWITCH Speed control switch faulty. Replace cruise control switch. Then re– Is control switch operation normal? (See page BE–81) check system. -
Page 902
BE–69 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System INSPECTION OF ACTUATOR CIRCUIT Turn ignition switch off. VACUUM HOSE Are there cracks or other damage on the vac– Vacuum hose faulty. uum hose? Replace vacuum hose. Then recheck sys– tem. ACTUATOR INSPECT CABLE FREEPLAY Adjust control cable freeplay. -
Page 903
BE–70 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System CONTINUED FROM PREVIOUS PAGE Disconnect connector from CC ECU and in– spect connector–on wire harness side as fol– lows. Short circuit in wire harness between ter– INSPECT STOP LIGHT SWITCH CIRCUIT Is there continuity between terminals 3 and minals 3 of ECU and terminal 2 of stop 16 with brake pedal depressed? light switch. -
Page 904
BE–71 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System INSPECTION OF SPEED SENSOR CIRCUIT SPEED METER CABLE INSPECT SPEED METER CABLE Meter cable faulty. Does not meter fluctuate when driving at a Replace meter cable. Then recheck system. steady speed? Turn ignition switch off. SPEED SENSOR Disconnect connector from combination meter. -
Page 905
BE–72 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System INSPECTION OF STOP LIGHT SWITCH CIRCUIT Turn ignition switch off. Is STOP fuse normal? Replace fuse. Short circuit in wire harness between termi– Is operation nor– nal 18 of CC ECU or terminal 1 of stop light mal? switch and fuse. -
Page 906
BE–73 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System INSPECTION OF PARKING BRAKE SWITCH CIRCUIT Turn ignition switch off. BRAKE FLUID LEVEL WARNING SWITCH INSPECT GROUND CONNECTION • Open circuit in wire harness between terminal 2 of brake fluid level warning Disconnect connector from brake fluid level warning switch. -
Page 907
BE–74 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System INSPECTION OF CLUTCH SWITCH CIRCUIT Turn ignition switch off. CLUTCH SWITCH INSPECT GROUND CONNECTION Open circuit in wire harness between termi– Disconnect connector from clutch switch. nal 2 of the clutch switch and ground. Is there continuity between terminal 2 of wire harness side connector and ground? INSPECT CLUTCH SWITCH CONTINUITY… -
Page 908
BE–75 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System INSPECTION OF PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH CIRCUIT Turn ignition switch off. PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH INSPECT GROUND CONNECTION Open circuit in wire harness between ter– Disconnect connector from park/neutral posi– minal 3 of park/neutral position switch tion switch. -
Page 909
BE–76 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System INSPECTION OF VACUUM CIRCUIT Turn ignition switch off. VACUUM HOSE Replace vacuum hose. Are there cracks or other damage on the vac– uum hose? VACUUM SWITCH • Open circuit in wire harness between INSPECT VACUUM SWITCH CIRCUIT Disconnect connector from vacuum switch. -
Page 910
BE–77 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System CONTINUED FROM PREVIOUS PAGE Disconnect connector from CC ECU and in– spect connector on wire harness side as fol– lows. Open circuit in wire harness between ter– INSPECT VACUUM SWITCH CIRCUIT minal 1 1 of CC ECU and terminal 1 of vac– Is there continuity between terminal 1 1 and uum switch. -
Page 911
BE–78 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System INSPECTION OF ECM SOLENOID CIRCUIT Start engine (idling). Short or open circuit in wire harness be– Is there battery positive voltage between tween terminal 6/26 of ECM and terminal 9 terminal 6126 of ECM and ground? of CC ECU. -
Page 912
BE–79 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System Cruise Control ECU Circuit Inspection of ECU Circuit Disconnect the connector from the ECU and inspect the connector on the wire harness side as shown below. Connection or Check for Tester Connection Condition Specified valve Measure item… -
Page 913
BE–80 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System Parts Inspection 1. INSPECT SWITCHES (Main Switch/Continuity) Terminal Switch position If continuity is not as specified, replace the switch. (Cruise Control Switch /Continuity) Terminal Condition Constant If continuity is not as specified, replace the switch. (Cruise Control Switch/Resistance) Measure the resistance value between terminals 2/5 and 4I5 or 2I2. -
Page 914
BE–81 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System (Clutch Switch /Continuity) Inspect the switch continuity between terminals. Terminal Condition Switch pin free (Clutch pedal depressed) Switch pin pushed in (Clutch pedal released) If continuity is not as specified, replace the switch. (Brake Fluid Level Warning Switch/Operation) See step 2 on page BE–39. -
Page 915
BE–82 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Cruise Control System 5. INSPECT VACUUM PUMP (3VZ–E Engine) (a) Connect a vacuum gauge to the ACT side of the pump. (b) Connect the positive (+) lead from the battery to terminal 1 and the negative (–) lead to terminal 2. (c) Check that there is a vacuum of 200 mmHg (7.87 in. -
Page 916: Audio System
BE–83 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System AUDIO SYSTEM Parts Location…
-
Page 917
BE–84 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System Wiring and Connector Diagrams… -
Page 918
BE–85 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System… -
Page 919
BE–86 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System… -
Page 920
BE–87 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System… -
Page 921
BE–88 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System System Description RADIO WAVE BAND The radio wave bands used in radio broadcasting are as follows: Frequency Designation Radio wave Modulation Amplitude modulation Frequency modulation method LF: Low Frequency MF: Medium Frequency HF: High Frequency VHF: Very High Frequency HINT: In this section, the term ”’AM”… -
Page 922
BE–89 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System MAINTENANCE OF TAPE PLAYER Head Cleaning (a) Raise the cassette door with your finger. Next using a pencil or like object, push in the guide. (b) Using a cleaning pen or cotton applicator soaked in cleaner, clean the head surface, pinch rollers and capstans. -
Page 923
BE–90 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System HOW TO USE DIAGNOSTIC CHART Audio system type and symbol used. HINT: Confirm the applicable type of audio system. Symbol for type of audio system the question applies to. HINT: If the audio system type is not applicable, proceed to next question below. Junction without black circle. -
Page 924
BE–91 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System Troubleshooting NOTICE: when replacing the internal mechanism (computer part) of the audio system, be careful that no part of your body or clothing comes in contact with the terminals of the leads from the IC, etc. of the re– placement part (spare part). -
Page 925
BE–92 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System Troubleshooting for ANTI–THEFT SYSTEM Turn Ignition key from LOCK position to ACC position. Display A: Display E: Display B. ANTI–THEFT SYSTEM ID Number is set. operation condition. (ID number input error 10 times or more. ”SEC”… -
Page 926
BE–93 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System Radio NO POWER COMING IN [R] Radio [S]: Radio + Tape Player [U]: Radio–Tape Player (Built–in Power Amplifier) [P] Radio–Tape Player (Separate Power Amplifier) [S][U][P] Is tape player operating normally? Radio faulty. Radio assembly faulty. Replace fuse. -
Page 927
BE–94 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System Radio POWER COMING IN, BUT RADIO NOT OPERATING [R] Radio [S] Radio + Tape Player [U] Radio–Tape Player (Built–in Power Amplifier) [P] Radio–Tape Player (Separate Power Amplifier) [S][U][P] Is tape player operating normally? Go to No. -
Page 928
BE–95 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System Radio EITHER SPEAKER DOES NOT WORK [R] Radio [S] Radio + Tape Player [U] Radio–Tape Player (Built–in Power Amplifier) [P] Radio–Tape Player (Separate Power Amplifier) [S][U][P] Radio faulty. Is tape player operating normally? Radio assembly faulty. -
Page 929
BE–96 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System EITHER AM OR FM DOES NOT WORK, RECEPTION Radio POOR (VOLUME FAINT), FEW PRESET TUNING BANDS [R] Radio [S] Radio + Tape Player [U] Radio–Tape Player (Built–in Power Amplifier) [P] Radio–Tape Player (Separate Power Amplifier) Problem with radio wave signals or location? Poor signals, poor location. -
Page 930
BE–97 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System Radio SOUND QUALITY POOR [E] Radio [S] Radio + Tape Player [U] Radio–Tape Player (Built–in Power Amplifier) [P] Radio–Tape Player (Separate Power Amplifier) Is sound quality always Is sound quality bad in cer– Poor signals, poor location. -
Page 931
BE–98 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System CANNOT SET STATION SELECT BUTTON, PRESET Radio MEMORY DISAPPEARS [R] Radio [S] Radio + Tape Player [U] Radio–Tape Player (Built–in Power Amplifier) [P] Radio–Tape Player (Separate Power Amplifier) [S][U][P] Radio assembly faulty. Can cassette tape be inserted in tape player? Replace fuse. -
Page 932
BE–99 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System CASSETTE TAPE CANNOT BE INSERTED Tape Player [S] Radio + Tape Player [U] Radio–Tape Player (Built–in Power Amplifier) [P] Radio–Tape Player (Separate Power Amplifier) [S][U][P] Remove foreign object. Is there a foreign object inside tape player? Tape player faulty. -
Page 933
BE–100 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System CASSETTE TAPE INSERTS, BUT NO POWER Tape Player [S] Radio + Tape Player [U] Radio–Tape Player (Built–in Power Amplifier) [P] Radio–Tape Player (Separate Power Amplifier) Is Radio operation normally? Tape player faulty. Radio assembly faulty. Check if CIG &… -
Page 934
BE–101 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System POWER COMING IN, BUT TAPE PLAYER NOT Tape Player OPERATING [S] Radio + Tape Player [U] Radio–Tape Player (Built–in Power Amplifier) [P] Radio–Tape Player (Separate Power Amplifier) Functions OK if different cassette tape in- Cassette tape faulty. -
Page 935
BE–102 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System EITHER SPEAKER DOES NOT WORK Tape Player [S] Radio + Tape Player [U] Radio–Tape Player (Built–in Power Amplifier) [P] Radio–Tape Player (Separate Power Amplifier) Tape player faulty. Is radio operating normally? Radio assembly faulty. Tape player faulty. -
Page 936
BE–103 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System SOUND QUALITY POOR (VOLUME FAINT) Tape Player [S] Radio + Tape Player [U] Radio–Tape Player (Built–in Power Amplifier) [P] Radio–Tape Player (Separate Power Amplifier) Functions OK if different cassette tape in– Cassette tape faulty. serted? Operates normally after cleaning the heads? Head dirty. -
Page 937
BE–104 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System Tape Player APS, SKIP, RPT BUTTONS NOT OPERATING [S] Radio + Tape Player [U] Radio–Tape Player (Built–in Power Amplifier) [P] Radio–Tape Player (Separate Power Amplifier) Functions OK if different cassette tape in– Radio assembly faulty. serted? Cassette tape faulty. -
Page 938
BE–105 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System ANTENNA–RELATED Antenna 24–a: Pole Antenna Extend fully. Is antenna extended? Temporarily install another antenna. Antenna faulty. Functions OK? Radio side faulty. 24–b: Motor Antenna [M] : Motor Antenna (Radio Linked Type) 0 : Motor Antenna (Except Radio–Linked Type) Temporarily install Does antenna extended when radio Motor antenna… -
Page 939
BE–106 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System NOISE PRODUCED BY VIBRATION OR SHOCK WHILE Noise DRIVING Is speaker properly installed? Install properly. Is each system correctly installed? With vehicle stopped, lightly tap each Each system faulty. system. Is noise produced? Noise produced by static electricity accumu–… -
Page 940
BE–107 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System NOISE PRODUCED WHEN ENGINE STARTS Noise Generator noise. Whistling noise which becomes high–pitched when accelerator strongly depressed, disap– pears shortly after engine stops. Whining noise occurs when A/C is operating. A/C noise. Fuel gauge noise. Scratching noise occurs during sudden accel–… -
Page 941
BE–108 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System Parts Inspection 1. INSPECT ANTENNA MOTOR (a) Connect the positive (+) lead from the battery to terminal 1 and the negative (–) lead to terminal 2. (b) Check that the motor turns (moves upward). NOTICE: These tests must be performed quickly (within 3–5 seconds) to prevent the coil from burning out. -
Page 942
BE–109 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Audio System REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION OF ANTENNA 1. REMOVE ANTENNA ROD HINT: Perform this operation with the battery negative (–) cable connected to the battery terminal. (a) Turn the ignition switch to ”LOCK” position. (b) Remove the antenna nut. (c) Press the ”AM”… -
Page 943
BE–110 BODY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM – Clock CLOCK Troubleshooting As shown in the illustration, those are clock circuit and connector diagrams. Inspect each terminal for applicable trouble. Specified Terminals Condition value Continuity Constant Turn light control switch ON Battery positive Constant voltage Turn ignition switch ACC Allowable error:… -
Page 944
BO–1 BODY – BODY… -
Page 945
BO–2 BODY – General Information GENERAL INFORMATION If there is a possibility the body and/or parts may be dam– aged, first remove the danger before performing repair operations. Example: 1. Apply protection tape to the body adjacent to the body parts when removing and installing. 2. -
Page 946
BO–3 BODY – Hood HOOD ADJUSTMENT OF HOOD HINT: Since the centering bolt is used as the hood hinge set bolt, the hood cannot be adjusted with it on. Substi– tute the bolt with the washer for the centering bolt. 1. -
Page 947: Front Door
BO–4 BODY – Front Door FRONT DOOR COMPONENTS…
-
Page 948
BO–5 BODY – Front Door COMPONENTS (Cont’d) -
Page 949
BO–6 BODY – Front Door ADJUSTMENT OF FRONT DOOR 1. ADJUST DOOR IN FORWARD/REARWARD AND VERTICAL DIRECTIONS Using SST, adjust the door by loosening the body side hinge bolts. SST 09812–00010 2. ADJUST DOOR IN LEFT/RIGHT AND VERTICAL DIRECTIONS Loosen the door side hinge bolts to adjust. 3. -
Page 950
BO–7 BODY – Front Door 4. REMOVE REAR VIEW MIRROR (w/o Ventilator Window) (a) (w/Remote Control Mirror) Disconnect the connector. (b) Remove three screws and the mirror. (wI Ventilator Window) (a) (w/ Remote Control Mirror) Disconnect the connector. (b) (w/o Remote Control Mirror) Remove the mirror cover, two screws and the mir–… -
Page 951
BO–8 BODY – Front Door 7–2. (w/o Ventilator Window) REMOVE FRONT LOWER FRAME Remove the bolt and the frame. 8. REMOVE REAR LOWER FRAME Remove the bolt and the frame. 9–1. (Semi Trim type) REMOVE INNER AND OUTER WEATHERSTRIP Pry loose the clips from the edge of the panel and remove the weatherstrip. -
Page 952
BO–9 BODY – Front Door REPLACEMENT OF GLASS 1. REMOVE GLASS CHANNEL WITH SCREWDRIVER OR LIKE OBJECT 2. APPLY SOAPY WATER TO INSIDE OF WEATHER– STRIP 3. INSTALL CHANNEL BY TAPPING IT WITH PLASTIC HAMMER ASSEMBLY OF FRONT DOOR (See pages BO–4 and 5) 1. -
Page 953
BO–10 BODY – Front Door 3. INSTALL OUTSIDE HANDLE WITH LOCK CYLINDER AND DOOR LOCK (a) Install the lock cylinder with the snap ring to the out– side handle. (b) Install the outside handle and lock cylinder with two bolts. (c) (w/Power Door Lock) Install the door lock and motor with three screws and the bolt, then connect the connector. -
Page 954
BO–11 BODY – Front Door (c) Seal the panel slit with the cotton tape. NOTICE: Do not block the trim clip seating with the tape. 12–1.(Semi Trim type) INSTALL OUTER AND INNER WEATHERSTRIP Install the claw of the clips into the upper panel slit and push the weatherstrip onto the panel. -
Page 955
BO–12 BODY – Front Door 14. INSTALL DOOR INSIDE HANDLE (See step 2 on page BO–6) (a) Connect the handle to the control links. (b) Push the inside handle in the door panel and slide it rearward. (c) Install the screw. 15. -
Page 956
BO–13 BODY – Moulding MOULDING Windshield Moulding COMPONENTS REMOVAL OF WINDSHIELD MOULDING LOCATION OF CLIPS AND FASTENER • For vehicles in the table below which have black moul– ding, refer to diagram type 1. • For other vehicles which have black or metallic mould– ing, refer to diagram Type 11. -
Page 957
BO–14 BODY – Moulding 1. REMOVE WIPER ARMS 2. REMOVE COWL LOUVER AND WEATHERSTRIP 3. REMOVE LOWER MOULDING WITH LOWER JOINT COVERS (a) Remove five screws from the clips. (b) Pry up a scraper to loosen the clips from the body. HINT: Tape the scraper tip before use. -
Page 958
BO–15 BODY – Moulding INSTALLATION OF WINDSHIELD MOULDING 1. INSTALL CLIP INTO MOULDING (See page BO–13) Install the clip to the appropriate place on the moulding. 2. APPLY ADHESIVE AT CLIP INSTALLATION AREA (a) Cut out the old adhesive around the clip installation area. -
Page 959
BO–16 BODY – Moulding Wheel Arch Moulding COMPONENTS REPLACEMENT OF FRONT WHEEL ARCH MOULDING 1. REMOVE FRONT WHEEL ARCH MOULDING (a) Remove five screws. (b) Using a screwdriver, pry up the wheel arch mould– ing, and remove it. HINT: Tape the screwdriver tip before use. 2. -
Page 960
BO–17 BODY – Windshield WINDSHIELD (Adhesive Type) PREPARE ITEMS LISTED Contents of set Part name and No. Quantity Main agent 500g (17.64 oz.) Adhesive set hardening agent 75g (2.65 oz.) 08850–00070 Primer G (for glass) 20g ( (0 – 150C or 32 – 59’F) 08850–00080 0. -
Page 961
BO–18 BODY – Windshield COMPONENTS REMOVAL OF WINDSHIELD 1. REMOVE FOLLOWING PARTS: • Inner rear view mirror • Sun visors and holders • Wiper arms • Cowl louver • Front pillar garnishes • Assist grip 2. REMOVE WINDSHIELD MOULDING (See page BO–13) 3. -
Page 962
BO–19 BODY – Windshield 4. REMOVE WINDSHIELD GLASS (a) Push piano wire through from the interior. (b) Tie both wire ends to the wooden blocks or like ob– jects. HINT: Apply adhesive tape to the outer surface to keep the surface from being scratched. NOTICE: When separating, take care not to damage the paint and interior and exterior ornaments. -
Page 963
BO–20 BODY – Windshield INSTALLATION OF WINDSHIELD (See pages BO–13 and 18) 1. CLEAN CONTACT SURFACE OF GLASS Using cleaner, clean the contact surface 15 – 30 mm (0.59 – 1.18) wide around the entire glass rim. 2. INSTALL DAM (a) Apply double–stick tape at a point as shown. -
Page 964
BO–21 BODY – Windshield 6. APPLY ADHESIVE (a) Cut off the tip of the cartridge nozzle to make a hole 5 mm (0.20 in.) in diameter. Fill the cartridge with adhesive. (b) Load the cartridge into the sealer gun. (c) Coat the glass with adhesive on all contact surfaces along the ridge. -
Page 965: Back Window
BO–22 BODY – Back Window BACK WINDOW COMPONENTS REMOVAL OF BACK WINDOW REMOVE BACK WINDOW (a) Using a screwdriver, loosen the weatherstrip from the body. NOTICE: Be careful not to damage the body paint. (b) Pry the lip of the weatherstrip outward from the in– terior part of the body flange.
-
Page 966
BO–23 BODY – Back Window DISASSEMBLY OF BACK WINDOW ASSEMBLY (Slide Glass type) 1. REMOVE FOLLOWING PARTS: • Back window slide glass stoppers • Four screws holding two fix frames 2. REMOVE SLIDE GLASS Pull apart the channels and remove two slide glass panes at the center area of the glass channel. -
Page 967
BO–24 BODY – Back Window INSTALLATION OF BACK WINDOW 1. CLEAN BODY AND GLASS Using cleaner, wipe off the contact surface of the body and the glass. 2. CLEAN WEATHERSTRIP Using cleaner, clean the weatherstrip surface. 3. INSTALL WEATHERSTRIP ON BACK WINDOW (a) Attach the weatherstrip to the back window. -
Page 968: Quarter Window
BO–25 BODY – Quarter Window QUARTER WINDOW (Xtra Cab) COMPONENTS REMOVAL OF QUARTER WINDOW 1. REMOVE BACK PANEL GARNISHES AND BACK PANEL TRIM (a) Remove the back panel lower garnish. (b) Remove the back panel upper garnish. (c) Remove three bolts and the back panel trim. 2.
-
Page 969
BO–26 BODY – Quarter Window 3. REMOVE REAR QUARTER TRIM (a) Remove four bolts, the seat belt anchors and the belt guide. (See pages BO–46 and 47) (b) Remove the screw and the hook. c) Remove the rear quarter trim. 4. -
Page 970: Moon Roof
BO–27 BODY – Moon Roof MOON ROOF COMPONENTS…
-
Page 971
BO–28 BODY – Moon Roof REMOVAL OF MOON ROOF (See page BO–31) 1. REMOVE REMOVABLE ROOF WITH SUN SHADE 2. REMOVE REMOVABLE ROOF INNER WEATHERSTRIP 3. REMOVE REMOVABLE ROOF BENDING 4. REMOVE REMOVABLE ROOF AUXILIARY CATCH 5. REMOVE WIND DEFLECTOR PANEL (a) Remove two outside deflector clips on the left and right sides. -
Page 972
BO–29 BODY – Moon Roof 9. REMOVE ROOF HEADLINING (a) Remove the roof headlining as shown, and leave it hanging. (b) Remove any double–stick tape remaining on the body. NOTICE: Do not damage the roof headlining. 10. REMOVE REMOVABLE ROOF HINGE CASE Remove two bolts and the hinge case. -
Page 973
BO–30 BODY – Moon Roof 4. INSTALL REMOVABLE ROOF BENDING 5. INSTALL REMOVABLE ROOF INNER WEATHERSTRIP 6. INSTALL REMOVABLE ROOF AUXILIARY CATCH Install the auxiliary catch with the bolt. 7. INSTALL WIND DEFLECTOR PANEL Install the deflector clips as shown in the illustration. 8. -
Page 974
BO–31 BODY – Moon Roof DISASSEMBLY OF REMOVABLE ROOF (See page BO–31 1. REMOVE HANDLE WITH HOLDER 2. REMOVE LEFT/RIGHT HINGE ASSEMBLY OF REMOVABLE ROOF 1. INSTALL LEFT/RIGHT HINGE (a) Install the hinge with two screws. (b) Torque the outside screw. Torque: 2.9 N–m (30 kgf–cm, 26 in.–Ibf) (c) Torque the inside screw. -
Page 975: Instrument Panel
BO–32 BODY – Instrument Panel INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENTS…
-
Page 976
BO–33 BODY – Instrument Panel COMPONENTS (Cont’d) -
Page 977
BO–34 BODY – Instrument Panel REMOVAL OF INSTRUMENT PANEL (See pages BO–36 and 37) 1. DISCONNECT BATTERY CABLE FROM NEGATIVE TERMINAL 2. REMOVE STEERING WHEEL (See page SR–4) 3. REMOVE STEERING COLUMN COVERS (See page SR–4) 4. REMOVE ENGINE HOOD RELEASE LEVER Remove two screws and the engine hood release lever. -
Page 978
BO–35 BODY – Instrument Panel 12–1.(Models Ex. 4–Speed M/T) REMOVE CLUSTER FINISH PANEL (a) Remove three screws and pull out the cluster finish panel. (b) Disconnect the connectors. (c) Remove two screws and the cup holder from the cluster finish panel. 12–2.(4–Speed M/T Models) REMOVE CLUSTER FINISH PANEL WITH METER HOOD (a) Remove two screws and pull out the cluster finish… -
Page 979
BO–36 BODY – Instrument Panel 17. REMOVE HEATER CONTROL Remove two screws and hang the heater control. 18. REMOVE RADIO (a) Remove four bolts (b) Disconnect the antenna cable and connectors. (c) Remove the radio with bracket. 19. REMOVE INSTRUMENT PANEL (a) Remove four bolts and the instrument panel. -
Page 980
BO–37 BODY – Instrument Panel (4–Speed M/T Models) (a) No.3, No.5 heater to register duct (b) Instrument panel No.2 register (c) No.2, No.3 Instrument stay (d) Mounting bracket (e) Cowl bracket… -
Page 981
BO–38 BODY – Instrument Panel 4–Speed M/T Models Mounting Bracket No. 3 Instrument Stay No. 2 Instrument Stay Cowl Bracket Instrument Panel Instrument Panel No. 2 Register Duct Heater to Register No. 3 Duct Heater to Register No. 5 N02903 INSTALLATION OF INSTRUMENT PANEL (See pages BO–36… -
Page 982
BO–39 BODY – One–Touch Tail Gate ONE–TOUCH TAIL GATE COMPONENTS REMOVAL OF TAIL GATE LOCK 1. REMOVE SERVICE HOLE COVER Remove twelve screws and the service hole cover. 2. DISCONNECT TAIL GATE LOCK LINK FROM TAIL GATE LOCK CONTROL 3. REMOVE TAIL GATE STAY (a) Disconnect the tail gate stay from the tail gate. -
Page 983
BO–40 BODY – One–Touch Tail Gate INSTALLATION OF TAIL GATE LOCK 1. INSTALL TAIL GATE LOCK TO TAIL GATE Install the tail gate lock with the two screws. 2. INSTALL TAIL GATE STAY (a) Install the tail gate stay and the bolt. Torque: 14 N–m (140 kgf–cm, 10 ft–lbf) (b) Connect the tail gate stay to the tail gate. -
Page 984
BO–41 BODY – Seat SEAT Front Seat COMPONENTS… -
Page 985
BO–42 BODY – Seat Rear Jump Seat COMPONENTS (Cont’d) -
Page 986
BO–43 BODY – Seat Belt SEAT BELT Front Seat Belt COMPONENTS… -
Page 987
BO–44 BODY – Seat Belt Rear Jump Seat Belt COMPONENTS (Cont’d) -
Page 988: Manual Type
BO–45 BODY – Seat Belt SEAT BELT [Emergency Locking Retractor (ELR) Type] 1. RUNNING TEST (IN SAFETY AREA) (a) Fasten the seat belt. (b) Drive the car at 10 mph116 km/h) and make a very hard stop. (c) Check that the seat belt is locked and cannot be ex– tended at this time.
-
Page 989
BO–46 BODY – Body Dimensions BODY DIMENSIONS General Information 1. BASIC DIMENSIONS (a) There are two types of dimensions in the diagram. (Three–dimensional distance) • Straight–line distance between the centers of two measuring points. (Two–dimensional distance) • Horizontal distance in forward/rearward between the centers of two measuring points. -
Page 990
BO–47 BODY – Body Dimensions Body Dimensions… -
Page 991
BO–48 BODY – Body Dimensions… -
Page 992
BO–49 BODY – Body Dimensions Frame Dimensions 2WD Regular Cab: Short Wheel Base Models… -
Page 993
BO–50 BODY – Body Dimensions 2WD Regular Cab: Short Wheel Base Models… -
Page 994
BO–51 BODY – Body Dimensions 2WD Regular Cab: Long Wheel Base Models… -
Page 995
BO–52 BODY – Body Dimensions 2WD Regular Cab: Long Wheel Base Models… -
Page 996
BO–53 BODY – Body Dimensions 2WD Regular Cab: Super Long Wheel Base Models… -
Page 997
BO–54 BODY – Body Dimensions 2WD Regular Cab: Super Long Wheel Base Models… -
Page 998
BO–55 BODY – Body Dimensions 2WD Xtra Cab Models… -
Page 999
BO–56 BODY – Body Dimensions 2WD Xtra Cab Models… -
Page 1000
BO–57 BODY – Body Dimensions 4WD Regular Cab: Short Wheel Base Models…