- Manuals
- Brands
- Waves Manuals
- Recording Equipment
- VOCAL RIDER
- User manual
-
Contents
-
Table of Contents
-
Bookmarks
Quick Links
Waves
VOCAL RIDER
User Guide
Related Manuals for Waves VOCAL RIDER
Summary of Contents for Waves VOCAL RIDER
-
Page 1
Waves VOCAL RIDER User Guide… -
Page 2: Table Of Contents
Chapter 1 – Introduction ………………3 1.1 Welcome………………….3 1.2 Product Overview ………………3 1.3 Concepts and Terminology…………….4 1.4 Components ………………..4 1.5 WaveSystem Toolbar……………….4 Chapter 2 – Quickstart Guide …………….5 Chapter 3 – Interface and Controls ……………6 3.1 Interface…………………..6 3.2 Controls …………………..7 Waves Vocal Rider User Guide…
-
Page 3: Chapter 1 — Introduction
All you need to do is set the target range of the vocal level in relation to the rest of the mix. Then, Vocal Rider adjusts the level so it stays within your target, raising or lowering the vocal volume, in real-time. And unlike compression, Vocal Rider doesn’t add any additional coloring to your track.
-
Page 4: Concepts And Terminology
Vocal gain riding is the final stage, during which the vocal level is fine-tuned by making small changes to its playback level, to make its position in the mix consistent throughout the song. Vocal Rider splits the elements of the mix into two main components: vocals and playback. •…
-
Page 5: Chapter 2 — Quickstart Guide
Chapter 2 – Quickstart Guide Insert Vocal Rider as the last plug-in on your vocal or vocal group track. Send your instrumental tracks, post fader, to a bus, just like a headphone mix. Set the sidechain input on Vocal Rider to the instrumental bus.
-
Page 6: Chapter 3 — Interface And Controls
Chapter 3 – Interface and Controls 3.1 Interface Waves Vocal Rider User Guide…
-
Page 7: Controls
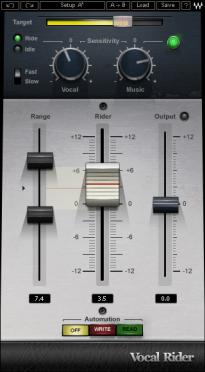
Range: 0 to -42 dBFS Default: -21 SPILL differentiates between vocal signal and unwanted ambient stage noise, to provide better tracking. (Vocal Rider Live components only) Range: -12 to -48 dBFS Default: -48 VOCAL SENSITIVITY controls the vocal detector sensitivity, which differentiates vocal content from noise floor, spill, and ambience, and identifies the beginnings and endings of words.
-
Page 8
Please note: To use this control, the instrumental mix bus must be assigned to the Vocal Rider side-chain input. MUSIC SENSITIVITY LED indicates when and how much Vocal Rider is affected by instrumental levels. Range: Soft Green to Bright Green When the LED is soft green, vocal riding is less affected by instrumental level;… -
Page 9
IDLE ARROW sets the Rider Fader value when there is no vocal activity. Typically, it is in the middle of the range, to avoid drastic gain changes between words. Range: -12 to +12 Default: 0 Waves Vocal Rider User Guide… -
Page 10
Range: 1 to 24 dB Default: 12 RIDER FADER is Vocal Rider’s automatic control, which moves according to the internal detectors’ algorithm to level-out the vocal, similar to manual fader riding. (The TARGET control is used to set the Rider Fader ‘0’ calibration.) -
Page 11
Though the Rider Fader moves automatically, it is treated by the host application as if automation is being written manually. When set to Read, the Rider Fader uses the automation lane to define its movement, disregarding Vocal Rider’s internal engine. OUTPUT trims the vocal output gain, post-auto riding; the CLIP LED shows when output is clipping.
Table of Contents for Waves VOCAL RIDER:
-
Waves Vocal Rider User Guide 8 ATTACK sets the vocal detection attack behavior, affecting both detection timing and fader riding speed. Range: Fast, Slow Default: Slow MUSIC SENSITIVITY determines the amount Vocal Rider adapts to changes in instrumental levels. (“Instrumental” refers to all tracks other than the vocal). Range: -12 to +12 dB Default: 0 Please note: To use this control, the instrumental mix bus must be assigned to the Vocal Rider side-chain input. MUSIC SENSITIVITY LED indicates when and how much V
-
Waves Vocal Rider User Guide 6 Chapter 3 – Interface and Controls 3.1 Interface
-
Waves Vocal Rider User Guide 4 1.3 Concepts and Terminology The vocal production process can be divided into several stages: recording, comping, mix positioning, sound character adjustment (Dynamics/EQ/Effects), and gain riding. Vocal gain riding is the final stage, during which the vocal level is fine-tuned by making small changes to its playback level, to make its position in the mix consistent throughout the song. Vocal Rider splits the elements of the mix into two main components: vocals and playback. • Vocal: All vocal track
-
Waves Vocal Rider User Guide 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Chapter 1 – Introduction ……………………………………………………………………………3 1.1 Welcome…………………………………………………………………………………………3 1.2 Product Overview …………………………………………………………………………….3 1.3 Concepts and Terminology…………………………………………………………..
-
Waves Vocal Rider User Guide 7 3.2 Controls TARGET sets the reference range for vocal mix positioning. Since Gain Riding is relative to the Target position, changing the Target setting will move the Rider Fader’s ‘0’ calibration, re-focusing the correct level range. Range: 0 to -42 dBFS Default: -21 SPILL differentiates between vocal signal and unwanted ambient stage noise, to provide better tracking. (Vocal Rider Live components only) Range: -12 to -48 dBFS Default: -48
-
Waves Vocal Rider User Guide 10 EFFECTIVE RANGE displays the total gain range available for automatic riding. Range: 1 to 24 dB Default: 12 RIDER FADER is Vocal Rider’s automatic control, which moves according to the internal detectors’ algorithm to level-out the vocal, similar to manual fader riding. (The TARGET control is used to set the Rider Fader ‘0’ calibration.) Range: —
-
Waves VOCAL RIDER User Guide
-
Waves Vocal Rider User Guide 3 Chapter 1 – Introduction 1.1 Welcome Thank you for choosing Waves! In order to get the most out of your new Waves plugin, please take a moment to read this user guide. To install software and manage your licenses, you need to have a free Waves account. Sign up at www.waves.com. With a Waves account you can keep track of your products, renew your Waves Update Plan, participate in bonus programs, and
-
Waves Vocal Rider User Guide 5 Chapter 2 – Quickstart Guide Insert Vocal Rider as the last plug-in on your vocal or vocal group track. Send your instrumental tracks, post fader, to a bus, just like a headphone mix. Set the sidechain input on Vocal Rider to the instrumental bus. Begin playing your song, then set the Vocal Sensitivity and Attack controls. Set the Target control by moving the transparent screen to the Vocal range peak. The main Rider
-
Waves Vocal Rider User Guide 9 RANGE MIN sets the lower boundary of the Rider Fader movement range, setting the maximum possible Rider Fader attenuation. Range: -12 to +11 dB Default: -6 RANGE MAX sets the upper boundary of the Rider Fader movement range, setting the maximum Rider Fader gain. Range: -11 to +12 dB Default: +6 IDLE ARROW sets the Rider Fader value when there is no vocal activity. Typically, it is in the middle of the range, to av
Questions, Opinions and Exploitation Impressions:
You can ask a question, express your opinion or share our experience of Waves VOCAL RIDER device using right now.
TABLE OF CONTENTS |
|||
|
Chapter 1 – Introduction …………………………………………………………………………… |
3 |
||
|
1.1 |
Welcome………………………………………………………………………………………… |
3 |
|
|
1.2 |
Product Overview ……………………………………………………………………………. |
3 |
|
|
1.3 |
Concepts and Terminology……………………………………………………………….. |
4 |
|
|
1.4 |
Components …………………………………………………………………………………… |
4 |
|
|
Chapter 2 |
– Quickstart Guide ……………………………………………………………………. |
5 |
|
|
Chapter 3 |
– Interface and Controls…………………………………………………………….. |
6 |
|
|
3.1 |
Interface…………………………………………………………………………………………. |
6 |
|
|
3.2 |
Controls …………………………………………………………………………………………. |
7 |
|
|
Chapter 4 |
– The WaveSystem…………………………………………………………………. |
12 |
|
|
4.1 |
The WaveSystem Toolbar ………………………………………………………………. |
12 |
|
|
4.2 |
Preset Handling …………………………………………………………………………….. |
12 |
|
|
4.3 |
Interface Controls ………………………………………………………………………….. |
14 |
Waves Vocal Rider
User Guide
2
Chapter 1 – Introduction
1.1 Welcome
Thank you for choosing Waves! In order to get the most out of your Waves processor, please take the time to read through this manual.
In conjunction, we also suggest you become familiar with www.wavesupport.net. There you will find an extensive Answer Base, the latest Tech Specs, detailed Installation guides, new Software Updates, and current information on Authorization and
Registration.
By signing up at www.wavesupport.net, you will receive personalized information on your registered products, reminders when updates are available, and information on your authorization status.
1.2 Product Overview
Vocal Rider is the first of Waves pioneering new series of Mix tools. As its name implies, it automatically rides vocal track levels. Instead of manually riding a mixing console fader, or tediously drawing in every level change on a DAW track, Vocal Rider does it for you, making it a true timesaver. All you need to do is set the target range of the vocal level in relation to the rest of the mix. Then, Vocal Rider adjusts the level so it stays within your target, raising or lowering the vocal volume, in real-time. And unlike compression, Vocal Rider doesn’t add any additional coloring to your track. From the recording studio to the concert stage, from the broadcast studio to the post house, Vocal Rider takes mixing to the next level.
Keep consistent vocal & dialog levels automatically.
Steady vocal levels without affecting their sound.
Achieve an open-sounding mix by avoiding over-compression.
Real-Time means zero latency and no pre-scan needed.
Intelligently adjusts vocal level based on dynamics of the music tracks.
Write the automatic riding to an automation track for fine tuning.
Waves Vocal Rider
User Guide
3
1.3 Concepts and Terminology
The vocal production process can be divided into several stages: recording, comping, mix positioning, sound character adjustment (Dynamics/EQ/Effects), and gain riding. Vocal gain riding is the final stage, during which the vocal level is fine-tuned by making small changes to its playback level, to make its position in the mix consistent throughout the song.
Vocal Rider splits the elements of the mix into two main components: vocals and playback.
•Vocal: All vocal tracks, with or without effects (as defined by the user)
•Music: The rest of the mix, minus the vocal tracks
1.4Components
WaveShell technology enables us to split Waves processors into smaller plug-ins, which we call components. Having a choice of components for a particular processor gives you the flexibility to choose the configuration best suited to your material.
Waves Vocal Rider includes four components:
•Vocal Rider Mono
•Vocal Rider Stereo
•Vocal Rider Live Mono
•Vocal Rider Live Stereo
Waves Vocal Rider
User Guide
4
Chapter 2 – Quickstart Guide
Insert Vocal Rider as the last plug-in on your vocal or vocal group track.
Send your instrumental tracks, post fader, to a bus, just like a headphone mix.
Set the sidechain input on Vocal Rider to the instrumental bus.
Begin playing your song, then set the Vocal Sensitivity and Attack controls.
Set the Target control by moving the transparent screen to the Vocal range peak.
The main Rider fader will begin to move automatically, leveling your vocal.
In Live situations, if the fader moves when no vocal signal is present, adjust the Spill control to differentiate unwanted ambient stage noise, for better tracking.
Limit the amount of automatic gain change by setting the range faders.
To correlate the vocal level to the instrumental level, adjust Music Sensitivity.
Arm your host to write automation, then Press Automation Write at any time to send the Vocal Rider Fader to your host application automation edit lane, make your manual edits, and then press Read.
Using your ears, find the sweet spot and trim using the output fader.
Waves Vocal Rider
User Guide
5
Writing Automation with Vocal Rider
After setting Vocal Rider according to your program material, follow the steps below.
Writing Automation
- In your DAW, set the vocal track’s automation mode to ‘Write’ or ‘Latch’.
- Enable automation for Vocal Rider’s main Rider Fader.
- Set Vocal Rider’s automation mode to ‘Write’.
- Hit Play.
Please note: The Vocal Rider interface window must be open during automation writing. All previously written automation will be lost in Write/Latch modes.
Reading Automation
- In your DAW, set the vocal track’s automation mode to ‘Read’.
- Set Vocal Rider’s automation mode to ‘Read’.
- Hit Play.
Editing Rider Fader Automation
Controlling Vocal Rider Using a Mouse or Control Surface
- In your DAW, set the vocal track’s automation mode to ‘Touch’.
- Set Vocal Rider’s automation mode to ‘Read’.
- Hit Play.
- Use the main Rider Fader to manually ride as needed.
When you release the Rider Fader, it will return to the previously written automation.
Using the main Rider Fader automation line in the track editor
- In your DAW, set the vocal track’s automation mode to ‘Read’.
- Set Vocal Rider’s automation mode to ‘Read’.
- Open the Rider Fader automation line in the track editor to manually draw in your edits.
Assigning Sidechain Input
Here’s how you assign the instrumental mix to Vocal Rider’s music Sidechain input:
Pro Tools
- Select all tracks (except for the vocals) currently assigned to the Master mix output. Shift+Ctrl+Alt and click the Output menu on one of the tracks. Select an unused mono bus; it may help to name it “Music Sidechain” or similar. All selected tracks should now display the Master output with a “+” sign, indicating they are also routed to another bus.
Or
On all tracks (except for the vocals) currently assigned to the Master mix output, create a post-fader Send going to an unused mono bus, which you can call “Music Sidechain” or similar. Set all those send faders to “0”.
- Insert Vocal Rider on the vocal or vocal group track. Open the Vocal Rider GUI and click on the Sidechain (key) menu. Select the “Music Sidechain” bus you have created.
Logic Pro
- Select all the tracks (except for the vocals) currently assigned to the Master mix output.
- In the Sends display box, select and assign an unused bus; it may help to name it “Music Sidechain” or similar. An Aux track is automatically created with that bus as an input; you can delete it, as it is unnecessary.
- Alt+click on the Send knob. It will set the send level on all selected tracks to “0”.
- Insert Vocal Rider on the vocal or vocal group track. Open the Vocal Rider GUI and click on the Sidechain menu. Select the “Music Sidechain” bus you have created.
Digital Performer
- Select all the tracks (except for the vocals) currently assigned to the Master mix output.
- In the Sends display box, select and assign an unused bus; it may help to name it “Music Sidechain” or similar.
- Ctrl+click on the Send knob. It will set the send level on all selected tracks to “0”.
- Insert Vocal Rider on the vocal or vocal group track. Open the Vocal Rider GUI and click on the Sidechain menu. Select the “Music Sidechain” bus you have created.
Cubase / Nuendo
- Insert Vocal Rider on your vocal track or group, and press the Sidechain button.
- For each track (except for the vocals) currently assigned to the Master mix output, select a Send route to the Vocal Rider Sidechain bus.
- Set the Send to active, and Ctrl+click to set its level to “0”. Repeat for each track currently assigned to the Master mix output. Please note: It may be preferable to use the Mix window.
Studio One
- Insert Vocal Rider on your vocal track or group, and press the Sidechain button.
- For each track (except for the vocals) that is currently assigned to the Master mix output, select a Send route to the Vocal Rider Sidechain bus.
Known Issues
- General: Vocal Rider GUI must be open in order to Write Rider Fader automation.
- General: When Vocal Rider is in Write mode, it is not recommended to make manual adjustments by over-riding the main Rider Fader during automation. Switch Vocal Rider to Read mode before making manual adjustments. (In your DAW, keep the track automation set to Write/Touch/Latch). Manual adjustments made using a Control Surface are also not recommended.
- Pro Tools: While playing a loop with Vocal Rider set to Write, and Pro Tools set to Write, only the first run will write automation; the second run will not Write and will not Read, but the Rider Fader will still move.
- Pro Tools: If the drawn automation is jagged and saw-like, press “Off” then “Write” again on the Vocal Rider automation.
- Logic: When bypassing Vocal Rider during Write mode, a flat line will be written at the last fader position.
- Logic: Music control is always available, even if Sidechain is not connected. In this case, it will act as an offset to the Target setting.
- Logic: When writing Rider Fader automation, it is not recommended to write automation for other controls, as it will disrupt the Rider Fader automation data.
- Logic/Digital Performer: Even though Sidechain can appear to be connected in Preview mode, it may not be connected. Toggle “Multi-Input Mode” / “Mono” to force the Sidechain connection.
На чтение 4 мин Просмотров 4.3к. Опубликовано 17.10.2018
Обновлено 17.10.2018
Vocal Rider и Bass Rider — это потрясающие автоматические компрессоры которые предугадывают и регулируют громкость аудио сигнала после чего уровень остается постоянным в пределах диапазона, который вы задаете. У Vocal Rider компенсация может быть двух типов абсолютной и зависящей исключительно от конкретного аудио или же относительно управляемым входным сайдчейн сигналом. Например, уровень вокала можно регулировать относительно громкости музыки опорного трека.
Рассмотрим Vocal Rider.
Элементы управления этого плагина интуитивно понятные. Вы можете установить входную чувствительность и скорость срабатывания при воспроизведении трека на свое усмотрение. Музыкальная чувствительность задает, насколько сильно этот плагин реагирует на входной сигнал сайдчейн. Вы можете ограничить величину изменения уровня фейдерами Range. Я обычно настраиваю довольно узкую полосу в пределах +-3dB, но это все зависит от трека. Cлайдер target рекомендуют устанавливать на среднюю громкость входного сигнала. Регулятор output позволяет снизить уровень выходного сигнала после обработки плагина, чтобы избежать клипирования. Переключатель Fast и Slow отвечают за то как быстро будет реагировать плагин на изменение атаки компрессии. Fast быстрее, slow медленнее.
Давайте послушаем как Vocal Rider удерживает громкость этого вокала на постоянном уровне.
Вы можете видеть, что Vocal Rider повысил тихие и понизил громкие части. Управление автоматизацией позволяет записать её в вашей DAW. В моем случае это Fl Studio. После чего вы можете отредактировать движение фейдера Rider. Чтобы вам включить и добавить автоматизацию к фейдеру rider и к параметрам которые и будут автоматизированы нужно настроить плагин. Для этого загружаем сам плагин на дорожку с вокалом. После чего переходим в настройки плагина VST wrapper seatings ->Stereo output и выставить значение 1. А также включите контролеры Stereo In и Stereo Aux in.
Установите ваш DAW в режим записи. Выберите пустой патерн на плейлисте, переведите сам плагин в режим Write и включите запись в Fl Sudio. После этого автоматизация будет записана.
После чего нужно переключить плагин в режим воспроизведения Read. Если нужно отредактировать автоматизацию, то нажмите в левом углу автоматизации левой кнопкой мышки и выберите Edit Pattern.
Теперь в открывшемся для того чтобы сделать автоматизацию так как надо. Нужно перейти в Menu->Edit->Turn into automation clip -> Accept.
После этого у Вас автоматизация станет такой какой она и должна быть и её легче будет редактировать.
Рассмотрим Bass Rider.
Он имеет те же функции что и Vocal Rider но без сайдчейн автоматизации. Настройте регуляторы скорости и чувствительности чтобы получить необходимый уровень громкости сигнала используйте ручку Artifacts, чтобы игнорировать щелчки от струн и другие типы шумов если этот трек с живым басом.
Так же вы можете использовать регулятор Spill, чтобы убрать посторонние шумы. Например, звук барабанов, просочившихся в микрофон во время записи бас гитары. Target и Output работают так же, как и у Vocal Rider.
У меня есть пример с живым басом давайте посмотрим, как он работает.
Вы можете слышать, как выравнивается бас я хочу показать вам автоматизацию которую мне пришлось бы прописать от руки если бы не помощь этого чудесного плагина Bass Rider.
И на самом деле это действительно экономит время. Плагин красиво удерживает соло поверх звучащих инструментов, ничто не выпрыгивает и не одна из фантомных нот не была потеряна. Все они звучат очень ясно. Vocal Rider и Bass Rider помогут вам автоматически и быстро контролировать некоторые из наиболее сложных элементов в музыке, попробуйте использовать эти плагины в ваших миксах.
Сергей
Привет, меня зовут Сергей. Музыка для меня как хобби. Занимаюсь созданием Hip-Hop минусов в Fl Studio уже продолжительное время.
Если вам понравился этот материал, то поделись с ним с другими. Так вы поможете в развитии этого сайта и у меня будет стимул в дальнейшем развивать этот проект.
Оцените автора
( 4 оценки, среднее 5 из 5 )
- Manuals
- Brands
- Waves Manuals
- Recording Equipment
- VOCAL RIDER





